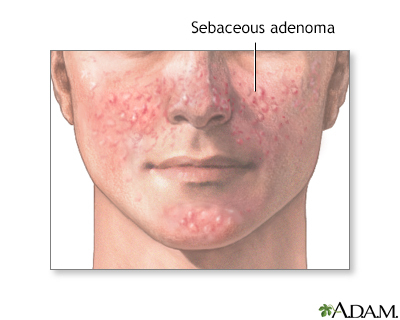
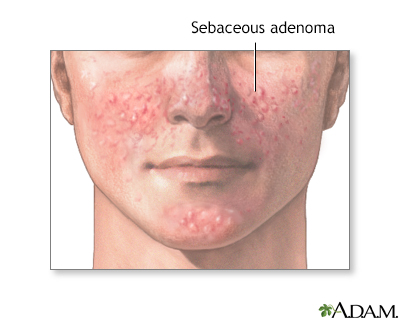
A sebaceous adenoma is a benign tumor originating from sebaceous glands. It often appears as a small, flesh-colored skin bump.
Sebaceous adenomas are typically slow-growing and manifest predominately in middle-aged or older individuals, especially in those with a history of prolonged sun exposure or with rare genetic conditions such as Muir-Torre syndrome. These bumps can develop anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the face, scalp, or torso.
Although considered benign, they can sometimes be mistaken for more serious skin lesions, making dermatological evaluation important for an accurate diagnosis. Treatment isn’t always necessary, but options like surgical excision or cryotherapy exist if removal is desired. Ensuring your content is clear and approachable, this introductory paragraph highlights the essentials about sebaceous adenomas, aiming to inform without overwhelming the reader.
Credit: ufhealth.org
Introduction To Sebaceous Adenoma
Welcome to an exploration of Sebaceous Adenoma, a topic both intriguing and essential for anyone vested in skin health. This benign phenomenon often sparks interest and sometimes concern. Let’s demystify it together.
Definition And Overview
Sebaceous Adenoma is a small, benign tumor. These growths form from sebaceous glands and are mostly harmless. Insight into their nature aids in understanding their impact on health.
Incidence And Prevalence
| Age Group | Incidence Rate |
|---|---|
| 50+ | Common |
| Under 50 | Rare |
Sebaceous Adenomas mostly occur in older adults. Rare in younger individuals, these growths signal a need for attention, not panic.
Sebaceous Glands And Their Function
- Located under your skin.
- Produce oil to lubricate skin and hair.
- Exist throughout the body except on palms and soles.
Sebaceous glands play a vital role in maintaining healthy skin. They keep the skin moisturized and prevent dryness.
Credit: perridermatology.com
Clinical Presentation Of Sebaceous Adenoma
The clinical presentation of Sebaceous Adenoma is distinct yet can be easily mistaken for other skin conditions. To accurately identify this benign tumor, we must understand its appearance, common locations, and the variations it can present.
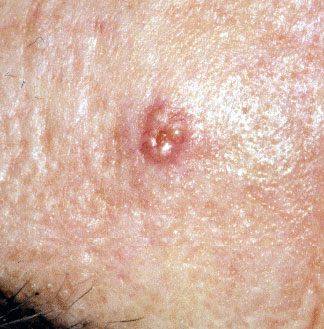
Typical Appearance And Characteristics
Sebaceous Adenomas typically emerge as small, pale yellow bumps. They’re renowned for their lobular shape and might have a central indentation. Their surface is often smooth, reflecting their benign nature. Below are key features that distinguish them:
- Size: Generally less than 2 cm in diameter
- Texture: Soft and sometimes slightly waxy
- Growth: Slow to develop, showing limited change over time
Common Locations On The Body
While these growths can appear anywhere, they have a preference for certain areas:
- Face: Particularly the forehead and cheeks
- Neck: Often where the skin is more exposed
- Back: Including the upper and mid-portion
Variations And Atypical Presentations
Atypical Sebaceous Adenomas break the usual mold with varying features:
- Larger size, potentially >2 cm
- Irritation or bleeding upon contact
- Uncommon shapes or textures
Recognizing these signs aids in effective diagnosis and management.
Pathogenesis And Etiology
Understanding the origin and development of sebaceous adenoma is essential. This condition features benign tumors, mostly affecting the sebaceous glands. Let’s explore the genetic and hormonal influences that play a role in its development, as well as its link to Muir-Torre Syndrome.
