Periodontal disease is caused by bacterial infections that affect the gums and bones supporting teeth. Treatment includes professional cleaning, medication, and surgery for advanced stages.
Periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease, poses a significant threat to oral health, potentially leading to tooth loss and contributing to systemic health issues. This condition stems from the accumulation of dental plaque and tartar, which harbor harmful bacteria that infect the gum tissue and destroy the bone.
Regular dental check-ups are crucial for early detection and management of gum disease. Non-surgical treatments, such as scaling and root planing, can effectively address early stages, while persistent or severe cases may require surgical intervention. Good oral hygiene, including daily brushing and flossing, is essential in preventing the onset and progression of periodontal disease, safeguarding your smile and overall well-being.
Introduction To Periodontal Disease
Welcome to our exploration of periodontal disease, a hidden threat lurking in the shadows of oral health. Often overlooked, this condition can have far-reaching effects beyond the mouth. This section will shine a light on what periodontal disease is and its significance in our everyday lives.
Understanding Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease, known to many as gum disease, is a silent affliction affecting the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth. It starts with a sticky film called plaque.
When plaque isn’t removed, it hardens to tartar. Over time, infection sets in, leading to damage to the gums and, eventually, the jawbone.
- Gingivitis: Early stage of gum disease
- Periodontitis: Advanced stage affecting the bones
The Prevalence And Impact Of Gum Disease
Gum disease is common yet serious. It affects a vast number of adults, but with early detection, it can be treated effectively.
| Prevalence | Consequences |
|---|---|
| Most adults over 30 | Can lead to tooth loss |
| Varies with age and habits | Linked to other health issues |
Preventive care and regular dental visits are key in managing gum disease before it escalates to severe stages.
The Anatomy Of Periodontal Health
Understanding the structure and health of your gums and teeth is key to preventing periodontal disease. This condition affects the tissues holding your teeth in place. It can result in tooth loss or other severe health complications if left untreated. Let’s dive into what makes up healthy gums and teeth, and why their wellness is vital.
Structure Of Healthy Gums And Teeth
Healthy gums snugly fit around each tooth. The pink tissue is firm and does not bleed easily. Below the surface, strong fibers connect the gums to the tooth. These fibers are invisible but vital.
- Teeth are anchored in sockets within the jawbone.
- They’re surrounded by gum tissue, also known as the gingiva.
- Periodontal ligaments attach teeth to the bone.
- The jawbone supports and holds teeth in place.
Enamel, the toughest substance in your body, covers the tooth’s crown. Below it lies the dentin, which encloses the pulp. The pulp contains blood vessels and nerves.
| Part | Function |
|---|---|
| Gums | Protects the tooth’s roots |
| Periodontal Ligaments | Stabilize the tooth |
| Enamel | Shields tooth from decay |
| Dentin | Supports enamel structure |
The Importance Of Periodontal Wellness
Good periodontal health is crucial for overall well-being. Infections in the gums can spread. They can lead to serious health issues elsewhere in your body.
- Avoid gum disease to prevent tooth loss.
- Healthy gums mean a healthier heart and lower diabetes risk.
- Regular dental visits are essential.
Dentists check for pockets between the gums and teeth. These pockets are not good. They can be a sign of periodontal disease. Clean teeth and gums often to prevent these pockets.
Brush twice a day and floss daily. Use fluoride toothpaste. A balanced diet is also helpful for gum health.
Remember, early detection and treatment of periodontal issues can save your smile!
Primary Causes Of Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease, destroys the supporting structures around your teeth. Understanding the primary causes of periodontal disease is vital in preventing and treating this serious condition. Let’s delve into what fuels its onset.
The Role Of Plaque And Tartar
Plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, constantly forms on teeth. Brushing and flossing daily removes plaque. However, plaque that stays on teeth can harden into tartar. Tartar shields bacteria and creates a much stronger base for infection. Professional dental cleans are necessary to remove tartar.
- Daily oral hygiene reduces plaque build-up.
- Professional cleaning is needed to remove tartar.
