Warthin’s Tumor is a benign salivary gland growth, commonly occurring in the parotid gland. It is noncancerous and typically affects older adults.
Warthin’s Tumor, or Warthin’s Tumour, is most frequently diagnosed in individuals between the ages of 60 and 70. This type of tumor is second only to pleomorphic adenoma as the most common benign salivary gland neoplasm. Men are more likely to develop Warthin’s Tumor than women, particularly those with a history of smoking, which significantly increases the risk.
Despite its growth, Warthin’s Tumor is often painless and presents as a soft, movable lump near the jawline. Treatment typically involves surgical removal, and prognosis is excellent due to its benign nature. Recognition and understanding of Warthin’s Tumor are crucial for timely diagnosis and management, ensuring the best possible outcome for affected patients.
Understanding Warthin’s Tumor: An Overview
Welcome to the engaging world of Warthin’s Tumor, a rare, intriguing condition that often goes unnoticed. This overview provides clarity and insight into its characteristics, history, and nomenclature.
Defining Warthin’s Tumor: Characteristics And Types
Warthin’s Tumor, also known as papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum, presents as a benign growth.
Let’s break down the features:
- Benign nature: Non-cancerous, with minimal risk of becoming malignant.
- Location specifics: Predominantly found in the parotid gland.
- Affects: Primarily observed in adults, particularly those in the 50s and 60s.
- Gender prevalence: Males are more commonly affected than females.
- Recurrence: May recur if not wholly excised.
Historical Perspective: Discovery And Terminology
Aldred Scott Warthin, a renowned pathologist, first identified this tumor in 1929.
| Year | Discoverer | Tumor Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1929 | Aldred Warthin | Warthin’s Tumor |
This historical discovery led to the tumor bearing Warthin’s name. The term encapsulates the essence of this peculiar glandular anomaly.

Credit: www.sciencedirect.com
Epidemiology And Demographics
Understanding the epidemiology and demographics of Warthin’s Tumour is key. It tells us who gets it and how often. Let’s explore the numbers and differences in people.
Prevalence And Incidence Rates Globally
Warthin’s Tumour is a rare condition. It affects a small fraction of the population. Exact global numbers are hard to find.
- Prevalence: Estimates vary, but it’s under 1%.
- Incidence: Each year, few cases per 100,000 people are reported.
Age, Gender, And Ethnic Disparities
Warthin’s Tumour shows up mostly in older adults. Most patients are in their 60s and 70s. It also seems to favor a certain gender and ethnicities.
| Age Group | Gender | Ethnicity |
|---|---|---|
| 60s-70s | More common in men | Higher rates in Caucasians |
This data helps doctors understand who might be at risk. It guides them to better diagnose and treat patients.
Etiology: Causes And Risk Factors
Understanding the etiologies and risk factors for Warthin’s Tumor is a stepping stone for better awareness and prevention. Let’s delve into what sparks the onset of this benign parotid gland condition.
The Role Of Smoking And Lifestyle Choices
Smoking is a significant risk factor for Warthin’s Tumor. Tobacco exposes the salivary glands to harmful substances. This encourages tumor formation. A lifestyle that includes chronic smoking can drastically increase one’s chances of developing this condition.
- Secondhand smoke also raises the risk.
- Regular exposure without direct smoking contributes to potential growth.
Reducing smoking or quitting entirely is crucial. This may decrease the probability of developing Warthin’s Tumors.
Genetic Predispositions And Other Contributing Factors
Genetics may play a role. Family history of Warthin’s Tumor increases susceptibility:
| Family History | Risk Increase |
|---|---|
| Direct family member with Warthin’s | Higher |
Other factors also contribute:
- Age: Typically affects people above 40 years.
- Gender: More common in males.
- Radiation exposure: Past radiation treatments to the head and neck area.
It is vital to be mindful of these risks. Early detection and intervention can be beneficial.