Genetic And Environmental Factors
Both hereditary elements and external factors contribute to sebaceous adenoma. The interaction between these influences decides its occurrence and progression:
- Genetic mutations can lead to abnormal cell growth.
- Environmental triggers, like UV radiation, may exacerbate the risk.
The Role Of Hormones In Development
Our hormonal balance significantly impacts sebaceous adenoma. Considering that these glands are hormone-sensitive:
- Changes in androgens levels, such as testosterone, are critical.
- Age-related hormonal shifts can increase occurrences in the elderly.
Association With Muir-torre Syndrome
Sebaceous adenoma is often a marker for Muir-Torre Syndrome (MTS), a genetic disorder:
- MTS is characterized by skin tumors and internal malignancies.
- It is important to test for MTS when sebaceous adenomas are diagnosed.
Diagnosis Of Sebaceous Adenoma
Sebaceous adenomas are benign skin tumours. Correctly diagnosing them is vital. The process involves several steps. Doctors use physical exams and patient history. They inspect the skin under a dermatoscope. Sometimes, a biopsy is necessary. Let’s look into these methods in detail.
Physical Examination And Patient History
Physical checks and patient’s past health guide doctors. They search for yellowish lumps on the skin. These could be sebaceous adenomas. Skin specialists ask about changes in the lump. They also ask if similar issues run in the family.
Dermatoscopic Features
Specialists use a dermatoscope to look closer. This tool shows the lump’s colors and patterns. It helps tell sebaceous adenomas from other skin problems. Key features include crown vessels and a central yellow area.
Biopsy And Histopathological Examination
When in doubt, doctors take a tissue sample. It’s called a biopsy. They study this sample under a microscope. This test, histopathology, checks for cancer cells. It confirms if the lump is a sebaceous adenoma. This step is crucial for accurate diagnosis.
Differential Diagnosis
Sebaceous Adenoma can look like other skin issues. Doctors need to check them well. They make sure it’s not something else. This is called Differential Diagnosis.
Distinguishing From Other Sebaceous Lesions
Sebaceous adenoma may look like other bumps that contain oil. But it has special features. Doctors look at the shape, size, and where it is on the body. Here’s how they tell them apart:
- Sebaceous Hyperplasia: Smaller, often has a central dent.
- Sebaceoma: Comes from deep skin, looks different under a microscope.
- Steatocystoma: Has a sack filled with oily liquid.
Separation From Malignant Conditions
A sebaceous adenoma is not cancer. But some bumps can be. To keep safe, doctors check for signs like:
- Rapid growth: Cancer spots can grow fast.
- Iregular borders: Cancer can have odd shapes.
- Color changes: If the color shifts a lot, it might be cancer.
They also may cut out a tiny part to test. This is called a biopsy.
Role Of Immunohistochemistry In Differential Diagnosis
Immunohistochemistry uses colors to tag parts of a cell. This helps doctors see if a lump is sebaceous adenoma or another condition. They look for markers that are common in certain bumps. This makes diagnosis accurate.
| Marker | Sebaceous Adenoma | Other Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Ema | Often positive | Varies |
| Cytokeratin | Positive in outer layer | Less specific |
Treatment Options For Sebaceous Adenoma
When it comes to treating Sebaceous Adenoma, several options are available. It’s a benign tumor that can still cause concern due to its appearance. Understanding the treatments helps in making an informed decision.
Surgical Methods
Surgical removal is often the go-to option for sebaceous adenomas. This method ensures the complete removal of the tumor. Below are types of surgical procedures:
- Excision – The adenoma is cut out of the skin.
- Curettage and electrodesiccation – The tumor is scraped and heat is used to treat the area.
- Cryotherapy – Freezing off the growth is another option.
These methods are quick with a short healing time.
Topical And Systemic Treatments
In certain cases, topical medications can help, especially when surgery is not an option. Systemic treatments may be needed if sebaceous adenomas are numerous, as in Muir-Torre syndrome.
- Retinoids – Vitamins A derivatives that can slow the growth.
- Isotretinoin – A strong oral medication for multiple tumors.
Consult a dermatologist for the best medication.
Consideration Of Cosmetic Outcomes
Weighing the impact on appearance is important with these treatments. Minor surgery can leave a small scar. Discuss options thoroughly with your dermatologist.
