A retention cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms when a duct or gland becomes blocked. It’s common in sinuses, ovaries, and skin.
Retention cysts, often noncancerous, arise from the accumulation of fluid due to blockage in the ducts of glands. These cysts can appear in various parts of the body, including the sinuses, where they are known as mucous retention cysts, and on the skin or inside the mouth, denoted as epidermal inclusion cysts or mucoceles, respectively.
Their presence in the ovaries is another frequent occurrence, sometimes referred to as ovarian cysts. Symptoms vary depending on the cyst’s location but often involve swelling, discomfort, or a noticeable lump. Treatment is not always necessary, as some retention cysts resolve on their own. Nevertheless, persistent or troublesome cysts may require medical intervention, which can range from medication to drainage or surgical removal. Understanding and identifying the characteristics of retention cysts can lead to effective management and relief from potential discomfort.
Introduction To Retention Cysts
Do you ever wonder what retention cysts are? These hidden fluid-filled sacs can sometimes cause discomfort or go unnoticed. This introductory section unveils retention cysts, their common presence, and why we should be aware of them. Let’s delve into the world of retention cysts together.
Understanding Retention Cysts
Retention cysts are small, benign sacs. They form when ducts or tubes in the body become blocked. This blockage traps secretions, leading to cyst formation. Common sites for these cysts include the sinuses, ovaries, and skin. Most people with retention cysts experience no symptoms. However, if cysts grow large, they can cause pain or pressure.
Prevalence And Significance Of Retention Cysts
Many people have retention cysts without knowing. They are often found during health check-ups or scans. Although retention cysts are mostly harmless, understanding their prevalence is crucial. It helps doctors determine when to act. A cyst’s location and size can make it significant. For instance, a large cyst in the sinus might impede breathing and require treatment.

Credit: en.wikipedia.org
Pathophysiology Of Retention Cysts
Understanding the pathophysiology of retention cysts is crucial to identifying effective treatment options. These cysts arise when a duct or gland becomes blocked. Fluid builds up behind the obstruction. This causes a cyst to form. Let’s explore the causative factors and underlying mechanisms that lead to their growth.
Causes Of Retention Cyst Formation
- Blocked Ducts: Secretions cannot escape, leading to cysts.
- Inflammation: Swelling narrows the ducts, causing blockages.
- Trauma: Injury can disrupt normal fluid flow and glands.
- Infections: They can trigger swelling and blockage.
- Hormonal Changes: They can alter secretion rates and compositions.
- Genetic Factors: Some people are more prone to retention cysts.
Underlying Mechanisms And Growth
Retention cysts typically start small. They grow as they collect more fluid. This growth is due to two key mechanisms:
- Continuous Secretion: The gland keeps making fluid.
- Impermeable Wall: The cyst wall doesn’t let fluid out.
Pressure inside increases as more fluid accumulates. This can cause pain and discomfort for some people. Regular monitoring is important to prevent complications.
Types Of Retention Cysts
Life throws us curveballs in various forms, one of which includes retention cysts. These cysts are pockets of fluid that can form in different parts of the body. This section delves into the types of retention cysts, exploring their locations and characteristics. Understanding these types will better equip you to recognize them.
Classification Based On Location
Retention cysts appear in several body areas, each with its unique impact. The classification by location helps doctors identify the best treatment approach.
- Maxillary Sinus: Often found in the sinuses, especially the maxillary sinus.
- Ovarian: These form on the ovaries and are common in women of childbearing age.
- Mucous: Usually seen in the lip, mouth, or other mucous membranes.
- Epidermoid: Occurring in the skin and containing keratin.
- Pilar: Also known as trichilemmal cysts, found on the scalp.
Common Characteristics Of Different Types
While varied in location, retention cysts share similarities across types:
| Location | Fluid Content | Visibility | Potential for Growth |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maxillary Sinus | Mucus | Hidden within the sinus | Can enlarge over time |
| Ovarian | Serous fluid or mucinous | Not visible externally | May grow with hormonal fluctuations |
| Mucous | Mucus | Often visible as a bump | Usually remains small |
| Epidermoid | Keratin | Visible under the skin | Grows slowly |
| Pilar | Keratin | Visible as a scalp lump | Can grow large |
In summary, retention cysts have diverse locations and shared characteristics. Early detection and treatment ensure they remain just a minor bump in the road.