Genetic And Lifestyle Factors
Genetics play a role in your susceptibility to gum disease. Even with good oral care, some may be more prone. Lifestyle choices also impact your risk:
| Smoking | Significantly increases risk |
| Stress | Makes it harder for the body to fight off infection |
| Diet | Poor nutrition can weaken your immune system |
| Illnesses | Certain conditions like diabetes increase risk |
The Stages Of Periodontal Disease
Welcome to our deep dive into the stages of periodontal disease. This type of oral health issue involves the structures around the teeth, including the gums and bone. Understanding the progression can help in early detection and treatment. Let’s explore the stages, from the earliest signs to the more advanced indicators of periodontal disease.
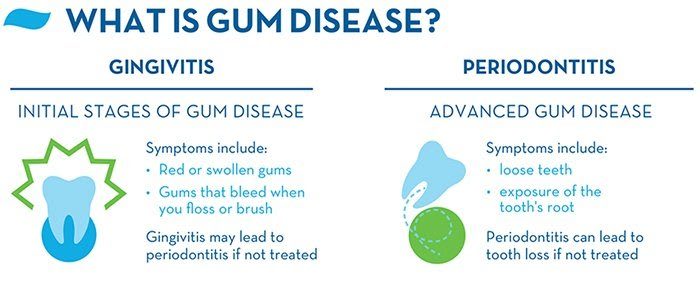
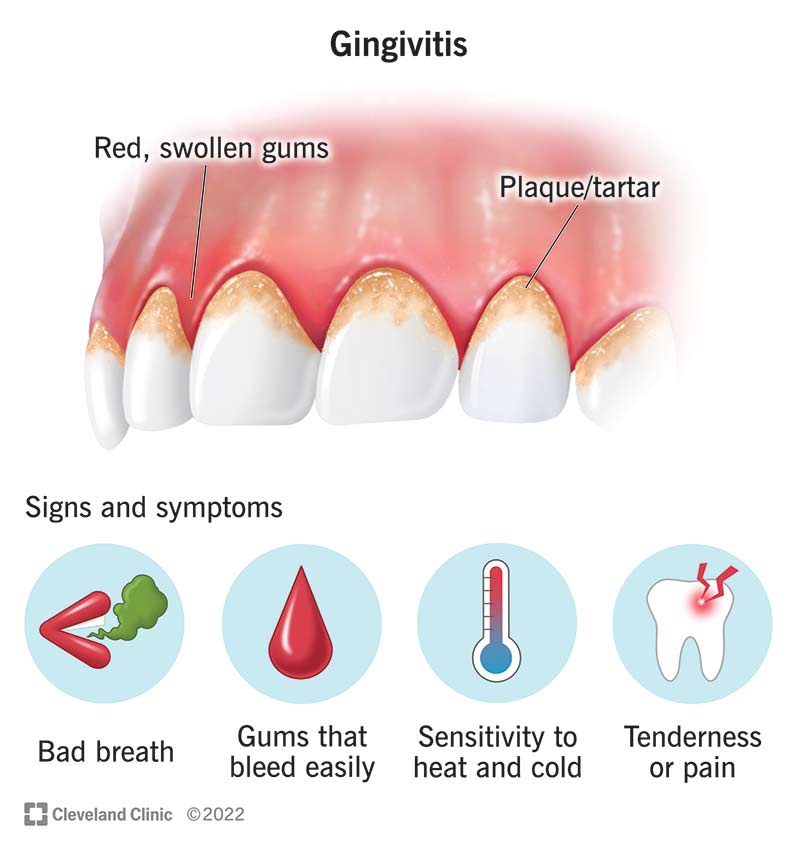
Gingivitis: The Early Stage
Gingivitis marks the beginning of periodontal disease. Plaque buildup on your teeth is its main cause. The symptoms might seem mild, but they shouldn’t be ignored. Signs include:
- Red or swollen gums
- Gums that bleed when you brush or floss
- A change in gum color from a healthy pink to red tones
Treating gingivitis is crucial to prevent progression. Regular dental check-ups, proper brushing, and flossing can reverse this stage. If left untreated, it can advance to periodontitis.
