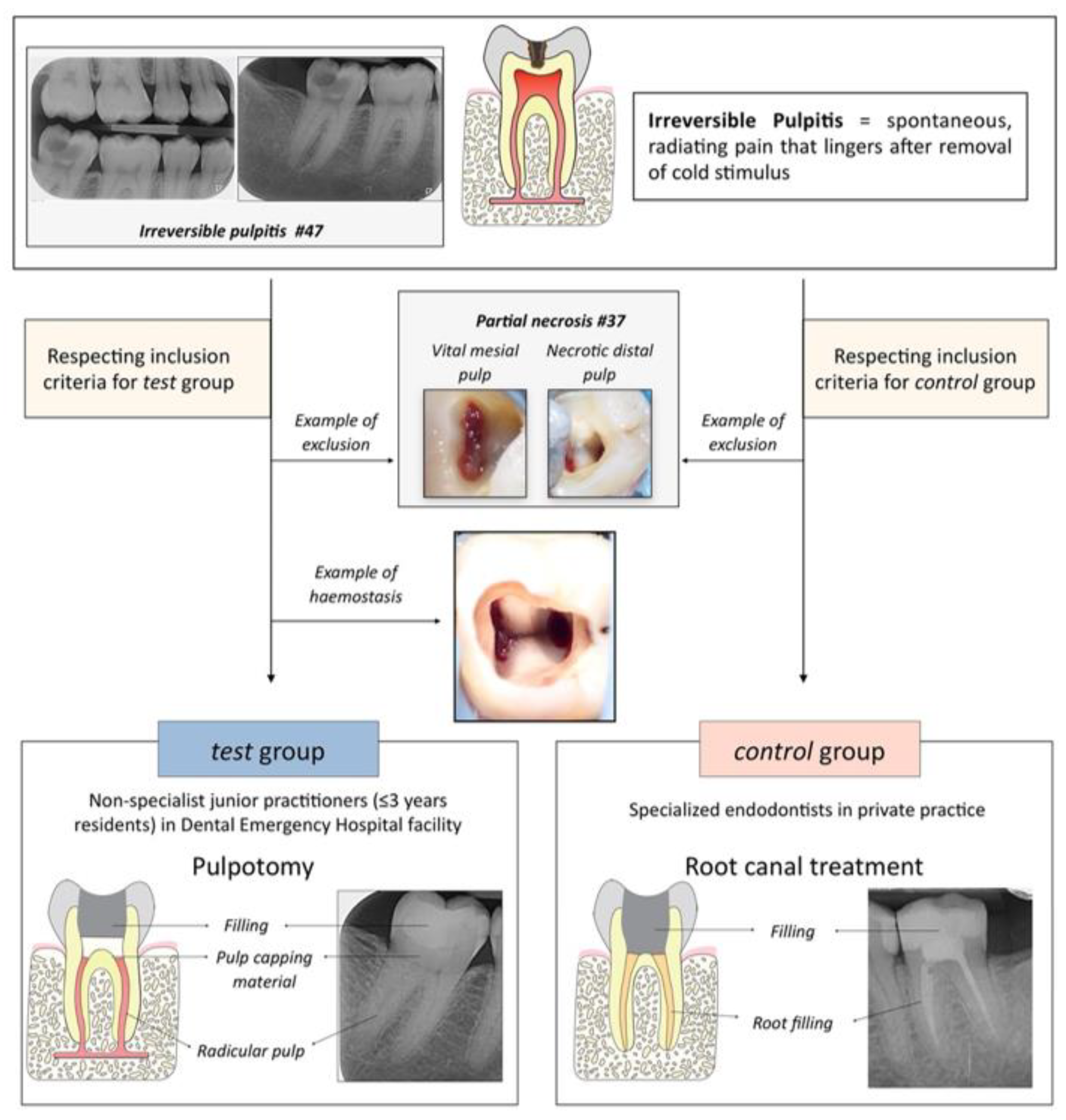
Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis is a painful dental condition marked by persistent toothache. It indicates that the nerve inside the tooth, known as the pulp, has been damaged beyond repair.
Dealing with a throbbing toothache can disrupt your daily life, making timely dental diagnosis and treatment essential. Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis often signals the need for a root canal procedure, as it involves the inflammation or infection of the dental pulp.