Clinical Manifestations Of Warthin’s Tumor
Warthin’s tumor is a benign growth, most commonly affecting the salivary glands. Patients might encounter unusual signs. Recognizing these symptoms is vital for early detection and treatment. We will discuss the typical indications of this condition and how to distinguish it from other similar ailments.
Common Symptoms And Presenting Signs
Individuals with Warthin’s tumor typically notice a painless mass in the area of their jaw or neck. This mass may grow slowly. It’s usually located near the ear, around the lower jaw.
- Bump or lump near the jaw
- Swelling in the neck area
- Mild discomfort while eating or swallowing
- Possibly alteration in the taste sensation
This condition often impacts adults, particularly those over the age of 40. Smokers are at a higher risk. It’s essential to seek medical attention promptly if you experience any of these symptoms.
Differential Diagnosis: Separating Warthin’s From Other Conditions
Differentiating Warthin’s tumor from other conditions relies on a careful evaluation. Clinical examination and imaging, like ultrasounds or MRIs, help in forming an accurate diagnosis. Some other conditions that may resemble Warthin’s tumor:
| Condition | Features |
|---|---|
| Malignant tumors | Fast-growing, often painful |
| Cysts | Fluid-filled, may increase in size |
| Sialadenitis | Inflammation of salivary glands, often painful |
Biopsy procedures like Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) might be necessary for an accurate diagnosis. While the clinical assessment provides insights, confirmatory tests are indispensable for differentiating Warthin’s tumor from other conditions.
Diagnosis Procedures
Diagnosing a Warthin’s Tumor is key to determining the right treatment approach. An accurate diagnosis involves gathering comprehensive patient information and conducting specific medical tests. Let’s delve into the procedures involved in diagnosing this benign salivary gland condition.
Physical Examination And Patient History
The first step in diagnosing Warthin’s Tumor is a careful physical examination. Doctors check for lumps near the ears, jaw, and neck. They assess any mass for its size, shape, and consistency.
Along with the examination, doctors take a detailed patient history. This includes asking about symptoms, health behaviors, and family medical history. Factors such as smoking can increase the risk of developing Warthin’s Tumor.
Imaging And Confirmatory Tests
Next, doctors use various imaging techniques to visualize the tumor. These may include:
- Ultrasound: Sound waves create images of the salivary glands.
- CT Scan: Detailed cross-sectional images show the tumor’s size and location.
- MRI: Magnets and radio waves provide detailed images of soft tissues.
For confirmation, a fine needle biopsy might be performed. This test involves taking a small sample of cells from the tumor. A pathologist examines these cells under a microscope. The goal is to rule out cancer and confirm a diagnosis of Warthin’s Tumor.
| Test Type | Purpose | Procedure |
|---|---|---|
| Ultrasound | Image soft tissue | Non-invasive sound waves |
| CT Scan | View size/location | X-rays in a circle |
| MRI | Detail soft tissue | Uses magnets, radio |
| Biopsy | Confirm Warthin’s | Needle collects cells |
Pathophysiology And Histological Features
The study of Warthin’s Tumor reveals intriguing aspects of its pathophysiology and histological features. This benign growth, most often found in the parotid gland, involves a complex interplay of cellular and molecular factors. Understanding these elements provides insight into how the tumor forms and behaves.
Understanding The Cellular And Molecular Basis
Warthin’s Tumor, or papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum, arises from the salivary gland. It features a unique mix of epithelial and lymphoid tissue.
- Epithelial cells form cystic structures.
- Lymphoid stroma supports these cysts.
- During its development, genetic and environmental factors may play roles.
- Mitochondrial DNA mutations have been associated with this tumor.
Histopathology: Microscopic Examination Findings
Under the microscope, Warthin’s Tumor presents distinct histological characteristics:
| Feature | Observation |
|---|---|
| Epithelial Layer | Oncocytic cells with abundant cytoplasm and round nuclei |
| Lymphoid Stroma | Dense lymphoid tissue with germinal centers |
| Cyst Formation | Bilayered epithelium lining cystic spaces |
| Double-Layered Epithelium | Columnar cells atop a basal layer of flattened cells |
The combination of lymphoid and epithelial structures forms the hallmark of this tumor type. This dual composition contributes to its classic appearance.