Periodontitis: The Advanced Stage
When gingivitis is not addressed, it escalates to periodontitis. Here, damage to the bone and fibers that hold your teeth in place occurs. Symptoms become more severe:
- Gums pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that harbor infection
- Bad breath that won’t go away
There are categories within periodontitis:
- Mild Periodontitis
- Moderate Periodontitis
- Advanced Periodontitis
Treatment might include deep cleaning, medication, or surgery. Early intervention can save your teeth and gums. Regular visits to the dentist and proper oral hygiene are key to managing periodontitis.
Symptoms And Diagnosis Of Gum Disease
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is an infection that affects the tissues and bones that surround and support the teeth. Untreated, it can become severe, possibly leading to tooth loss. Knowing the symptoms and seeking professional diagnosis are critical steps in managing periodontal health.
Recognizing The Signs Of Periodontal Disease
Being aware of the early signs of gum disease can head off complications down the road. Look out for these symptoms:
- Swollen or red gums
- Bleeding while brushing or flossing
- Receding gums that make your teeth look longer
- Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in your mouth
- Sensitive teeth or discomfort when chewing
Professional Diagnosis And Assessment
A dentist or periodontist can diagnose gum disease through:
- Examining your gums for signs of inflammation
- Measuring the depth of the spaces between your gums and teeth
- Checking teeth movement and sensitivity
- Reviewing X-rays to detect bone loss
An accurate diagnosis may require a full periodontal assessment. This comprehensive evaluation will steer the course of treatment and help protect your oral health.
Credit: crest.com
Risk Factors And Preventive Measures
Keeping your gums healthy is critical for overall oral health. Periodontal disease, a serious gum infection, can wreak havoc on your smile if left unchecked. Understanding the risk factors and embracing preventive measures can help safeguard your mouth from this dental adversary.
Identifying At-risk Populations
Periodontal disease doesn’t spare anyone, but certain groups may face a higher risk. Recognizing who is at increased risk can prompt early intervention.
- Smokers: Smoking is one of the top risk factors for gum disease.
- Diabetics: Individuals with diabetes are more prone to infections, including gum disease.
- Age: Older adults tend to have a higher prevalence of periodontal disease.
- Genetics: A family history can increase susceptibility, regardless of oral hygiene.
- Medications: Certain drugs can affect gum health, leading to possible issues.
Effective Preventive Practices
Preventing periodontal disease is manageable with the right habits and care. Here are some effective strategies:
- Brush regularly: Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss daily: Flossing removes plaque and food particles between teeth.
- Routine dental visits: See your dentist or hygienist regularly for cleanings and check-ups.
- Quit smoking: Giving up tobacco can markedly reduce the risk of developing gum disease.
- Eat balanced: A healthy diet supports strong teeth and gums.
By taking these steps, you can decrease your chance of periodontal disease. Start protecting your oral health today!
Non-surgical Treatments For Periodontal Disease
Non-Surgical Treatments for Periodontal Disease can offer relief and healing without the need for invasive procedures. Gum disease, or periodontitis, can cause painful inflammation, damage to bones, and tooth loss. But, with the right care, the progression can be halted or even reversed. Here, we explore pain-free methods to combat this ailment.
Professional Cleaning And Scaling
A cornerstone in the fight against periodontal disease is Professional Cleaning and Scaling. This process removes tartar and plaque that brushing alone can’t touch.
Dentists use special tools to clean below the gum line, a key area in preventing periodontal issues. This gentle technique can greatly reduce inflammation and discomfort.
- Cleaning teeth surfaces
- Removing hidden tartar
- Targeting gum pockets
Medications And Antibacterial Mouthwashes
Medications play a vital role in managing gum disease. Antibiotics can fight infections that harm gums and bones. They come in various forms.
| Medication Type | Usage |
|---|---|
| Mouthwash | Directly reduces bacteria in the mouth |
| Pills or Capsules | Works internally to combat infection |
Using Antibacterial Mouthwashes is simple yet effective. A daily swish can diminish harmful bacteria and offer fresh breath.
