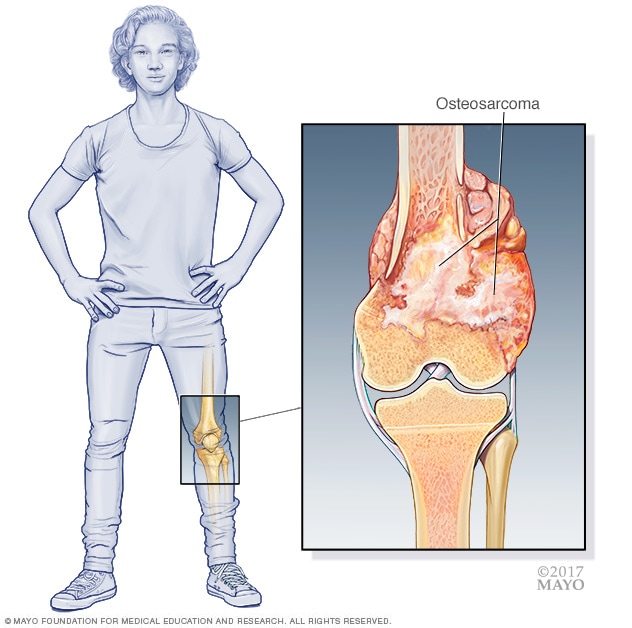
Osteosarcoma is a type of bone cancer that typically affects the long bones near growth plates. It is most prevalent in teenagers and young adults.
As the most common form of bone cancer, osteosarcoma poses a significant health concern, particularly for those in their adolescent growth spurts. This aggressive cancer originates in the cells that form bones and often manifests in areas like the knee, the thigh bone, and the upper arm.
Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving survival rates, making awareness of its symptoms, which can include pain and swelling in the affected area, vital. Research and advances in treatment strategies continue to enhance outcomes for patients diagnosed with this challenging cancer. By ensuring that those affected understand their diagnosis and the available interventions, better prognoses become achievable. Regular screenings and attention to bone health can also play a pivotal role in managing osteosarcoma.
Understanding Osteosarcoma
Osteosarcoma stands as a fierce opponent in the realm of bone cancers. It’s a condition that needs clear explanation. This article sheds light on the basics, the who, and the how of Osteosarcoma.
Defining Osteosarcoma
Osteosarcoma is a type of cancer that hits hard at bones. Often showing up in long bones, like legs or arms, it mostly targets young individuals but doesn’t spare others.
Epidemiology And Demographics
- Age: Teens get hit the most, but it can touch any age.
- Numbers: About 1,000 new cases appear in the U.S. yearly.
- Gender: Slightly more common in males.
- Risk factors: Past radiation therapy or family history may increase risk.
The Pathophysiology Of Osteosarcoma
Osteosarcoma kicks off when cells behave badly, turning into cancer cells. These rebels grow uncontrollably, forming a mass. It can spread around, invading nearby spots or journeying to lungs or other bones.
Understanding this growth helps doctors and researchers find better ways to attack it.

Credit: www.acco.org
Classification And Types
Understanding Osteosarcoma requires knowledge of its classifications and types. These categories help doctors plan the best treatment strategies. Let’s explore the various ways osteosarcoma is classified, based on histology, location, and genetics.
Histological Subtypes
Osteosarcoma’s histological subtypes describe how cancer cells look under a microscope. These subtypes indicate different tumor behaviors and potential responses to treatment:
- Osteoblastic – Most common, showing bone formation.
- Chondroblastic – Contains cartilage-like areas.
- Fibroblastic – Consists of fibrous tissue.
- Telangiectatic – Contains blood-filled spaces.
- Small Cell – Composed of small round cells.
Anatomical Distribution Of Osteosarcoma
The location of osteosarcoma matters for diagnosis and treatment:
- Long bones – Often affects legs or arms.
- Flat bones – Can occur in skull or pelvis.
- Juxtacortical – Situated on the bone’s surface.
Most cases develop around the knee and upper arm bones.