Symptoms that you may experience include heightened sensitivity to hot and cold, sharp pain when biting or chewing, and a constant, aching pain that doesn’t subside. Understanding the signs and seeking professional care is crucial to alleviate pain and prevent further complications such as abscess formation. Early intervention can save the tooth and restore oral health, emphasizing the importance of recognizing and addressing Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis promptly.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Introduction To Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis
Imagine a toothache that just won’t go away. This could be a sign of Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis (SIP). It’s a common, painful condition in teeth. Addressing it quickly is key to prevent more problems. Let’s dive in and understand what SIP really means.
Defining Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis
Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis is a dental term. It describes a state where the tooth’s pulp is damaged beyond repair. The pulp is full of nerves and blood vessels. It can become inflamed and infected. This can lead to constant, severe pain. The pain might even wake you from sleep. It often reacts badly to hot or cold foods.
Prevalence And Importance Of Early Diagnosis
SIP is not rare. Many people face this issue due to decay or injury. Catching it early can mean a simpler fix. Ignoring it can lead to big problems like abscesses or tooth loss. Early signs include pain when biting or sensitivity to temperatures. Dentists can spot it with exams or X-rays. Early treatment is crucial to save the tooth and halt infection.
Understanding Pulmonary Anatomy And Physiology
Understanding Pulmonary Anatomy and Physiology may appear out of place while discussing Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis. However, it’s essential to know that a detailed grasp of human anatomy, including both dental and pulmonary systems, aids in comprehensive healthcare.
Anatomical Structure Of Dental Pulp
Dental pulp is the innermost part of a tooth. It holds nerve tissues and blood vessels. These tissues are crucial for a tooth’s health and function. To visualize dental pulp, think of it nestled in the core of each tooth. This soft tissue resides inside a space called the pulp chamber, which extends into smaller canals known as root canals.
- Main components: Connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves.
- Location: Within the pulp chamber and root canals.
- Purpose: Vital for tooth nutrition and sensation.
Physiology And Functions Of Dental Pulp
The dental pulp may look simple, but it has essential roles. These include helping grow and develop the tooth during its formation. It also manages nutrients that keep the tooth alive. Plus, the nerves in the pulp let you feel cold, heat, or pain in a tooth.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Formation | Contributes to tooth creation and growth. |
| Nutrition | Delivers nutrients to the tooth through blood vessels. |
| Sensation | Carries sensory information through nerves. |
| Defense | Produces substances that protect the tooth from infection. |
Pathophysiology Of Irreversible Pulpitis
Irreversible pulpitis marks a serious phase in dental health. Pain is often the alarm that something is wrong. Understanding the transformation that leads to irreversible pulpitis helps in managing dental pain.
The Progression From Reversible To Irreversible Pulpitis
Dental pulp can heal or worsen; it depends on the stress it faces.- Initial tooth pain might denote reversible pulpitis.
- Without treatment, this pain can turn into irreversible pulpitis.
Biological Mechanisms Underlying Irreversible Pulpitis
The pulp becomes irritated and inflamed.
Blood flow changes in the pulp cause severe pain.- Bacteria invade the pulp, leading to an immune response.
- Immune cells fight bacteria but can harm the pulp.
- Pain means the pulp cannot heal on its own.
Etiological Factors
Teeth feel pain too, and Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis is one such hurtful condition. Understanding ‘Etiological Factors’ shines a light on why this dental problem happens. When the soft core of a tooth, called the ‘pulp,’ gets hurt and cannot heal, it usually leads to this toothache. Now, let’s drill down into what causes this pain and how tiny germs play a big part.
Common Causes Of Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis
- Deep Decay: Holes in teeth go deep and reach the pulp.
- Bumps and Hits: Teeth getting hit can lead to big problems.
- Old & Large Fillings: Sometimes, past fixes don’t last and hurt the pulp.
- Cracks in Teeth: Tiny lines in teeth can let bad things inside.
Role Of Bacteria And Dental Caries
Bacteria are tiny bugs that love sweets and make acids. This acid can eat teeth and cause holes called ‘caries’. Once these holes get big, these bugs reach the tooth’s heart, causing infection and a lot of pain. It’s a common path to Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis – and a big reason to brush and floss daily!