Readers must note the presence of lymphocytes, plasma cells, and occasional germinal centers within the lesion. Doppler studies show high vascularity which aids in diagnosis.
Surgical Treatment And Management
Warthin’s Tumor, primarily a benign growth in the salivary glands, usually requires surgical intervention. Treatment efficacy and optimal patient outcomes hinge significantly on the type of surgery executed and postoperative care. Below we explore the common surgical approaches along with the requisite postoperative care to mitigate complications and promote swift recovery.
Common Surgical Interventions And Techniques
The primary goal in treating Warthin’s Tumor is complete removal with minimal risk. Surgery stands as the cornerstone treatment. Here are the frequent interventions:
- Superficial Parotidectomy – This technique involves excising the tumor with a portion of the parotid gland.
- Total Parotidectomy – For larger or recurrent tumors, surgeons may remove the entire gland.
- Enucleation – In select cases, removing just the tumor is feasible.
Surgeons often deploy magnification and nerve monitoring to preserve facial nerve function. Patient-specific factors dictate the optimal technique.
Postoperative Care And Complication Management
Successful recovery from surgery is critically anchored in effective postoperative care. Here are key considerations:
| Postoperative Care | Complication Management |
|---|---|
| Regular wound assessment | Immediate attention to hematoma |
| Ensuring drain management | Antibiotics for infection prevention |
| Facial nerve function monitoring | Therapies for facial nerve weakness |
| Pain management with prescribed medication | Interventions for excessive pain or discomfort |
Follow-ups are vital to check surgical site healing and discuss any concerns. Patients may also require therapy to regain normal facial nerve function.
Addressing complications promptly ensures patients rebound with full health. Surgeons and healthcare teams must stay alert for any signs of infection, hemorrhage, or facial nerve trauma.
Radiation And Chemotherapy
Exploring Treatment Options: When dealing with Warthin’s Tumor, also known as papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum, understanding the application of radiation and chemotherapy becomes pivotal. These treatments play key roles in battling various cancers. Yet, their effectiveness and approach for Warthin’s Tumor may differ from common expectations.
Role Of Radiation Therapy In Treatment
Despite its reputation, radiation therapy is not a standard treatment for Warthin’s Tumor. This benign salivary gland tumor often requires surgical removal. Radiation steps in only in unique cases:
- Recurring tumors that surgery alone cannot manage.
- Treatment for residual disease post-surgery.
- As a palliative measure when symptoms persist.
Radiation therapy may lessen symptoms. It can make daily life easier. It is not a cure for Warthin’s Tumor.
Chemotherapy: Indications And Outcomes
Like radiation, chemotherapy is not a frontline treatment for Warthin’s Tumor. This tumor is usually non-cancerous. Chemo is mostly for cancer. The drug specifically targets fast-growing cancer cells. Yet, chemo may come into play if:
- There’s a rare case of malignancy.
- A patient cannot undergo surgery.
- The tumor shows atypical behavior.
In such cases, outcomes can vary. Success with chemotherapy depends on individual factors. It includes the person’s health and the tumor’s response. It’s a tailored approach, solely determined by a medical professional.
Non-surgical Therapeutic Approaches
For those facing Warthin’s Tumor, non-surgical options offer hope. Minimally invasive treatments support the body’s fight against this benign salivary gland tumor. They often come with fewer side effects than traditional surgery. Let’s explore how modern medicine provides alternative paths to wellness.
Advancements In Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy stands out in non-surgical treatment. It uses drugs designed to attack specific tumor markers. This approach spares healthy cells, leading to a smoother recovery.
- Focuses on molecular and genetic factors.
- Minimizes damage to normal tissues.
- Offers a personalized treatment plan.