- Rinse once daily
- More effective alongside brushing and flossing
- Improves overall gum health
Credit: my.clevelandclinic.org
Surgical Treatments For Advanced Periodontal Disease
When gum disease advances, it can damage gums, teeth, and bones. Sometimes, a deep cleaning is not enough. Then, surgeons step in to treat this condition. Let’s explore the surgical options that can help bring smiles back to health.
Flap Surgery And Tissue Regeneration
Flap surgery helps by cleaning the roots of a tooth. It allows the access needed to remove tartar deep below the gum line. The surgeon makes tiny cuts in the gum. The gum is then lifted back, forming a flap. This process exposes the roots for more effective scaling and root planing.
- After cleaning, the gums get secured back into place.
- Sometimes, damaged bone may also be reshaped.
Tissue regeneration encourages the body to rebuild bone and gum tissue. If the bone has been severely damaged, a small piece of mesh-like fabric is inserted between the bone and gum tissue. This fabric prevents the gum from growing into the area where the bone should be, allowing the bone and connective tissue to regrow.
Dental Implants And Bone Grafts
Dental implants are for when teeth are lost due to periodontal disease. Implants are modern solutions for missing teeth. The process involves inserting a metal post in place of the tooth root.
| Step 1 | Place the implant in the jaw where the tooth is missing. |
|---|---|
| Step 2 | Once the jaw heals, a false tooth is attached to the implant. |
In the case of insufficient bone mass, bone grafts come into play. These grafts provide a platform for regrowth, helping in strengthening the jaw to support future implants.
- The graft may come from the patient or be made of synthetic materials.
- It is placed into the areas of missing bone.
- Over time, it supports the regrowth of bone, providing stability.
Innovative Therapies In Periodontology
Innovative therapies in periodontology open doors to advanced treatment options. These methods aim to effectively tackle periodontal disease. They offer hope for better patient outcomes and enhanced tissue regeneration. In this exploration, there are two particularly cutting-edge therapies to consider: Laser Treatment and Photodynamic Therapy, as well as The Use of Growth Factors and Gene Therapy.
Laser Treatment And Photodynamic Therapy
Laser treatment in periodontology uses intense light to target and remove infected gum tissue. This minimally invasive alternative boasts less pain and quicker recovery times compared to traditional surgery.
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) works differently. It combines a photosensitizing agent with a specific wavelength of light to kill bacteria and reduce inflammation. Together, these advanced treatments strive to preserve the teeth and gums.
- Reduces bacteria responsible for periodontitis
- Minimally invasive with fast recovery
- Potential for reduced gum damage compared to traditional surgery
The Use Of Growth Factors And Gene Therapy
An exciting frontier in periodontal therapy involves the application of growth factors. These proteins can stimulate tissue regeneration, aiding in the healing process.
Meanwhile, gene therapy is still in its experimental phases. It could revolutionize periodontal treatment by targeting the disease at a genetic level. This may lead to permanent solutions for periodontitis.
| Treatment | Method | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Factors | Proteins that aid tissue regeneration | Promotes healing, can speed recovery |
| Gene Therapy | Alters genes to combat periodontal disease | Addresses the root cause, potential for lasting effects |
Both growth factors and gene therapy signify progress towards more effective periodontal disease management. The future of these therapies may just redefine periodontal care.
Periodontal Maintenance After Treatment
Periodontal Maintenance After Treatment is crucial for your gum health. Once you have undergone treatment for periodontal disease, consistent upkeep is your best defense against recurrence. Proper care ensures the longevity of your gums and overall dental health. Let’s walk through the essentials of post-treatment care and the lifestyle changes that can help sustain periodontal health.
Post-treatment Care And Monitoring
After periodontal treatment, regular check-ups with your periodontist are mandatory. These visits allow for early detection of any possible infections. During these appointments, your periodontist will clean your teeth to prevent plaque buildup, imperative in avoiding further gum problems.
- Professional Cleaning: Your dental team will perform thorough cleanings.
- Examination: They will check for signs of periodontal disease.
- Home Care: Brush twice daily and floss regularly.