For visible areas, less invasive treatments might be more suitable. They potentially offer better cosmetic outcomes. The choice of treatment depends on the adenoma’s size, number, and location.
Prognosis And Follow-up
Sebaceous Adenoma may raise concern due to its growth or appearance. Understanding its long-term outlook and follow-up process is crucial for managing this condition. Regular monitoring ensures early detection of any changes. The information below outlines what patients can expect.
Long-term Outlook
Sebaceous adenomas are generally benign skin lesions. They infrequently signify underlying health issues. Most cases exhibit minimal risk for malignancy. Early diagnosis and treatment contribute to a positive long-term outlook.
Surveillance Strategies For Recurrence
- Regular skin exams – every 6 to 12 months
- Photographic documentation – tracks changes over time
- Self-checks at home – patients learn to recognize new growths
Monitoring For Associated Syndromes
Rarely, sebaceous adenomas link to Muir-Torre syndrome. Such cases require careful observation.
| Exam | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Dermatological Assessment | Annually |
| Genetic Counseling | As recommended |
| Cancer Screening | Based on family history |
Regular health checks and professional guidance drive the best outcomes for sebaceous adenoma patients.
Complications And Risks Associated With Sebaceous Adenoma
Sebaceous adenomas are generally benign, but awareness of potential complications and risks remains paramount for patients. Recognizing these concerns can help manage expectations and ensure prompt treatment if necessary.
Possibility Of Malignant Transformation
Though rare, sebaceous adenomas can sometimes herald more serious conditions. One such concern is their potential to develop into sebaceous carcinoma. Regular monitoring of the growths for any changes in size, color, or shape is crucial for early detection of malignant transformation.
Psychological Impact Of Cosmetic Appearance
Sebaceous adenomas, predominantly found on the face and scalp, can affect self-esteem and social interactions. The visibility of these growths may lead to unwanted attention or questions, potentially impacting a person’s psychological well-being.
Complications Of Treatment
- Infection: Post-treatment infections can occur, requiring medication.
- Scarring: Surgical removal may result in scars, affecting cosmetic outcomes.
- Recurrence: There’s a chance adenomas might reappear, necessitating further treatment.
Sebaceous Adenoma In The Context Of Sebaceous Neoplasms
When discussing sebaceous neoplasms, sebaceous adenoma is a pivotal entity. These benign growths occur in the sebaceous glands, which are oil-producing glands in the skin. They usually appear as small, yellowish, and sometimes lobulated lumps. Under the microscope, sebaceous adenomas showcase a distinct architecture that separates them from other sebaceous tumors. Understanding these differences is crucial in dermatology.
Comparing Sebaceous Adenoma With Sebaceous Carcinoma
Sebaceous adenoma and sebaceous carcinoma are both types of sebaceous neoplasms. However, adenomas are benign, while carcinomas are malignant and can spread. Sebaceous adenoma typically has a well-defined outline and a lower number of layers of cells. In contrast, sebaceous carcinoma often appears with irregular borders, a higher number of cell layers, and can invade nearby tissues.
The Spectrum Of Sebaceous Tumors
- Sebaceous Hyperplasia – an enlargement of sebaceous glands.
- Sebaceoma – a benign tumor with more basaloid cells.
- Sebaceous Adenoma – a benign tumor with mature sebaceous cells.
- Sebaceous Carcinoma – a potentially aggressive malignancy.
Sebaceous adenoma is a benign tumor characterized by mature sebaceous cells and is generally non-threatening. Their features provide insights into a broader range of sebaceous tumors, varying from mere gland enlargement to outright malignancy.
Clinical Significance In Genetic Syndromes
Sebaceous adenomas are important markers in Muir-Torre syndrome, a rare genetic disorder. People with this syndrome have a higher risk of developing sebaceous neoplasms and internal malignancies, like colon cancer. Early identification of sebaceous adenomas can lead to prompt genetic counseling and surveillance for associated cancers.
Credit: www.mountsinai.org
Conclusion
Understanding sebaceous adenomas is crucial for maintaining skin health. Early detection and consultation with a dermatologist can prevent potential complications. Remember, while typically benign, monitoring changes in your skin is essential. Embrace regular check-ups for peace of mind and effective management of any skin anomalies.