Symptoms And Clinical Presentation
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation of Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis reveal a dental pulp that can no longer heal itself. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for timely and accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Characteristic Symptoms Of Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis
- Sharp, lingering tooth pain when exposed to hot or cold temperatures.
- Pain that remains for an extended period after the stimulus is gone.
- Spontaneous pain that occurs without any apparent cause.
- Difficulty in pinpointing which tooth hurts.
- Pain that intensifies when lying down or changes with posture.
- Swelling and tenderness in the nearby gums may suggest acute inflammation.
Differential Diagnosis: Distinguishing From Similar Conditions
This involves distinguishing Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis from conditions with similar symptoms. Notable differences help in accurate diagnosis:
| Condition | Symptoms | Distinguishing Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Symptomatic Reversible Pulpitis | Short, sharp pain | Pain subsides when stimulus removed |
| Dental Abscess | Constant, severe pain | Visible pus drainage or swelling |
| Periodontal Disease | Gum inflammation | Bleeding gums, loose teeth |
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Diagnostic Procedures
Identifying Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis requires detailed diagnostic procedures. Dentists perform a sequence of evaluations. These assessments confirm the condition. Accurate diagnosis is crucial. It ensures the best treatment plan. This blog post outlines the main diagnostic procedures. It will focus on clinical and radiographic techniques used in dental practices.
Clinical Examination Techniques
Clinical examination is the frontline approach to diagnose Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis. Dentists start with a patient’s history. They ask about pain. Is the pain sharp? Does it linger? Responses guide further examination.
- Visual inspection: Dentists look for visible signs on the tooth and surrounding gums.
- Palpation: They check for swelling by gently pressing on the gums.
- Percussion testing: Tapping on the tooth highlights areas of sensitivity or pain.
- Cold and heat tests: These indicate the health of the pulp inside the tooth.
- Electric pulp testing: A small electric current tests pulp vitality.
Radiographic Assessment And Interpretation
After the clinical examination, radiographs or X-rays provide deeper insights. These images show the tooth’s internal structure. Dentists spot abnormalities not visible during the clinical exam.
| Type of Radiograph | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Periapical | Checks the root’s condition and surrounding bone. |
| Bitewing | Reveals the upper and lower teeth in one area. |
| Panoramic | Offers a full view of the mouth in one image. |
Interpretation of these images is key. Dentists look for dark spots, signaling decay. They search for changes in the root canal. These signs point to nerve damage due to pulpitis.
Treatment Modalities
When facing Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis, prompt treatment is key. This condition means the tooth’s pulp is damaged and won’t heal. Ignoring it can lead to more pain and further dental issues. Luckily, dentists have effective treatment methods. Know the options to manage pain and fix the problem permanently.
Immediate Pain Management Strategies
Dealing with the immediate pain is the first step. Here’s what helps:
- Over-the-counter painkillers: Ibuprofen or acetaminophen can reduce pain quickly.
- Cold compress: Apply it to the cheek to ease swelling and discomfort.
- Avoid hot or cold foods: They can trigger more pain.
Remember, these are short-term fixes. Visit your dentist as soon as possible.
Root Canal Therapy: Procedure And Prognosis
A root canal is a common long-term solution for Irreversible Pulpitis. Here’s how it works:
- Dentist numbs the area.
- They make a small opening on top of the tooth.
- Infected pulp gets removed gently.
- They clean and shape the inside of the tooth.
- The tooth is filled and sealed with a material.
Many root canals are successful. The tooth can last a lifetime with proper care.
Complications And Consequences
Symptomatic irreversible pulpitis refers to a painful condition in the dental pulp. It’s not just a simple toothache. Neglecting it can lead to serious problems. Let’s dive into what those might be.
Potential Complications Without Treatment
Leaving symptomatic irreversible pulpitis untreated invites a host of issues:
- Dental Abscess: This is a pocket of pus that forms in the tooth. It can cause severe pain.
- Tooth Loss: When the pulp dies, the tooth might not be saved. It may need removal.
- Bone Loss: Infection can eat away at the jawbone, weakening your tooth’s support.
Systemic Implications Of Irreversible Pulpitis
Problems can spread beyond the mouth:
- Facial Swelling: Infection can cause noticeable swelling on one side of the face.