Lifestyle Changes For Sustained Periodontal Health
Maintaining good periodontal health involves more than just dental visits; it’s a lifestyle. Making a few adjustments to your daily routine can go a long way.
| Lifestyle Change | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Quit Smoking | Reduces risk of gum disease resurgence |
| Healthy Diet | Provides nutrients for gum recovery |
| Stress Reduction | Decreases likelihood of teeth grinding |
A balanced diet, rich in vitamins and minerals, supports gum regeneration. Regular exercise improves blood flow to your gums. Stress management, such as meditation or yoga, may limit harmful behaviors like grinding teeth or clenching jaws.
- Follow a consistent oral hygiene routine.
- Use mouthwash to reduce bacteria.
- Avoid sugary snacks and acidic drinks.
- Stay hydrated to maintain saliva production.
The Role Of Oral Hygiene In Preventing Periodontal Disease
The Role of Oral Hygiene in Preventing Periodontal Disease plays a pivotal part in maintaining not only oral health but overall well-being. Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, begins with bacterial growth in the mouth and may end with tooth loss due to destruction of the tissue surrounding your teeth. Yet, such outcomes are preventable with diligent oral hygiene practices.
Brushing And Flossing Techniques
Effective brushing and flossing are keys to keeping periodontal disease at bay.
- Brush twice daily for two minutes with a fluoride toothpaste.
- Use a soft-bristled brush to prevent gum irritation.
- Employ a proper brushing technique:
- Hold the brush at a 45-degree angle to the gums.
- Move the brush back and forth gently in short strokes.
- Brush the outer, inner, and chewing surfaces of teeth.
- Don’t forget to brush the tongue to remove bacteria.
- Floss once daily to remove plaque and food particles your brush can’t reach.
- Use about 18 inches of floss, winding most around one of your middle fingers, and the rest around the opposite middle finger.
- Holding the floss tightly between your thumbs and forefingers, guide it between your teeth using a gentle rubbing motion.
- When the floss reaches your gum line, curve it into a C shape against one tooth. Gently slide it into the space between the gum and the tooth.
- Hold the floss tightly against the tooth, gently rubbing the side of the tooth, moving the floss away from the gum with up and down motions.
The Importance Of Regular Dental Visits
Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are crucial to catching and addressing periodontal issues before they escalate.
- Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar that regular brushing and flossing might miss.
- Dentists can spot early signs of gum disease, offering treatments to halt progression.
- Regular visits may include charting and measuring the space between teeth and gums, an indicator of periodontal health.
- Periodic X-rays can reveal hidden signs of gum disease and bone loss.
Periodontal Disease And Overall Health
Periodontal disease, often known as gum disease, reaches beyond the mouth. It can touch your entire body. This means your gums’ health can reflect on your overall well-being. Gum disease starts quiet but becomes a loud warning for other health issues. It’s more than just teeth—it’s about keeping your whole body happy and healthy. Now, let’s dig into how gum health can change things from head to toe.
Link Between Gum Disease And Systemic Conditions
Gum disease likes to travel—it can link arms with other conditions and walk throughout your body. The bacteria causing gum issues don’t just stay put; they wander and can make other health problems worse. Here’s a snapshot:
- Heart disease: Same bad bacteria can make your heart unhappy.
- Diabetes: Struggle with blood sugar? Gum disease can join the fight.
- Pregnancy: It can even reach unborn babies, affecting their health.
Science says that tender gums might signal bigger health troubles.
Impact Of Periodontal Health On Quality Of Life
Happy gums mean a happier you. Unhappy gums turn smiles upside down. With painful chewing, soreness, and bad breath, life gets less fun. But good gum care can flip the script. Look at how:
- Better breath: Fresh breath makes friendlier conversations.
- Pain-free meals: Enjoy eating without a “ouch” at each bite.
- Confident smiles: Sparkly teeth without the red, puffy gum look.
For a top-notch life, keep your gums in check. They’re the heroes behind every laugh, every meal, every first impression.
Remember, fighting periodontal disease is a battle for your entire body’s wellness. Pick your weapons: a toothbrush, floss, and regular dentist visits. Win the war for your health, starting with your gums.
