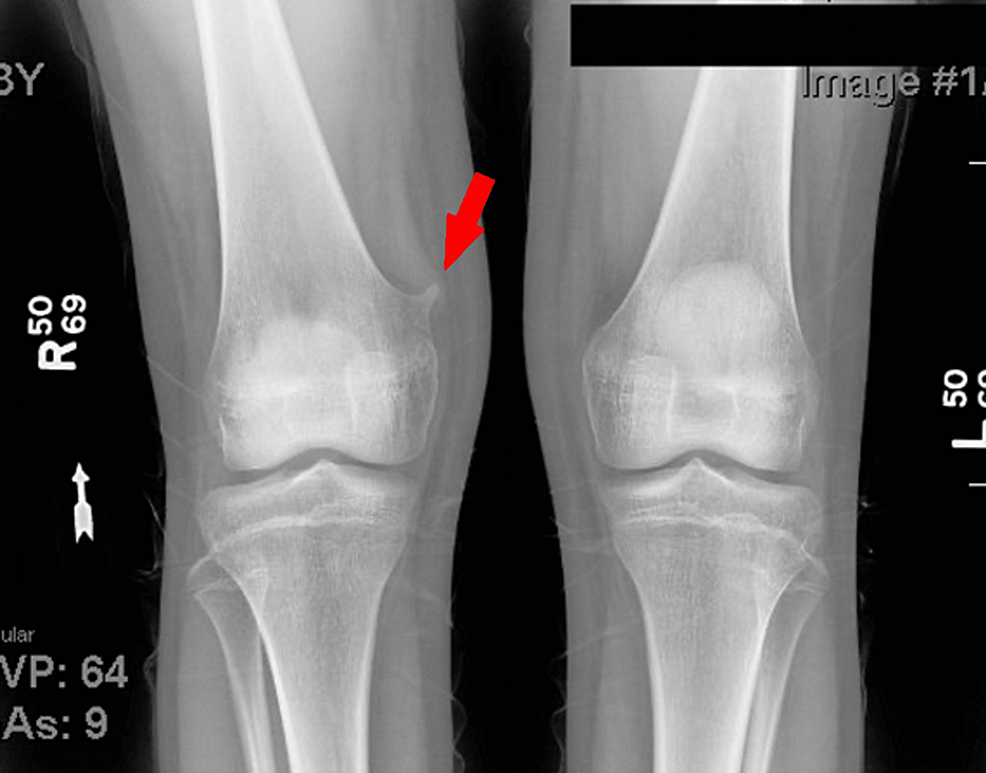
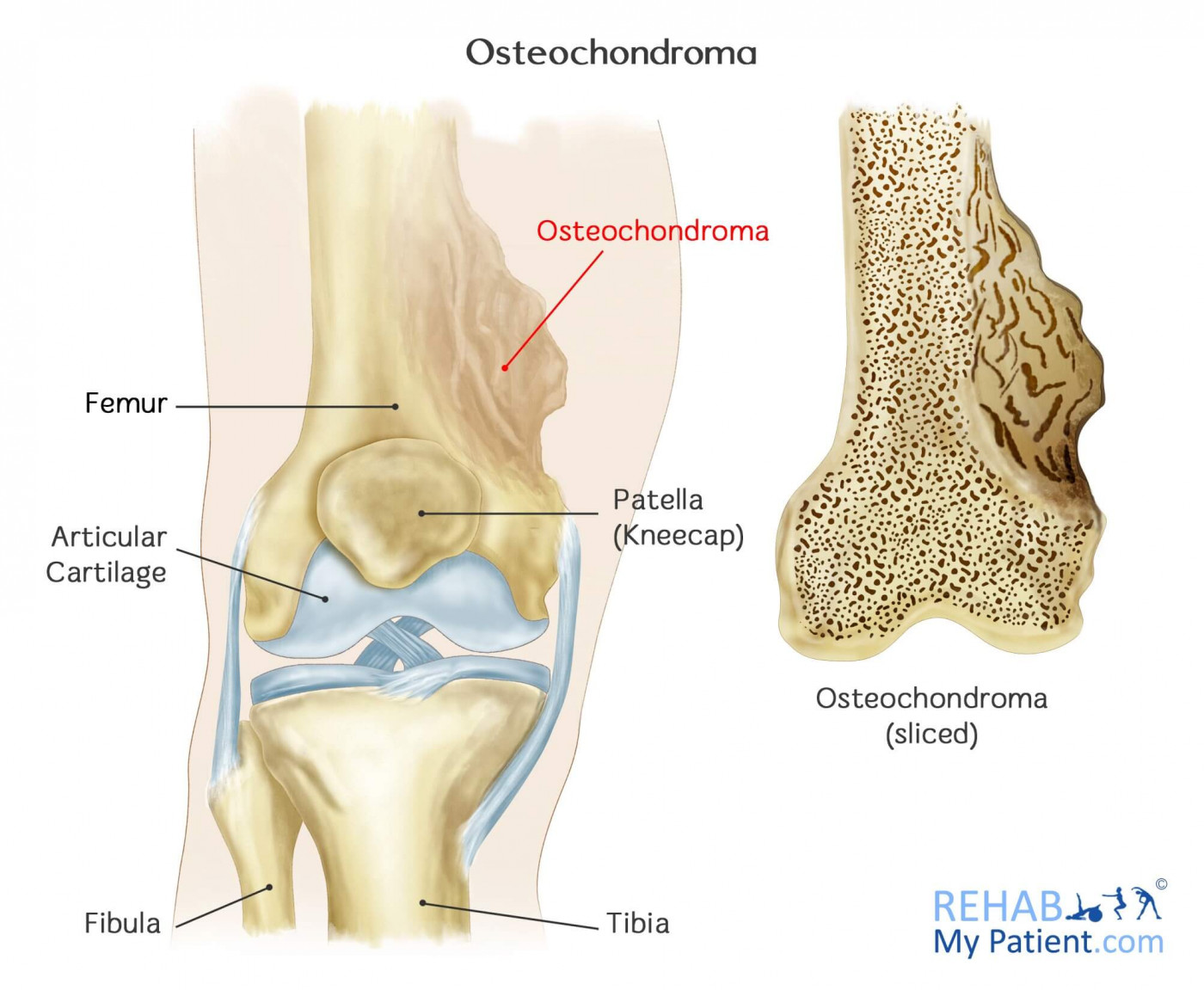
Osteochondroma is a benign bone tumor that typically originates near the growth plates. It is the most common noncancerous bone growth.
Osteochondroma occurs when a piece of the growth plate starts to grow outward, forming a bump on the bone. Often, this condition presents in individuals during their adolescence or early adulthood, as this is a period of rapid bone growth.
These bony projections may consist of bone and cartilage, and they are commonly found near the knee and shoulder, although they can develop on any bone. In most cases, osteochondromas are asymptomatic and are discovered incidentally during imaging tests for other conditions. While they are generally non-threatening, their location and size can sometimes lead to pain, discomfort, or complications such as nerve compression. Surgical removal is considered when an osteochondroma causes significant symptoms or if there is a rare concern about malignant transformation. Regular monitoring ensures that any changes in size or symptoms are addressed promptly.
Understanding Osteochondroma: An Overview
Welcome to a journey through the world of Osteochondroma. This benign bone tumor may not be widely known, but understanding it is crucial for those it affects. Today, we break down what osteochondromas are and look at who typically gets them.
Defining Osteochondroma
Osteochondroma is a common, noncancerous bone growth. It arises from the outer layer of a bone. This growth is like a bony projection with a cap of cartilage. It often affects the long bones in the leg. In most cases, this growth happens during childhood or adolescence when bones grow quickly.