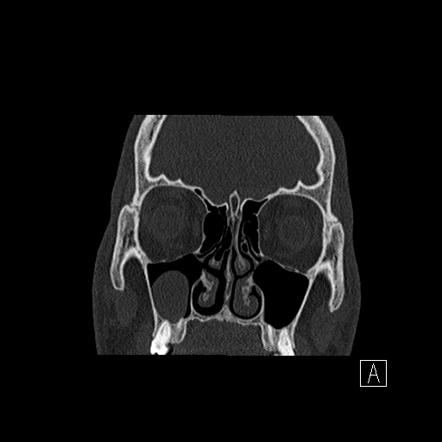
Credit: radiopaedia.org
Symptoms Of Retention Cysts
A retention cyst, often hidden from view, may exist without notice. On occasion, it announces its presence through a variety of symptoms. The symptoms can be as quiet as a whisper, or as loud as a shout, affecting daily routines. Let’s explore the signs that a retention cyst could be the uninvited guest in your body.
Identifying Common Symptoms
Retention cysts, benign in nature, can form in various organs. The symptoms experienced are tied to the cyst’s location. Common indicators may include:
- Sense of fullness or pressure in the affected area
- Discomfort or pain, particularly if the cyst is large
- Swelling or visible lumps on the skin
- Functional disturbance in nearby organs or structures
- Secondary infections that can cause redness and tenderness
For instance, a maxillary sinus retention cyst may lead to nasal congestion or pressure. A cyst in the ovaries might cause abdominal discomfort. Each location triggers distinct effects.
When To Seek Medical Attention
Certain symptoms warrant immediate medical review. Be vigilant and seek medical care if you notice:
| Location | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Ovarian Cysts | Severe abdominal pain, fever |
| Maxillary Sinus Cysts | Difficulty breathing, persistent headaches |
| Dental Cysts | Tooth displacement, acute pain, swollen gums |
Not all discomfort signifies a critical condition, but consistency or severity of symptoms is key. If pain intensifies, swelling increases, or new symptoms arise, contact a healthcare provider.
Diagnosis Of Retention Cysts
The journey to uncovering the mystery of retention cysts begins with a precise diagnosis. These cysts, often hidden and symptomless, require expert detection techniques to ensure the health of affected individuals. This section delves into the key diagnostic steps for identifying retention cysts.
Clinical Assessment
Doctors start with a careful examination of the affected area. They check for swelling and discomfort. Medical history offers clues to the nature of the cyst. Common sites are the sinuses, ovaries, and skin.
Imaging And Diagnostic Tests
In-depth analysis follows the initial check-up. Various tools help doctors see inside the body. This helps them confirm the presence of a retention cyst.
- Ultrasound – Waves create images of soft tissues.
- CT Scan – X-rays offer a detailed picture of the body’s structure.
- MRI – Magnetic fields provide a clear view of soft tissues.
Occasionally, doctors may use endoscopic techniques. They insert a tube with a camera into the body. This lets them see the cyst directly. For definite analysis, a biopsy might be essential. The lab checks cells from the cyst under a microscope.