- Fever: Your body might react with a fever as it tries to fight the infection.
- General Malaise: Feeling unwell overall is a common sign of a spreading infection.
Preventive Measures
Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis is a painful dental condition that no one wants to experience. The best strategy against this dental threat is prevention. Here are effective measures to keep pulpitis at bay and ensure a healthy smile.
Effective Oral Hygiene Practices
Maintaining a top-notch oral hygiene routine is crucial in preventing pulpitis. Brush your teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste. Flossing daily reaches areas your toothbrush can’t. Replace your toothbrush every three months, or sooner if bristles fray.
- Brush your teeth for two minutes.
- Use fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss once a day.
- Replace your toothbrush regularly.
Regular Dental Check-ups And Early Interventions
Regular dental visits are key for early detection and treatment of oral issues.
| Check-up Frequency | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Every 6 Months | Identifies problems early on |
| As Recommended | Professional cleaning and guidance |
Dentists can spot signs of trouble before they worsen. They provide essential treatments to prevent pulpitis. Listen to their advice. They may recommend sealants or fluoride treatments.
Advancements In Pulpitis Treatment
Symptomatic irreversible pulpitis often means enduring toothache and discomfort. It’s a signal that the dental pulp is hurt and can’t fix itself. Doctors are finding new ways to treat pulpitis. These methods ease pain better and help save more teeth.
Innovative Endodontic Techniques
Root canal therapy has transformed with new tools and practices. This means treating teeth is quicker and hurts less. Here are key changes:
- Nickel-titanium files: These bend more and don’t break as easily. They clean roots better, too.
- GentleWave Procedure: It uses sound waves to clean. It reaches spots that regular tools can miss.
- 3D imaging: Dentists see teeth and roots in 3D. This helps them plan and do treatments more safely.
Such technologies mean a better dental visit. They also help heal teeth fast.
Emerging Pharmacological Therapies
New medicines help fight pulpitis without surgery. They can save teeth and stop pain. Check out these exciting drug therapies:
| Medicine | How It Helps |
|---|---|
| Anti-inflammatory drugs | Calm swelling and reduce pain |
| Collagen-based materials | Help rebuild tooth parts |
| Regenerative medicine | Encourage cells to repair the tooth from within |
Such treatments are brand-new and getting better. They aim to fix the tooth with fewer side effects.
The Role Of Patient Education
The Role of Patient Education is pivotal in managing Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis.
Educated patients can prevent this painful condition. They also ensure treatment success by following dentist advice. Let’s dive into how to educate patients effectively.
Educating Patients On Risk Factors And Prevention
Understanding risk factors is the first step in prevention. Patients should be aware of these to protect their oral health:
- Poor oral hygiene leads to pulpitis. Regular brushing and flossing are crucial.
- High sugar intake can cause tooth decay. Limiting sugary foods and drinks keeps teeth healthy.
- Dental trauma from sports or accidents can damage teeth. Wearing mouth guards during activities helps prevent injury.
Preventative measures include:
- Regular dental check-ups.
- Using fluoride toothpaste.
- Sealing back teeth.
Importance Of Patient Compliance In Treatment Success
Success in treating pulpitis largely depends on patient compliance. Following the dentist’s plan is key:
- Timely treatment: Don’t ignore symptoms. Early dental care prevents complications.
- Medication adherence: Take all prescribed medicines as directed.
- Post-treatment care: Follow all aftercare instructions to avoid re-infection.
Remember, effective communication ensures patients understand their role in the healing process.

Credit: www.sciencedirect.com
Pain Management: Medications And Techniques
Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis often brings intense tooth pain. This condition can disrupt daily life. Prompt and effective pain management is crucial. Patients seek both medications and techniques to soothe the pain. Understanding both options can help manage the discomfort effectively. Let’s explore the tools for battling pulpitis pain.