Genetic And Molecular Classifications
Researchers have identified genetic factors influencing osteosarcoma risk:
- TP53 and RB1 genes mutations increase risk.
- Mutant genes can lead to hereditary patterns.
- Molecular markers potentially guide targeted therapies.
Understanding genetic changes helps predict behavior and tailor treatments.
Risk Factors And Etiology
Understanding Osteosarcoma’s risk factors reveals much about its origins. Certain elements could increase the chances of developing this bone cancer. Here, we will look at genetic predispositions, environmental influences, and the impact of previous medical treatments on osteosarcoma risk.
Genetic Predispositions And Mutations
Genes play a key role in osteosarcoma risk. Some individuals inherit genetic mutations that make them more prone to this cancer. Below are genes linked to a higher risk:
- RB1 gene: Linked with hereditary retinoblastoma
- TP53 gene: Associated with Li-Fraumeni syndrome
- RecQ helicases: Cause conditions that heighten the risk
Family history of these gene mutations demands increased vigilance for osteosarcoma.
Environmental And Lifestyle Factors
External factors also influence osteosarcoma risk. Lifestyle choices and environmental exposures can indirectly affect bone health. Notable factors include:
- Exposure to ionizing radiation
- Intake of certain chemicals, like beryllium or asbestos
Limiting these exposures can help reduce risk.
Previous Radiotherapy And Bone Disorders
History of radiotherapy can elevate osteosarcoma risk. Bones previously treated with radiation are at risk. History of bone disorders, such as Paget’s disease of bone, also contributes. Detailed below are key points to consider:
- Monitor radiation-treated areas regularly for changes.
- Understand that certain noncancerous bone conditions could lead to osteosarcoma.
Individuals with these backgrounds should discuss monitoring strategies with their healthcare providers.
Symptoms And Clinical Presentation
Osteosarcoma is a type of bone cancer that affects people of all ages. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment. Understanding the symptoms can lead to earlier diagnosis and better outcomes. Let’s recognize the signs and how they may progress.
Common Signs And Symptoms
People with osteosarcoma often experience a range of symptoms. These signs can vary but usually include:
- Bone pain that may increase at night or during physical activity
- Swelling or lumps on the bones or joints, often noticeable on the arms or legs
- Limited range of motion in the nearby joints, making movement difficult
- Bone fractures that occur more easily than expected, often without a clear cause
Symptom Progression
Over time, osteosarcoma symptoms can develop and become more serious:
- The pain becomes consistent and may worsen with activity.
- Swelling and lumps become more visible, causing discomfort.
- Normal activities like walking or lifting can become increasingly difficult.
If any of these symptoms are noticed, it’s essential to seek medical advice promptly.
Differential Diagnosis
Osteosarcoma shares symptoms with other conditions. It’s important for doctors to rule out:
- Bone cysts – benign fluid-filled areas
- Other bone tumors – like Ewing sarcoma or bone metastases
- Inflammatory or infectious conditions – such as osteomyelitis
- Benign bone lesions – noncancerous growths
Accurate diagnosis often involves X-rays, MRIs, or biopsies. These tools help doctors identify osteosarcoma accurately.
Diagnostic Procedures
When someone shows signs of bone pain or swelling, doctors may suspect a bone tumor, such as osteosarcoma. This type of cancer starts in bone cells and grows quickly. To find out if it is osteosarcoma, doctors use several tests. This section explores the main steps doctors take to diagnose osteosarcoma.
Imaging Techniques in Osteosarcoma DiagnosisImaging Techniques In Osteosarcoma Diagnosis
Doctors use special pictures of bones to look for cancer. We call these pictures “imaging techniques.” They show if a bone tumor is there and how big it is. Some common types are:
- X-rays: They can show if the bone has changes that look like cancer.
- CT scans: These give a 3D picture and help see the tumor better.
- MRI: This test uses magnets to get very detailed pictures of the bone.
- PET scans: They can show if cancer has spread to other body parts.
Role Of Biopsy In Confirming Osteosarcoma
Even if the pictures show a tumor, doctors need to test a small piece of it. This test is a “biopsy.” Doctors take a tiny bit of the tumor and look at it under a microscope. This is how they make sure it is osteosarcoma.