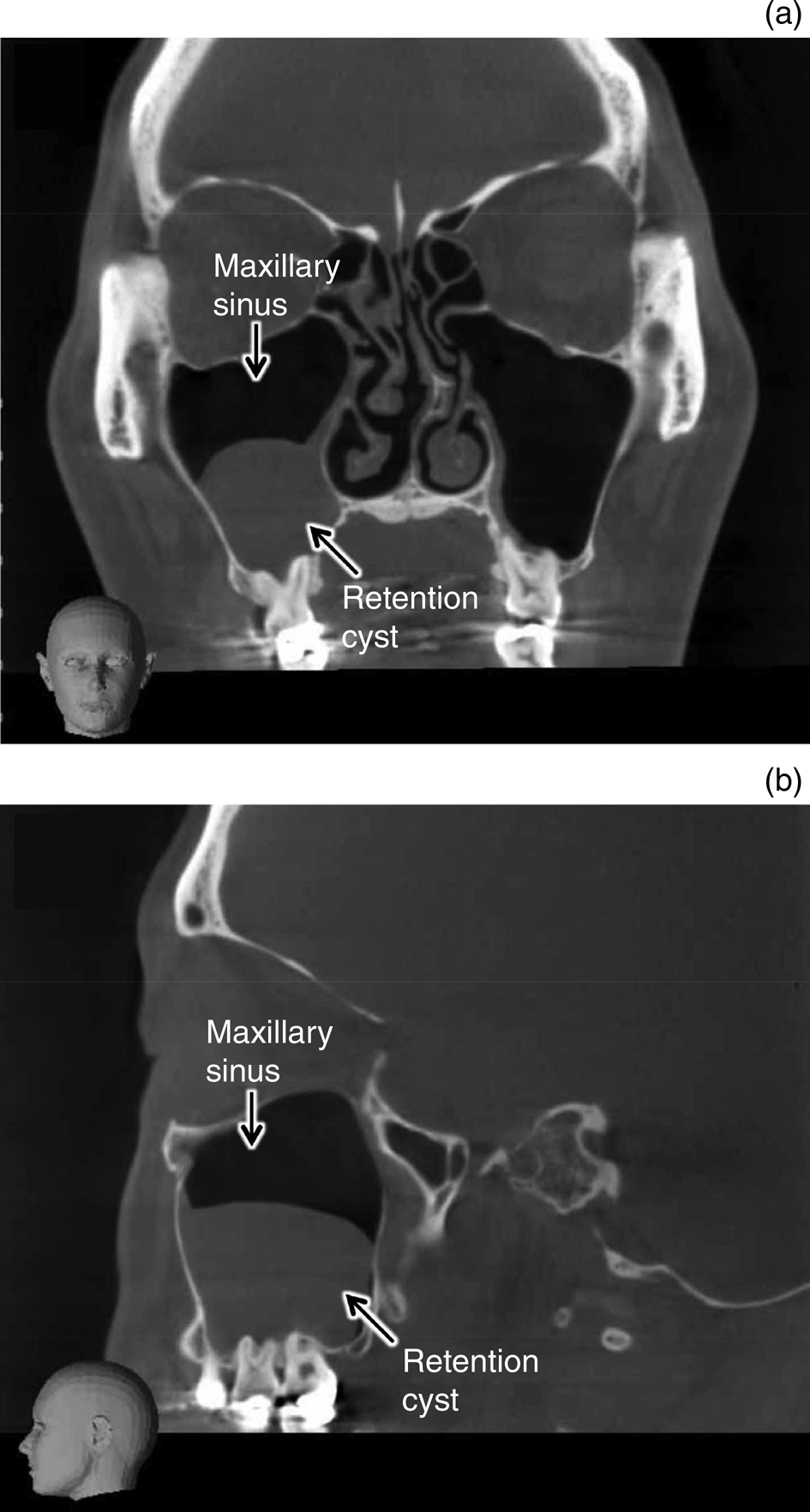
Credit: www.cambridge.org
Complications Associated With Retention Cysts
Retention cysts, often painless, are silent issues inside our bodies. But without proper attention, they can cause problems. Understanding potential complications keeps us informed and health-conscious. Let’s explore what can happen if these cysts remain unchecked.
Potential Risks Of Untreated Cysts
- Infection: Cysts may become infected, leading to pain and swelling.
- Size Growth: They can grow larger, creating discomfort and pressure.
- Blockages: Cysts might block normal functions of organs.
- Bursting: A burst cyst releases contents, triggering inflammation.
Long-term Consequences
Chronic pain can emerge from the constant pressure of growing cysts. Some cysts become so large they distort surrounding tissues. This can impair the function of nearby organs. Over time, there’s a potential for scar tissue development, leading to stiffness or other discomforts.
| Consequence | Details |
|---|---|
| Repeated Infections | They may keep coming back, requiring more medical intervention. |
| Systemic Symptoms | Fever or malaise can occur if the cystic issue isn’t resolved. |
| Decreased Function | Important body functions might slow or stop near the cyst area. |
Remember, not all retention cysts cause serious issues. Many remain stable and symptom-free. Some might even resolve on their own. Yet, people should keep an eye on them. Early detection and management can prevent these complications.