Analgesics And Antibiotics In Managing Pulpitis
Pain from pulpitis requires strong medicines. These medicines are called analgesics. Over-the-counter options, like ibuprofen, help reduce swelling and pain. Sometimes, doctors prescribe stronger painkillers. Antibiotics may not be needed. Unless there is swelling or fever, they might not help much.
| Medication Type | Use | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Over-the-counter Analgesics | To relieve mild to moderate pain | Ibuprofen, Acetaminophen |
| Prescription Analgesics | For severe pain | Oxycodone, Tramadol |
| Antibiotics | For signs of infection | Amoxicillin, Clindamycin |
Non-pharmacological Pain Relief Methods
Apart from medicines, other techniques help ease pulpitis pain. Cold compresses reduce swelling. Elevating your head when resting limits blood flow to the area. This can lessen throbbing. Some patients find relief with meditation or focused breathing.
- Cold Compress: Apply to cheek to decrease swelling.
- Elevation: Keep head raised to reduce pain intensity.
- Meditation: Manage discomfort through relaxation.
- Focused Breathing: Use controlled breathing to distract from pain.
Case Studies And Clinical Trials
Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis takes a front seat in dental pain management. Exploring case studies and clinical trials, dentists gain insights into the best treatment approaches. These studies shed light on successes, challenges, and the evolution of care strategies. Let’s dive into some of the most significant findings from recent research.
Review Of Notable Case Studies On Pulpitis
Notable case studies provide a window into real-life encounters with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis. They reveal symptom patterns, treatment steps, and patient outcomes. We’ll look at specific cases to understand varied presentations of this condition. These stories help practitioners recognize pulpitis signs earlier and decide on timely intervention.
- Case 1: A teen with severe toothache shows advanced pulpitis after neglect.
- Case 2: A middle-aged patient presents with swollen gums and a history of sensitivity, leading to a pulpitis diagnosis.
Insights From Recent Clinical Trials
Clinical trials test new methods to treat or manage symptomatic irreversible pulpitis. They help dentists improve patient care. Recent trials have compared anesthetics, studied pain relief methods, and measured healing times.
| Trial Name | Focus Area | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Anesthetic Efficacy | Pain Management | New anesthetic proves more effective for immediate relief. |
| Laser Therapy Impact | Tissue Healing | Laser treatment shortens recovery time by 30%. |
With the information gathered through clinical trials, dentists can offer better advice. They ensure their patients receive the most innovative and effective care.
Long-term Prognosis And Outcomes
Dealing with Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis means addressing severe dental pain and infection. Endodontic treatment, commonly known as root canal therapy, becomes essential. This procedure can relieve pain and save the tooth. Understanding the long-term success and quality of life post-treatment helps patients know what to expect.
Success Rates Of Endodontic Treatments
Root canal treatments have a high success rate. Effective techniques ensure teeth can last a lifetime. Here’s a breakdown:
- Proper cleaning and sealing of the canal space increase success.
- Using modern equipment and materials improves outcomes.
- Post-procedure care by patients is crucial for treatment longevity.
| Time After Treatment | Success Rate |
|---|---|
| 1 Year | 90% |
| 5 Years | 85% |
| 10+ Years | 80% |
Quality Of Life Post-treatment
Root canal therapy aims to remove pain and restore function. Here’s what patients generally experience:
- Immediate pain relief following the procedure.
- Ability to chew and bite without discomfort.
- Normal appearance of teeth is maintained.
Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene are keys to maintaining these benefits long-term.
Challenges In Endodontic Practice
Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis presents unique difficulties for dental professionals. The correct endodontic treatment can be tough. These challenges require skill, patience, and the most up-to-date practices. Let’s dive into some of the main hurdles faced during these procedures.
Dealing With Complex Anatomy
Teeth roots can be tricky. They twist, turn, and sometimes have extra canals. Finding and treating all areas of the infected pulp is a must. Tools like magnification glasses and 3D imaging help dentists see better. Dentists must be like detectives, searching for hidden parts of nerves.
- Root Canal Anomalies: Hidden, extra, or divided canals.
- C Shaped Canals: Unusual, hard-to-treat shapes.
- Calcification: Hardened tissues blocking access to canals.
Overcoming Treatment Resistance
Sometimes, the usual treatment doesn’t work. Bacteria can hide and withstand the usual medications. That’s why dentists must always learn and use new techniques and treatments.
Advanced technology like ultrasonics helps get rid of stubborn bacteria. Dentists also use modern irrigation solutions that can reach deep into the tooth. These treatments help when the usual methods fail.
- Ultrasonic Instruments: Break up bacteria and debris.