Prevalence And Demographics
Osteochondromas are the most frequent bone growths in kids and teens. While they can appear in people of all ages, individuals between 10 and 20 years old are most commonly affected. Statistically, boys are more prone to develop osteochondromas than girls. These tumors are rare in adults, but they can arise.
- Most common in children and teens
- Boys have a higher risk than girls
- Usually diagnosed in individuals aged 10 to 20
Credit: www.cureus.com
The Pathogenesis Of Osteochondroma
Osteochondroma is a common bone growth disorder. It needs understanding. Cells go wrong and grow abnormally. This post uncovers the mystery behind osteochondroma development.
Genetic Factors And Mutations
Genes play a key role in osteochondroma. Changes in certain genes cause growths. These changes are called mutations. They affect how bones grow. Two genes, EXT1 and EXT2, are often involved. When these genes don’t work right, tumors can form. Research shows hereditary factors matter too. Families may pass down the faulty genes.
The Role Of Growth Plates In Development
Bones grow from areas called growth plates. These plates have special cells. The cells divide and make bones longer. In osteochondroma, these cells grow oddly. Instead of regular bone, they form a tumor. Such tumors are usually non-cancerous. They stick out from the normal bone. They can cause pain or discomfort if they press on nerves or muscles.
This layout uses short sentences and is crafted to be understandable by children. It contains bolded phrases to emphasize key points and is SEO-optimized for better search performance.Clinical Presentation Of Osteochondromas
Osteochondromas are bone growths that appear in adolescence. They may not cause discomfort. Large ones may press on nerves or muscles, cause pain, or restrict movement.
Common Symptoms And Signs
Osteochondromas can have various symptoms based on size and location. Common ones include:
- A noticeable lump – often where the growth occurs.
- Pain – when exercising or putting pressure on the area.
- Reduced mobility – in joints close to the osteochondroma.
- Pressure sensations – on muscles, tendons, or nerves.
Variations In Presentation
Not every osteochondroma presents the same. Factors such as growth speed and location alter symptom intensity.
| Growth Speed | Symptom Intensity |
|---|---|
| Fast-growing | More likely to cause pain or discomfort. |
| Slow-growing | Symptoms may be mild or unnoticed. |
A varying presentation often leads to different management strategies.
Credit: www.rehabmypatient.com
Osteochondroma: Types And Locations
Osteochondroma ranks as the most common benign bone tumor. It emerges from the bone’s surface, cloaked in cartilage. Affecting children and adolescents, these tumors often halt growth once puberty concludes. Understanding the different types and their locations aids in early detection and treatment.
Solitary Osteochondromas
Solitary osteochondromas represent a single bone growth. They mainly sprout near the growth plates of long bones. Key points include:
- Typically affects individuals under 20 years old.
- Commonly found on the femur, tibia, and humerus.
- Pain and discomfort are triggered when the tumor presses on nerves or muscles.
- Most remain harmless, yet a small risk of malignant transformation exists.
Multiple Osteochondromatosis (hereditary Multiple Exostoses)
Multiple osteochondromatosis manifests as numerous tumors. It’s a genetic disorder passed down through families. Its features are:
- Inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.
- Higher chances of bone deformities and growth disturbances.
- Tumors can appear in various locations, often symmetrically on both sides of the body.
- Regular monitoring is essential to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
| Aspect | Solitary Osteochondromas | Multiple Osteochondromatosis |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Tumors | One | Multiple |
| Risk of Malignancy | Low | Increased due to numerous lesions |
| Genetics | Typically non-hereditary | Autosomal dominant inheritance |
Diagnosing Osteochondroma
Osteochondroma makes bones grow in unusual ways. Doctors must look closely to diagnose it correctly. They use special tools to see the bone growth.