Note: There are two main biopsy methods:
- Needle biopsy: A needle gets a piece of the tumor.
- Surgical biopsy: Doctors do a small surgery to get a bigger piece.
Diagnostic Challenges And Misdiagnosis
Diagnosing osteosarcoma can be tricky. Sometimes other medical conditions can look like osteosarcoma in pictures. These may be non-cancerous bone diseases. Doctors must be very careful. They use all the information from tests to make the right diagnosis. Key points include:
| Challenge | Detail |
|---|---|
| Similar Symptoms | Other bone diseases have similar signs as osteosarcoma. |
| Image Overlap | Pictures may not clearly show the cancer from other conditions. |
| Biopsy Errors | Getting the wrong biopsy spot may lead to a misdiagnosis. |
Staging And Prognosis
Understanding Osteosarcoma staging and prognosis offers insights into treatment options and outcomes. Knowing the stage of cancer helps doctors plan the best course of action. It gives a glimpse of what to expect in the journey ahead. Prognosis, or the likely outcome of the disease, depends on many factors, including the cancer stage. Let’s dive into the details of staging systems, prognostic factors, and what these mean for survival rates and outcomes in Osteosarcoma.
Staging Systems For Osteosarcoma
Doctors use staging systems to assess the spread and severity of cancer. Two main systems are the TNM system and the stage grouping system. TNM stands for tumor (size), nodes (lymph involvement), and metastasis (spread). Stage grouping considers these to assign a stage from I to IV, with IV being the most advanced.
Prognostic Factors
Several factors influence Osteosarcoma outcomes:
- Tumor size: Smaller tumors tend to have a better outlook.
- Location: Where the tumor is can affect recovery chances.
- Metastasis: If cancer has spread, prognosis may worsen.
- Response to treatment: How cancer responds can change the outlook.
Survival Rates And Outcomes
Survival rates provide a general guide but don’t predict individual outcomes. They are based on previous patients’ experiences, usually over five years. Factors like age, tumor location, and whether cancer has spread are crucial. Osteosarcoma has a survival rate of about 60-80% for localized stages but drops significantly when metastasized.
Treatment Strategies
Tackling a diagnosis like osteosarcoma calls for a strong plan. The fight against this bone cancer involves more than one approach. Each patient gets a tailored treatment strategy. This can include surgery, drugs, or new methods from clinical trials. Our aim is to stop cancer and save limbs.
Surgical Interventions In Osteosarcoma
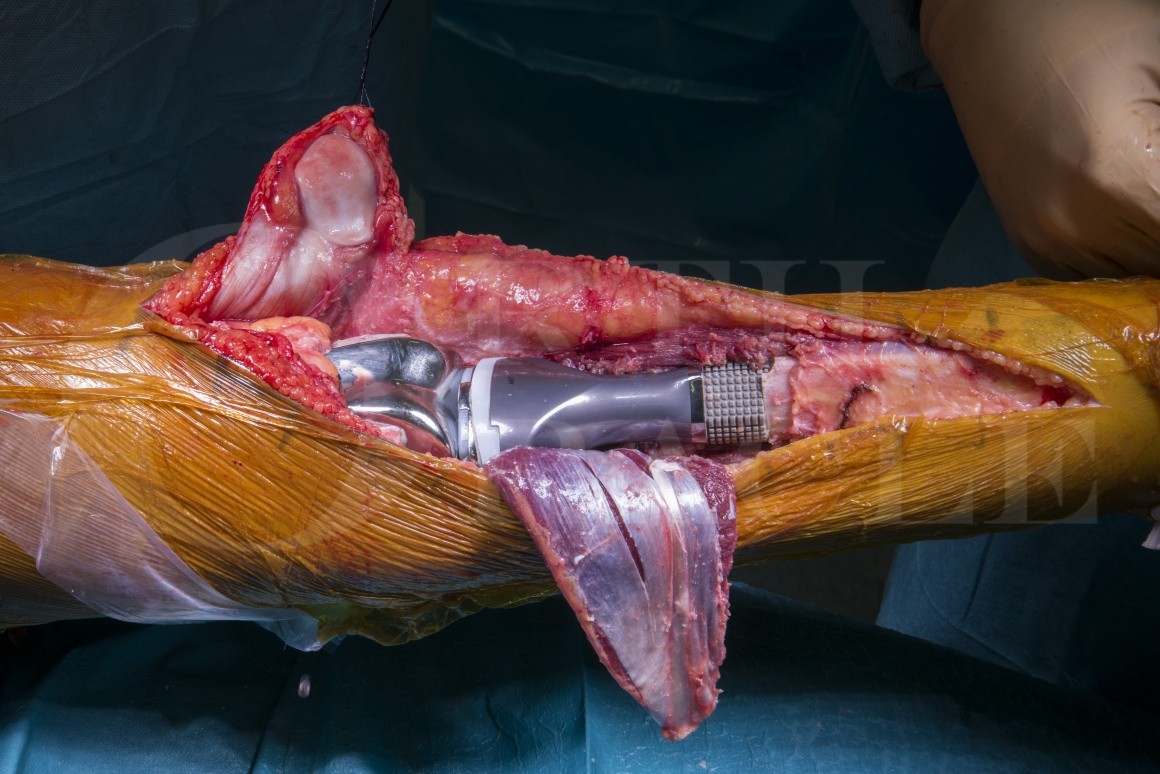
Surgery is a key step in treating osteosarcoma. The goal is to remove all cancer cells. Limb-sparing surgery is common. It takes out the tumor and a bit of healthy tissue around it. Doctors try to save the patient’s limb. In some cases, an amputation might be necessary. After removing the tumor, a prosthesis or bone graft may help restore function.