Alternative And Supportive Treatments
Beyond targeted therapies, other non-invasive treatments are gaining attention. These therapies aim to bolster overall health and manage symptoms.
| Treatment Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Acupuncture | Reduces pain and stimulates healing. |
| Herbal Medicine | Utilizes natural compounds for treatment. |
| Counseling | Supports emotional well-being. |

Credit: en.wikipedia.org
Prognosis And Survival Rates
Understanding the future with Warthin’s Tumor is crucial for patients and their families. This benign condition often has favorable outcomes. However, knowledge of survival rates and prognosis factors offers further reassurance and aids in informed decision-making.
Statistics On Long-term Outcomes
Warthin’s Tumor generally has an excellent prognosis. Most patients can expect a normal lifespan following diagnosis and treatment. Let’s explore the key statistics demonstrating long-term outcomes:
- survival rate is typically high, above 90% post-treatment.
- recurrence is uncommon, with less than 10% of cases noting a return.
- Effective treatment often means a single surgical procedure with no further issues.
Factors Influencing Prognosis
Several factors can impact the prognosis of Warthin’s Tumor:
- Age — younger patients generally recover faster.
- Tumor size and location — smaller, well-positioned tumors simplify treatment.
- Presence of symptoms — asymptomatic patients often have a smoother treatment journey.
- Treatment approach — complete removal typically results in the best outcomes.
- Patient’s overall health — good health can speed up recovery.
Follow-up Care And Surveillance
After treating a Warthin’s Tumor, attentive follow-up care and surveillance become pivotal. Regular monitoring helps ensure the health and well-being of patients post-treatment. Let’s explore the structured approach to post-treatment monitoring and the importance of being vigilant for any signs of recurrence.
Guidelines For Post-treatment Monitoring
Consistent follow-up appointments are key to monitoring health after Warthin’s Tumor therapy. Medical experts often recommend periodic evaluations.
- Initial follow-up visits every 6 months for the first year
- Annual check-ups thereafter, depending on individual cases
During visits, doctors usually perform:
- Physical examinations of the head and neck
- Imaging tests like ultrasound or MRI as necessary
- Review of symptoms and any changes the patient has noticed
Recognizing And Responding To Recurrence
Knowing the signs of recurrence plays a crucial role in early detection and treatment. Patients should watch out for:
| Sign | Action |
|---|---|
| New lumps or swelling near the original tumor site | Contact doctor immediately for evaluation |
| Pain in the face, neck, or jaw | Schedule an urgent medical consultation |
| Changes in hearing or swallowing | Report to a healthcare provider for prompt assessment |
Staying informed and maintaining open communication with healthcare professionals drives successful long-term outcomes for Warthin’s Tumor patients.
Patient Quality Of Life And Support Systems
Warthin’s Tumor may bring challenges to those diagnosed. Patients often face changes in their daily lives. They need strong support systems. High-quality care is vital. Let’s explore how these factors impact day-to-day life and mental health.
Impact On Daily Living And Emotional Well-being
A Warthin’s Tumor diagnosis can affect a person’s routine. Symptoms can cause discomfort. Regular medical appointments become necessary. This can lead to stress and anxiety.
- Eating: Difficulties may arise due to swelling or discomfort.
- Communication: The tumor can impact speaking and confidence.
- Work: Energy levels may decrease, affecting job performance.
Patients need compassion and understanding. Loved ones and professionals help maintain a sense of normalcy. Coping strategies are essential for emotional stability. Tailored exercises and therapies enhance well-being.
Role Of Support Groups And Counseling Services
A strong network uplifts those with Warthin’s Tumor. Support groups offer a community to share experiences. Counseling provides a space to address fears and emotions.
| Service | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Support Groups | Connections, shared stories, practical advice. |
| Counseling | Professional guidance, coping techniques, emotional support. |
Seeking help early can aid in adjustment and recovery. Friends, family, and specialized groups provide invaluable aid. This network ensures no one faces their journey alone.