Nutritional Considerations For Periodontal Health
Nutritional considerations play a crucial role in maintaining periodontal health. A well-balanced diet not only supports general well-being but also helps in preventing gum disease, or periodontitis. For those aiming to keep their gums healthy, understanding dietary factors and incorporating certain vitamins and supplements is essential.
Dietary Factors Affecting Gum Disease
Eating habits directly impact gum health. Foods high in sugar and starch can increase plaque formation, leading to gum inflammation. On the other hand, crunchy fruits and vegetables can help clean teeth naturally. Consider these points:
- Reduce sugary snacks to lower plaque build-up.
- Avoid acidic beverages that erode tooth enamel.
- Choose whole grains over refined options to reduce inflammation.
Vitamins And Supplements For Gum Health
Vitamins and supplements can be powerful allies in fighting periodontal disease. Essential nutrients help repair and maintain gum tissue, fight infection, and enhance overall dental health. The useful vitamins include:
| Vitamin/Supplement | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Vitamin C | Boosts gum regeneration and immunity |
| Vitamin D | Reduces the risk of gum inflammation |
| Calcium | Strengthens bone that supports teeth |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Decreases gum swelling and tenderness |
Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen for tailored advice and dosage information.
Technology And Periodontal Diagnostics
Understanding the role technology plays in diagnosing periodontal disease is crucial in modern dental care. Fast-paced advancements offer unprecedented precision in detecting and managing this common yet serious gum infection. With these technological strides, dental professionals can offer better, more personalized treatments to patients.
Advancements In Imaging And Detection
New imaging technologies provide a clearer picture of the health of gums and teeth. Dentists now use tools like digital x-rays and 3D imaging to uncover the hidden details of periodontal health. This level of detail aids in catching periodontal disease early on.
- Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) offers three-dimensional views that traditional x-rays cannot match.
- Digital radiographs reduce radiation exposure and give instant access to images.
- Diagnodent uses laser fluorescence to detect decay and other issues not visible to the naked eye.
Digital Innovations In Periodontal Care
Digital tools are transforming periodontal treatment plans. Software for patient education, digital charting, and electronic scalers have revolutionized patient experiences. Tailored treatments are now the norm.
| Technology | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Intraoral Cameras | Allow patients to see what the dentist sees. |
| Electronic Scalers | Provide efficient plaque and calculus removal. |
| Periodontal Lasers | Promote faster healing and less discomfort. |
This integration of technology ensures more accurate diagnoses, effective treatments, and better patient outcomes. The fight against periodontal disease is now stronger and smarter than ever.
Insurance And Cost Management For Periodontal Treatment
Tackling gum disease should not break the bank. Understanding insurance benefits and cost-saving methods makes treatment achievable. Get to know how insurance assists and learn strategies to manage the costs.
Understanding Periodontal Treatment Coverage
Insurance policies vary widely. Before starting treatment, check your plan. Learn what treatments are covered and what your out-of-pocket costs might be.
- Basic vs. Major Procedures: Coverage can differ between basic cleanings and major surgeries.
- Annual Maximums: Plans often have a cap on how much they will pay yearly.
- Waiting Periods: Some policies require a wait before covering certain procedures.
- Pre-Approval: Your dentist may need to submit a plan for approval prior to treatment.
Cost-effective Strategies
Save money while receiving necessary care. Apply these strategies.
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Preventative Care | Regular check-ups can prevent the need for more expensive treatments. |
| Discount Plans | Some dentists offer plans giving discounts on various treatments. |
| Payment Plans | Many dental offices provide payment options to spread out costs. |
| Health Savings Accounts | Use pre-tax dollars to pay for treatment, saving money overall. |
| Alternative Treatments | Discuss less costly treatment alternatives with your dentist. |
Challenges In Periodontal Disease Treatment
The treatment of periodontal disease presents several obstacles. These challenges can affect both the effectiveness of treatment plans and patient outcomes. Understanding these issues is crucial for managing the condition successfully.