Chemotherapy And Targeted Therapies
Drugs can also fight osteosarcoma. Chemotherapy uses strong medicines to kill cancer cells. It’s often given before and after surgery. This shrinks the tumor and tackles any remaining cells. New targeted therapies focus on specific parts of cancer cells. They aim to stop the cancer while protecting normal cells.
- Drugs like high-dose methotrexate, doxorubicin, and cisplatin are common in chemotherapy.
- Targeted therapies could involve immunotherapy where the body’s defense system fights cancer.
Emerging Treatments And Clinical Trials
Science keeps bringing new hope. Clinical trials test pioneering treatments. Patients may access new drugs or methods that are not yet widely available. These trials are vital for progress against osteosarcoma. They offer patients cutting-edge options. Always chat with a doctor before joining a trial. This ensures the treatment suits the patient’s specific needs.
- Gene therapy targets the genetic changes causing cancer.
- Vaccine therapy helps the immune system attack cancer cells.
The Multidisciplinary Approach
Osteosarcoma is a type of bone cancer. It requires a team of doctors. Each doctor has a special role. Together, they create a strong treatment plan. This approach uses many types of care. It may improve your chance of recovery.
The Role Of Orthopedic Oncologists
Orthopedic oncologists are main doctors for bone cancers. They know about different treatments. They perform surgeries like limb-sparing surgeries. This helps save the affected limb.
Incorporating Rehabilitation In Treatment Plans
- Rehab helps you move after surgery.
- Physical therapists design exercise programs.
- These exercises help make muscles and joints strong.
Collaboration With Radiation Oncologists
Radiation oncologists focus on radiation therapy. They work with other doctors. They aim to kill cancer cells. Their work is vital for treatment success.
Pediatric Osteosarcoma
Osteosarcoma is the most common type of bone cancer in children and teens. It typically affects the long bones in the legs and arms. Pediatric osteosarcoma is a serious condition that requires immediate attention and care.
Differences In Pediatric Vs. Adult Osteosarcoma
Pediatric osteosarcoma and adult osteosarcoma have distinct features. These differences are not just in age but also in how the disease starts and how it might respond to treatment. For children, the disease is often linked to their rapid bone growth during puberty.
- Location: More common near growth plates in children.
- Aggressiveness: Tends to be more aggressive in pediatric cases.
- Response to Treatment: Children often have a better response to chemotherapy.