Case Studies: Real-life Scenarios
Exploring real-life scenarios sheds light on the diverse experiences of individuals with Warthin’s tumor. These case studies offer insights into the journey patients and medical professionals take from diagnosis to treatment and beyond. They provide a window into the challenges faced and the victories achieved during this process.
Successful Treatment And Recovery Stories
Countless patients have navigated the road to recovery from Warthin’s tumor. Their stories often highlight:
- Timely diagnosis through attentive healthcare.
- Expert surgical intervention leading to complete removal.
- Minimal side effects post-treatment.
- Swift return to daily activities.
One such case involved a 45-year-old teacher. She underwent a successful parotidectomy. Her tumor was removed without complications. Follow-up care ensured she returned to teaching within weeks.
Challenges And Complications: Lessons Learned
Not all cases proceed smoothly. Some patients face unexpected trials. Yet, these challenges offer valuable lessons:
- Recognition of rare complications matters.
- Patient education on possible outcomes is crucial.
- Continuous monitoring may be necessary for some.
A 58-year-old man encountered nerve pain post-surgery. His recovery included physical therapy. His resilience teaches us about the importance of comprehensive aftercare.
Public Health Perspective And Awareness
Understanding Warthin’s Tumor is crucial for public health. Education and awareness can lead to early detection, which often results in better outcomes. Sadly, knowledge about Warthin’s Tumor is not widespread. This lack of awareness calls for targeted public health strategies to increase knowledge and improve patient support.
Educational Initiatives And Preventive Strategies
Educational campaigns can spread vital information about Warthin’s Tumor. Schools, clinics, and community centers are key places for these initiatives. Health professionals can lead talks and distribute flyers to teach communities.
- Organize free screenings in local areas to promote early diagnosis.
- Develop educational materials for schools and workplaces.
- Use social media to reach a wider audience effectively.
Encouraging healthy lifestyles is also essential. Risk factors like smoking increase the likelihood of developing Warthin’s Tumor. Prevention strategies may include:
- Anti-smoking campaigns aimed at reducing tobacco use.
- Encouraging regular dental check-ups for early symptoms detection.
Role Of Healthcare Policy And Access To Care
It’s important that all individuals have access to healthcare for early diagnosis and treatment. Policies should ensure that no one is left behind due to cost or location.
Investment in healthcare infrastructure can ensure equitable access to diagnostic tools. Health insurance policies can cover screenings and treatments related to Warthin’s Tumor.
| Policy Action | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
| Expand insurance coverage | Increased screenings |
| Better funding for rural clinics | Improved access in remote areas |
Consistent clinic visits and patient follow-ups enhance the continuity of care for those with Warthin’s Tumor. Partnerships between local health agencies and national organizations can amplify impact.
Finally, supporting research into Warthin’s Tumor can inform future policy and lead to more effective treatments and preventive measures.
Future Directions: Research And Development
The journey to comprehending Warthin’s Tumor continues with exciting advancements on the horizon. Scientists and doctors are working tirelessly to unveil new treatments and understand the genetic codes behind this growth. Let’s explore the promising research and the potential for groundbreaking discoveries in this field.
Emerging Therapies And Clinical Trials
The quest for improved therapies keeps gaining momentum. Innovative drugs and novel treatment strategies are constantly emerging.
- Targeted drug delivery systems are in development.
- Research on immunotherapy offers hope for enhanced treatment options.
- Clinical trials are exploring the efficacy of new medications and therapies.
Active participation in clinical trials offers patients access to cutting-edge treatments. It also helps doctors find better ways to combat Warthin’s Tumor.
Potential Breakthroughs In Genetics And Biotech
The genetic puzzle behind Warthin’s Tumor intrigues researchers. Breakthroughs in this area could lead to personalized medicine strategies.
- Scientists are identifying genetic markers linked to the tumor’s development.
- Advances in biotechnology pave the way for gene editing techniques.
- Genome mapping projects have the potential to unveil new diagnostic methods.