- Effective Irrigation: Cleans out the canals thoroughly.
- Antibiotic Pastes: Target and kill resistant bacteria.
Patient Case Management
Dealing with Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis requires a focused Patient Case Management strategy. This means understanding the condition. It also means finding the best treatment for the patient. A good plan helps reduce pain and saves the tooth if possible. Our goal is to ease the patient’s discomfort and restore dental health quickly and efficiently.
Developing A Comprehensive Treatment Plan
Crafting a treatment plan for Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis starts with diagnosis. We must ask the patient about their pain. We also look at their dental history. X-rays often help us see the problem. The aim is to stop the pain and prevent infection.
- Examination: Visual inspection and tests determine the tooth’s condition.
- Diagnosis: Pinpoint the issue using symptoms and dental records.
- Treatment options: Discuss with the patient. They can be root canal treatment or tooth extraction.
- Prevention: Offer advice on how to avoid future dental issues.
- Follow-up care: Schedule visits to check healing and recovery.
Multidisciplinary Approach And Referral Process
Sometimes, Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis takes more than one expert to manage. That’s when a multidisciplinary approach comes in. Various dental specialists may join to give the best care.
Coordinated care is key. The general dentist might work with an endodontist for root canals. They may also team up with a pain specialist. Referral to another dentist is sometimes needed. This ensures specialized care for complex cases.
| Step | Action | Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Assess need for specialist | General Dentist |
| 2 | Referral to Endodontist | Endodontist |
| 3 | Advanced pain management | Pain Specialist |
| 4 | Final treatment and follow-up | Referring Dentist |
Legal And Ethical Considerations
When dealing with Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis, understanding the legal and ethical responsibilities is crucial. It ensures both the patient’s rights and the dental practitioner’s protections. In the field of endodontics, these considerations are a top priority. Recognition of patient autonomy, informed consent, and a clear approach to potential complications, define the quality of care.
Informed Consent In Endodontic Procedures
Ensuring that patients give informed consent before procedures is a legal and ethical must-do. The consent process involves a clear explanation of:
- The diagnosis of Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis
- Proposed treatment plan
- Possible risks and benefits
- Alternative treatment options
Consent must be voluntary and come from the patient or a legal representative if the patient is under age or incapacitated. Documentation of this process is a safeguard for all involved.
Handling Medical Errors And Malpractice
In case of medical errors or malpractice, the dental practitioner has the obligation to inform the patient as soon as possible. Openness in such situations is not only an ethical duty but also a legal requirement in many regions. A structured approach to errors includes:
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Acknowledge the error |
| 2 | Inform the patient |
| 3 | Discuss rectification measures |
| 4 | Implement changes to prevent future errors |
Addressing errors transparently minimizes legal ramifications and maintains the trust relationship with the patient. Regular training on ethical practice helps dental teams be prepared for these delicate situations.
Future Directions In Pulpitis Research
Exploring the frontier of dental science shines a light on groundbreaking methods to tackle Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis. This condition, marked by severe, persistent tooth pain, has challenged dental professionals for years. Innovative research offers hope for more effective treatments, focusing on saving teeth rather than removing them. Let’s dive into the exciting potential changes on the horizon.
Potential For Regenerative Endodontic Procedures
Regenerative endodontics is a thrilling area of research that might transform dental care. Scientists aim to repair damaged dental pulp using the body’s natural healing abilities. This approach could significantly reduce the need for traditional root canals.
- Stem cell therapy to regenerate pulp tissue
- Growth factors to stimulate healing
- Biodegradable scaffolds to support tissue development
Technological Innovations And Clinical Applications
Tech advancements pave the way for more precise diagnostics and treatment of pulp diseases. Novel imaging techniques allow dentists to see dental pulp in detail.
- Digital radiography for better resolution
- Advanced Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT)
- Non-invasive laser therapy for pain relief
These tools will enable earlier detection and targeted treatments, preserving more natural tooth structure.
Conclusion
Understanding symptomatic irreversible pulpitis is crucial for maintaining oral health. Timely intervention can alleviate pain and prevent complications. Always consult with a dental professional if you experience persistent tooth discomfort. Remember, early diagnosis and treatment are key to preserving your smile.
Protect your teeth by staying informed and proactive about dental symptoms.