Challenges In Treating Pediatric Patients
Treating bone cancer in children comes with unique challenges.
- Developing Bones: Careful consideration is taken to not affect growth.
- Emotional Support: Support for the child and family is vital.
- Long-term Effects: Treatments can affect future health.
Fertility Preservation And Growth Considerations
Long-term side effects of cancer treatments can affect children. These include potential impacts on fertility and bone growth. Discussing these topics early is important for future health and family planning.
| Consideration | Importance |
|---|---|
| Fertility Preservation: | Options available before treatment begins. |
| Monitoring Growth: | Regular check-ups to track bone development. |
Psychosocial Implications
Osteosarcoma can present tough challenges. Beyond the physical struggle, patients often face emotional and psychological hurdles. The path to recovery includes more than medical treatment; it involves addressing the mental and social aspects influencing a patient’s well-being. In this part of our discussion, we dive into the psychosocial implications linked with osteosarcoma, emphasizing mental health, support mechanisms, and life quality post-treatment.
Mental Health Challenges For Patients
Dealing with osteosarcoma brings profound mental health challenges. The diagnosis alone triggers fear and uncertainty. Patients may experience:
- Anxiety about health and treatment outcomes.
- Depression due to illness-related changes in lifestyle.
- Stress from financial concerns and healthcare decisions.
Timely mental health support is crucial. It helps patients navigate these turbulent waters with resilience and hope.
Support Systems And Counseling
Robust support systems act as a lifeline for osteosarcoma patients. Elements of such support include:
- Family and friends providing emotional backing and practical help.
- Healthcare professionals offering guidance and reassurance.
- Peer support groups connecting patients to others with similar experiences.
Patient counseling further equips them to handle emotional distress. Therapists and counselors deliver tools for better coping strategies.
Quality Of Life And Survivorship
Life after osteosarcoma may look very different. Survivors often ponder:
- How to reclaim normalcy in daily life.
- Ways to manage lingering treatment side effects.
- Strategies for maintaining positive mental health.
Improving quality of life involves comprehensive care plans, survivorship programs, and healthy lifestyle adaptations. Patients learn to create a fulfilling life post-osteosarcoma.
Recurrent Osteosarcoma
Osteosarcoma is a type of bone cancer that can sometimes come back after treatment. When it returns, it’s called recurrent osteosarcoma. This can be a challenging time for patients and their families. Understanding the management, treatment options, and the importance of follow-up can help in navigating this phase.
Managing Recurrences
When osteosarcoma comes back, doctors will first try to find where the cancer is. They do this using scans and tests. The goal is to manage the cancer and keep the person healthy for as long as possible.
Treatment Options For Recurrent Disease
Treatment for recurrent osteosarcoma depends on where the cancer is and what treatments were used before. Here are some common methods:
- Surgery: Doctors may operate to remove the tumor.
- Chemotherapy: Special medicine can help to fight the cancer cells.
- Radiation: High-energy rays can destroy cancer cells.
Each option is chosen based on many factors. The doctor will suggest the best plan for each person.
Monitoring And Long-term Follow-up
After treatment, regular check-ups are very important. The doctors will keep a close watch to see if the cancer returns. It helps to catch any changes early.
| Check-up Schedule | Tests Involved |
|---|---|
| Every 3-6 months | Scans, Blood tests |
| Once a year | Physical exam, X-rays |
Staying up to date with these appointments is a key part of care.
The Future Of Osteosarcoma Research
The Future of Osteosarcoma Research shines with the promise of innovative treatments and diagnostic approaches. Advancements in medical science hint at a new horizon that’s brimming with hope for those affected by this challenging bone cancer.
Innovations In Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine is set to revolutionize how osteosarcoma is treated. By analyzing a patient’s unique genetic makeup, doctors can tailor treatments that are more effective and have fewer side effects. This approach aims to match each individual with the optimal therapy, potentially improving outcomes dramatically. As research delves deeper, personalized medicine could offer bespoke treatment plans that target the cancer’s specific characteristics.