Genetic research not only helps in early detection but could also spare patients from undergoing invasive treatments. This marks a significant potential shift from a one-size-fits-all approach to individualized care plans.
| Area of Research | Current Status | Future Prospects |
|---|---|---|
| Therapeutic Development | New drugs under trial | Promising treatments to emerge |
| Genetic Research | Identifying genetic markers | Shift towards personalized therapy |
Controversies And Ethical Considerations
Warthin’s Tumor, or Warthin’s adenolymphoma, often involves tricky decisions for both doctors and patients. The controversies and ethical considerations surrounding its treatment bring significant challenges. As we shed light on these issues, understanding this benign parotid gland tumor becomes clearer.
Debate Over Treatment Modalities
The right approach to treating Warthin’s Tumor can spark debate. Medical experts sometimes disagree on the path forward. This mostly happens with size and symptoms of the tumor. Choices range from surgery to watchful waiting. The decision impacts patient health and peace of mind.
- Surgical removal – often seen as a definitive treatment.
- Radiation or conservative management – may be favored in certain scenarios.
These opposing views present a dilemma. Each has its risks and benefits. Weighing these against patient preferences can be tough. It is a balance between medical evidence and individual circumstances.
Ethical Dilemmas In Patient Care And Clinical Trials
Ethical dilemmas often arise in medical settings. This is true when discussing Warthin’s Tumor. One key issue relates to informed consent in patient care. Patients must understand their options. This includes their right to choose or refuse treatment.
Clinical trials are another area of controversy. They are essential for advances. The challenge is to enroll patients while ensuring their rights are protected. This means clear communication about the trial’s purpose, processes, risks, and benefits.
- The value of patient autonomy.
- The need for clear information about treatment options.
- Respect for patient decisions.
Respecting patient choices is vital. It’s about treating patients with dignity and consideration. Such ethical commitments guide the care journey for those with Warthin’s Tumor.
International Perspectives And Variations In Care
Understanding Warthin’s Tumor requires a global lens. This rare, benign tumor affects the salivary glands. Around the world, treatments vary.