Treatment Options For Retention Cysts
Treatment Options for Retention Cysts can vary based on size, location, and symptoms. These fluid-filled sacs often occur in the sinuses, eyelids, or ovaries. Understanding the best approach to treatment is crucial. It can range from simple watchful waiting to more complex surgical methods. To ensure effective management, exploring all available options is key.
Conservative Management
Observation is the first step in managing retention cysts. Not all cysts cause problems. Doctors might suggest waiting and watching. Over time, some cysts may shrink or resolve without any intervention.
Medications can help when symptoms appear. For sinuses, decongestants or antihistamines may reduce swelling. In cases of infection, antibiotics serve as a go-to solution.
Lifestyle Changes aid in managing symptoms. Hydration helps thin the mucus. A humidifier can add moisture to dry environments.
Warm Compresses can relieve discomfort. Applying gentle heat eases pain and can encourage cyst drainage.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery becomes an option when cysts persist, grow, or cause pain.
Marsupialization involves making a cut in the cyst. The aim is to create an opening for drainage. For certain retention cysts, like those on the eyelid, it’s often the choice treatment.
Excision is the complete removal of the cyst. This option is more invasive. It’s ideal when retention cysts are recurrent or potentially harmful.
Endoscopic Surgery offers a less invasive procedure. It’s commonly applied for sinus retention cyst removal. A small camera guides specialists during cyst excision.
Post-Surgical Care is essential. Follow doctors’ instructions closely to prevent infections and ensure good healing.
- Choose the best treatment approach by consulting with a healthcare professional. It’s vital to consider cyst type, symptoms, and personal health history.
- Non-surgical options may be sufficient for many cysts. Discuss conservative management with a doctor first.
- When surgery is necessary, explore all surgical interventions. Understand the risks and recovery process of each procedure.
Minimally Invasive Procedures For Retention Cysts
Minimally Invasive Procedures for Retention Cysts offer relief without major surgery. These procedures mean less pain and quicker recovery. Doctors can remove cysts using tiny tools through small cuts. Let’s explore some methods used to tackle these stubborn cysts.
Endoscopic Techniques
Endoscopic approaches involve a small camera on a flexible tube. The camera enters through the mouth, nose, or a tiny opening in the skin. This way, surgeons see and remove cysts without large cuts. The benefits are many, including:
- Less discomfort post-procedure
- Minimal scarring
- Quick return to daily activities
| Step | Process |
|---|---|
| 1 | Insert endoscope |
| 2 | Find cyst |
| 3 | Remove cyst |
Endoscopic methods need skill. Only trained specialists should perform them.
Laser-assisted Removal
Laser removal uses concentrated light beams to eliminate cysts. It is precise and targeted. The procedure has steps:
- Numb the area
- Aim laser at cyst
- Vaporize cyst tissue
This method offers quick healing and minimal blood loss. It suits surface cysts and some deeper ones. Laser removal demands expertise in using advanced laser equipment for safety.
Preventative Measures And Lifestyle Changes
Attention to preventative measures and lifestyle changes is key in managing health risks. Retention cysts, although common, require such vigilance. Simple steps and tweaks in daily habits can go a long way. Understand these to reduce your risk of developing troublesome cysts.
Reducing The Risk Of Developing Retention Cysts
Retention cysts often emerge without warning. Yet, certain actions can curb their occurrence. A proactive approach to health fortifies the body's defenses. Here's what you can do:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water each day to keep tissues healthy.
- Good Hygiene: Regular cleansing reduces pore-clogging impurities.
- Balanced Diet: Eat a variety of fruits, vegetables, and fibers for internal balance.
- Regular Check-Ups: Early detection through medical exams can prevent complications.
Lifestyle Adjustments For Those At Risk
People prone to retention cysts might benefit from specific lifestyle adjustments. Embrace changes to safeguard health:
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity boosts circulation and immune response.
- Smoke Cessation: Avoid smoking to maintain optimal mucous membrane health.
- Stress Management: Techniques like yoga or meditation may reduce hormonal fluctuations.
- Skin Care: Use non-comedogenic products to minimize the chance of blocked ducts.
Conclusion
Understanding retention cysts is the first step in managing them. Awareness and timely medical attention can lead to better outcomes. Remember to consult with healthcare professionals for advice tailored to your situation. Taking control of your health is crucial for overall well-being.
Stay informed and proactive in your healthcare journey.