The Potential Of Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a groundbreaking field that focuses on empowering the body’s own immune system to identify and attack osteosarcoma cells. Ongoing studies are testing the efficacy of vaccines that spur an immune response specifically towards cancer cells. Key developments include the use of checkpoint inhibitors and CAR T-cell therapies, which show promise in enhancing survival rates for osteosarcoma patients.
Genomic Studies And Future Directions
The scourge of osteosarcoma is further combated with the aid of advanced genomic studies. By mapping the tumor’s genome, researchers acquire invaluable clues about what drives its growth. This data serves as a roadmap for developing powerful new drugs. Our grasp of the genetic factors at play in osteosarcoma lays the groundwork for a future where precision medicine becomes a norm rather than an exception. Anticipation is high for the clinical trials and treatments that this research will yield.
Preventive Measures
Osteosarcoma is a type of bone cancer that often affects young individuals. Understanding preventive measures may help to reduce risk factors associated with this disease. Let’s dive in and explore proactive steps which include lifestyle interventions, genetic counseling, and enhancing public awareness.
Lifestyle Interventions And Risk Reduction
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can play a key role in reducing the risk of many diseases, including cancers like osteosarcoma. Important lifestyle changes include:
- Balanced diet: Consuming foods rich in vitamins and minerals supports overall health.
- Regular exercise: Physical activity strengthens bones and boosts the immune system.
- Limiting alcohol: Alcohol moderation may reduce cancer risk factors.
- No smoking: Avoiding tobacco is crucial for healthy bones and overall well-being.
Genetic Counseling And Screening
For individuals with a family history of osteosarcoma, genetic counseling and screening are valuable:
- Seek genetic counseling to assess risk levels.
- Consider genetic screening if advised by a healthcare professional.
- Robust follow-up care is essential for early detection and management.
Public Awareness And Education
Increasing society’s understanding of osteosarcoma is vital. Key efforts include:
- Community programs: Education programs can help to inform the public about risk factors.
- School initiatives: Integrating health education into school curriculums empowers youth with knowledge.
- Online resources: Accessible information on trustworthy websites offers guidance for interested individuals.
Credit: www.orthoracle.com
Societal And Economic Impact
Osteosarcoma doesn’t just affect patients’ health; it also has a significant impact on society and economies worldwide. From steep treatment costs to strains on healthcare systems and unequal access to care, the repercussions of this disease extend beyond the personal tragedies faced by patients and their families.
Cost Of Osteosarcoma Treatment
Osteosarcoma treatment comes with a hefty price tag. It often involves surgery, chemotherapy, and sometimes, radiation therapy. Costs can include:
- Hospital stays
- Medical procedures
- Medication
- Physical therapy
- Follow-up care
These expenses can mount over time, placing substantial financial strain on families and insurance systems. For many, it leads to economic hardship.
The Burden On Healthcare Systems
As a complex type of cancer, osteosarcoma requires extensive resources from healthcare systems. The burden reflects through:
- Long-term care needs
- Advanced medical equipment
- Specialist medical personnel
Healthcare facilities must balance these demands with existing resources, sometimes diverting attention from other patients. This strain can cause ripple effects that impact service delivery across the board.
Global Disparities In Treatment Access
Access to osteosarcoma treatment varies greatly around the world. In high-income countries, patients benefit from:
- Latest treatments
- Specialized care
- Research breakthroughs
In contrast, low-income countries face:
- Lack of facilities
- Scarcity of medical professionals
- Fewer treatment options
This divide leads to differing outcomes. Patients in wealthier countries often enjoy higher survival rates. Meanwhile, those in poorer regions struggle with access, and consequently, survival.
Legal And Ethical Considerations
Facing osteosarcoma brings not just medical challenges, but legal and ethical ones too. Patients, families, and healthcare professionals often navigate complex decisions. What are the rights of patients? How does one give informed consent? These questions are central to ethical care. This section explores key topics in the ethical treatment of osteosarcoma.
Informed Consent In Treatment
Informed consent is crucial in healthcare. It means that patients understand their condition, treatment options, and risks before deciding on care. When it comes to osteosarcoma, explaining treatment details in clear language is essential.