Cultural beliefs and medical infrastructure shape these differences. Let’s explore how different countries tackle Warthin’s Tumor.
Treatment Approaches Across Different Cultures
In some cultures, natural remedies prevail. Others lean on advanced medical surgeries. Here’s a snapshot:
- Traditional Chinese Medicine often uses herbs.
- Western countries may prefer surgical removal.
These approaches reflect deep cultural values. They show the respect for harmony in Eastern practices. They also show the trust in technology in the West.
Comparing Healthcare Systems And Outcomes
Different healthcare systems yield various outcomes:
| Country | Healthcare System | Survival Rate |
|---|---|---|
| USA | Privatized | High |
| Sweden | Public | High |
| India | Mixed | Varies |
The table showcases different recovery rates. These depend on the healthcare system in place.
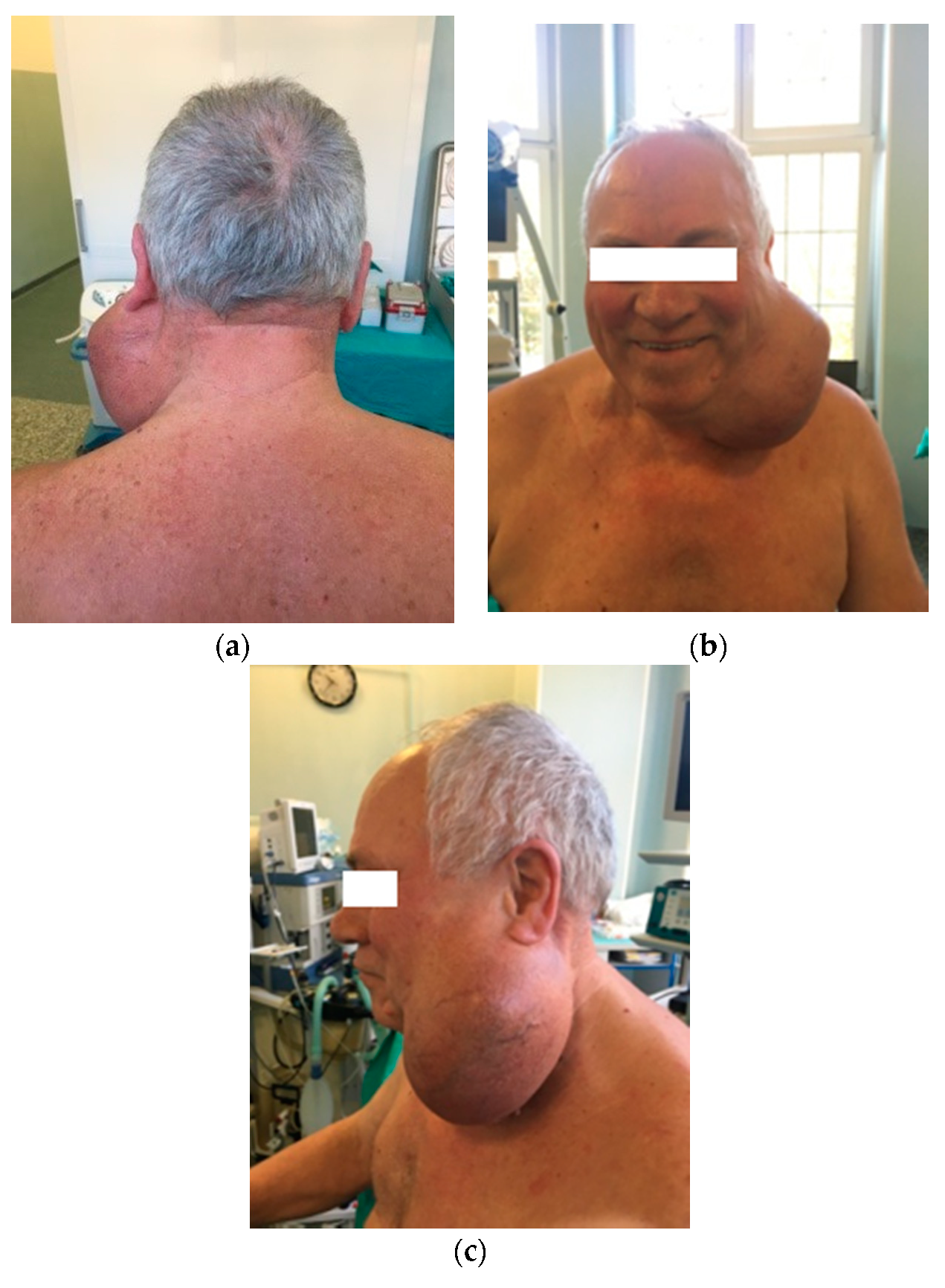
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Conclusion: Synthesizing The Information On Warthin’s Tumor
With the complexities of Warthin’s tumor unraveled, this section aims to consolidate what we’ve learned. Key points will be summarized, and thoughts on the progression of understanding and treatment presented. We aim for clarity and insight for those seeking knowledge on Warthin’s tumor.
Summarizing Key Points And Takeaways
- Warthin’s tumor is a benign salivary gland growth.
- It’s often found in the parotid gland.
- Smokers have a higher risk.
- Diagnosis involves imaging tests and sometimes a biopsy.
- Treatment usually means surgery and has a high success rate.
- Regular check-ups are important post-treatment.
Final Thoughts On Advancing Understanding And Treatment
Research continues to bring new insights into Warthin’s tumor. Awareness grows, and treatments improve. Staying updated on scientific developments helps patients and doctors alike. Together, we move towards a future where Warthin’s tumor imposes minimal impact on lives.
Conclusion
Understanding Warthin’s Tumor is key to recognizing this benign glandular issue. Through diligent observation and timely medical consultations, individuals can effectively manage this condition. Remember to discuss any concerns with a healthcare professional for appropriate guidance and treatment options. Early detection remains a cornerstone in ensuring a positive outcome.
Stay informed and proactive about your health.