Managing Treatment-resistant Cases
Treatment-resistant cases are a significant hurdle in periodontal care. Certain patients may not respond to conventional therapies, necessitating alternative approaches.
- Bacterial resistance: Over time, bacteria can become resistant to antibiotics.
- Complex biofilms: These structures protect bacteria from treatments.
- Genetic factors: Individual genetics may influence treatment response.
- Host response: The body’s inflammatory response can complicate treatment.
Advanced treatments, such as laser therapy or localized medication delivery, may be required for these patients.
Patient Compliance And Education
Patient education and compliance are critical for successful periodontal disease treatment. Patients must understand the treatment plan and its importance.
- Regular dental visits: These are essential for monitoring and adjusting treatment plans.
- Home care routines: Daily brushing and flossing prevent plaque buildup.
- Risk factor management: Lifestyle choices, such as smoking, impact treatment outcomes.
- Medication adherence: Taking prescribed medications as directed is crucial.
Dentists often use visual aids, models, or apps to enhance understanding and engagement.
Recent Research And Emerging Trends In Periodontology
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, affects millions globally. Understanding its causes and finding effective treatments is key for dental health. Recent periodontology research is uncovering new insights and paving the way for innovative strategies to combat this common yet serious condition. Let’s delve into the latest findings and explore what the future holds for periodontal disease management.
Current Studies On Periodontal Disease Pathogenesis
Scientists keep uncovering how periodontal disease progresses. New studies focus on microbial interactions in the mouth and immune responses to these bacteria. Genetic factors are also under investigation, as they may determine a person’s susceptibility to the disease.
Here are some key findings from recent studies:
- The role of specific bacteria in causing inflammation and tissue damage.
- How environmental factors like smoking and diet affect periodontal health.
- The impact of pre-existing conditions such as diabetes on periodontal disease development.
Future Directions In Treatment And Prevention
As we learn more about periodontal disease, the door opens to new treatments. Research is aimed at:
- Developing targeted therapies that can disrupt harmful bacterial colonization.
- Creating vaccines to prevent the disease.
- Designing personalized treatment plans based on individual genetic makeup.
Probiotics and gene editing are also potential areas for future breakthroughs. These advances promise a future where periodontal disease is no longer a threat to oral or overall health.
Patient Testimonials And Case Studies
Reading patient testimonials and examining case studies provide valuable insights. These real-life stories and experiences offer hope and guidance to those battling periodontal disease.
Success Stories In Managing Periodontal Disease
Meet John, Sarah, and Alex. They each conquered periodontal disease. They followed their dentist’s advice closely. Today, they enjoy healthy gums and teeth.
- John: He had bleeding gums. After treatment and proper hygiene practices, his condition improved significantly.
- Sarah: Sarah faced receding gums. But with timely intervention, she saw reattachment of her gums.
- Alex: Suffered from bad breath and loose teeth. His disciplined aftercare routine paid off, resulting in a stronger, fresher smile.
Lessons Learned And Best Practices
The cases reveal important takeaways and effective strategies. Here’s what works:
- Regular Dental Visits: Early detection makes a big difference.
- Diligent Home Care: Brush twice, floss daily, and use mouthwash.
- Professional Cleanings: Regular cleanings prevent tartar buildup.
John, Sarah, and Alex all stress discipline. They follow these practices to maintain their oral health. Sticking to these best practices is crucial.
| Case | Challenge | Intervention | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. John’s Story | Bleeding Gums | Improved Hygiene + Regular Cleaning | Healthy Gums |
| 2. Sarah’s Experience | Receding Gums | Periodontal Therapy + Grafting | Regeneration of Gums |
| 3. Alex’s Journey | Loose Teeth and Bad Breath | Rigorous Aftercare + Lifestyle Changes | Stronger Teeth and Fresher Breath |

Credit: www.scottgreenhalghdds.com
Conclusion
Understanding periodontal disease is key to maintaining oral health. Quick identification of symptoms can lead to effective treatment. Regular dental check-ups and good hygiene are vital. If you’re experiencing signs of gum disease, consult a dentist promptly. Protect your smile; prioritize your periodontal health.