Patients or their guardians must sign consent forms. This formality records their understanding and agreement to the proposed plan. Medical teams must ensure patients are aware of all facets of treatment, including potential side effects and outcomes.
Ethical Dilemmas In Experimental Therapies
New therapies for osteosarcoma can save lives. But they come with ethical questions. Is it right to offer treatments still under study? Patients must understand the experimental nature of these therapies.
- Risks versus potential benefits of new treatments must be clear.
- Patient autonomy should be respected in the decision-making process.
- Participation in clinical trials must be voluntary, with freedom to withdraw.
Patient Rights And Advocacy
Patient rights include privacy, receiving care, and getting information about one’s health condition. Advocacy supports these rights. Advocates can be family, friends, or legal representatives. They help patients make informed decisions.
Strong advocacy ensures that patient voices are heard and their rights protected throughout their osteosarcoma journey. Advocacy is about standing up for patient-centered care in a complex healthcare system.
Navigating Insurance And Financial Support
Patient Stories And Experiences
Osteosarcoma paints a challenging picture for those affected. But behind the statistics are real people with inspiring stories. These narratives of courage and community support offer insights and hope. They show how determination, science, and solidarity can light up the darkest times.
Survivor Testimonials
Listening to survivors share their personal battles with osteosarcoma can be profoundly moving. Each testimonial is a beacon of strength to others fighting this disease.
- John’s Victory: Diagnosed at 16, John underwent surgery and chemotherapy. His tale underscores resilience and the power of positive thinking.
- Emily’s Journey: Emily shares her experiences with experimental treatments. Her story highlights the importance of medical advancements.
The Role Of Support Groups And Communities
Support groups and communities serve as lifelines for patients and families. They offer understanding, resources, and encouragement at every step.
| Support Group | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Families Fighting Osteosarcoma | Guidance, companionship, and shared experiences. |
| OsteoWarriors | Hope through stories, survivor tips, and community events. |
Learning From Patient Journeys
Patient journeys with osteosarcoma are rich with lessons. They show the importance of early detection, innovative treatments, and never giving up.
- Early Detection: Patients underscore frequent check-ups.
- Innovative Treatments: Stories reveal how new therapies are saving lives.
- Continuous Hope: Even in tough times, patient narratives inspire perseverance.
Credit: www.mayoclinic.org
Resources And Helpful Organizations
Navigating the journey with Osteosarcoma can be challenging. Great support helps. Understanding the disease, treatment options, and finding the right care are key steps. Many organizations dedicate themselves to assisting patients and families. Below, explore various resources and organizations committed to helping those affected by Osteosarcoma.
Osteosarcoma Research Foundations And Charities
Research is vital in the fight against Osteosarcoma. Leading foundations provide funding, promote cutting-edge research, and aim for a cure. They offer information and support programs too.
- Osteosarcoma Institute – Advancing research and offering therapist directories.
- The Liddy Shriver Sarcoma Initiative – Supports scientific inquiries and collaborations.
- Sarcoma Foundation of America – Advocates for increased research and drug development.
Educational Resources And Advocacy Groups
Educational materials and advocacy are crucial. Knowledge empowers patients and families. Established groups provide comprehensive guides on Osteosarcoma care.
- National Cancer Institute – Offers detailed educational content on various cancers, including Osteosarcoma.
- American Cancer Society – Provides resources on cancer treatment, statistics, and research.
- CancerCare – Delivers free, professional support services to anyone affected by cancer.
Connecting With Experts And Specialists
Immediate access to experts can inform and reassure. Specialist networks facilitate connections with leading Osteosarcoma professionals.
- Oncology Nursing Society – Connects patients with nurses specializing in cancer care.
- American Society of Clinical Oncology – Provides a directory of oncology professionals.
- Musculoskeletal Tumor Society – Lists specialists focused on bone and soft tissue tumors.
Conclusion
Osteosarcoma may seem daunting, but knowledge is power. Early detection and innovative treatments are key. Support systems and medical advancements offer hope. For those affected, ongoing research promises better outcomes. Let’s stay informed and proactive in the fight against this bone cancer.