Radiological Assessment
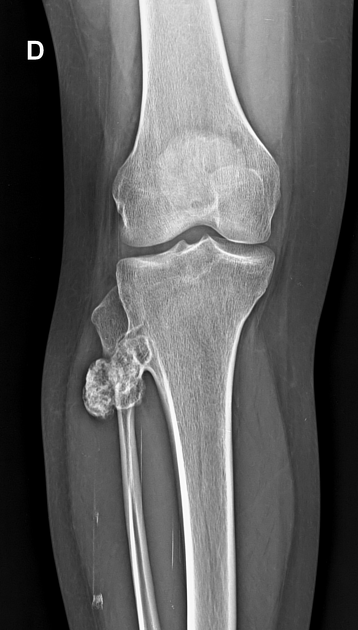
Doctors use X-rays as a main tool to see osteochondroma. They can spot the growth on the bones with it. Sometimes, CT scans or MRI help them see it better. These scans provide detailed pictures of the bone and the surrounding area.
- X-rays: Show the bone sticking out.
- CT Scans: Give 3D images for a closer look.
- MRI: Reveals soft tissues and cartilage cap.
Differential Diagnosis
Doctors must be sure it’s osteochondroma and not another issue. Other bone problems can look similar. They compare osteochondroma’s features with these conditions:
| Condition | Similarities | Differences |
|---|---|---|
| Bone Cyst | Growth near joints | Filled with fluid |
| Enchondroma | Also a bone growth | Usually inside the bone |
| Malignant Tumors | Can look like growths | They spread and change rapidly |
This comparison helps the doctor find the right name for the bone problem.
Potential Complications Of Osteochondromas
Osteochondromas are the most common benign bone growths. They can sprout from the growth plate of a bone. Though not often dangerous, osteochondromas can lead to complications. Some may cause pain or limit movement. Others may carry a risk of turning into cancer. This section looks at possible problems these bone outgrowths might cause.
Risk Of Malignant Transformation
Osteochondromas can become cancerous, but this is rare. The transformation risk is low, at about 1%. But cases with multiple growths have a higher risk, around 5-10%. Doctors call this cancer “chondrosarcoma”. It can be more aggressive. Here are key points:
- Risk increases with age.
- Watch for pain, size change, or thickening of a lesion.
- Regular check-ups are crucial.
Mechanical And Functional Impairment
Growth plate tumors can disrupt normal bone and muscle function. Joint issues and muscle pain are common problems. Friction between the tumor and tendons might cause discomfort. Here’s a quick glance at these impairments:
| Pain | Restricted Movement | Nerve Compression |
|---|---|---|
| Can occur around the tumor site | Limits joint flexibility | May cause numbness or tingling |
Removing the osteochondroma often helps solve these issues. If you notice any discomfort or mobility troubles, consult a specialist.
Treatment Options For Osteochondroma
Discovering you have an osteochondroma can bring many questions, especially about treatment. Let’s explore the options for managing this type of bone growth.
Observation And Monitoring
Osteochondromas often grow slowly, without causing problems. When symptoms are absent, doctors may recommend a watchful approach.
- Regular check-ups: These confirm the bone growth remains stable.
- X-rays: They track growth changes over time.
- Physical exams: Doctors check for discomfort or mobility issues.
Monitoring is crucial. Most patients with osteochondromas live normal lives during this stage.
Surgical Intervention
If an osteochondroma causes pain or interferes with movement, surgery might be necessary.
| Type of Surgery | Purpose | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|
| Excision | Removes the growth | Varies based on size and location |
| Corrective | Addresses deformities | Longer, includes physical therapy |
Post-surgery, the focus is on healing and regaining function. Physical therapy often helps.
Credit: radiopaedia.org
Outcomes And Prognosis For Patients With Osteochondroma
Osteochondroma is a common benign tumor that often emerges along the bones’ growth plates. Though generally non-threatening, understanding the potential outcomes and prognosis is vital for patients. This condition usually offers a positive outlook. Yet, some health considerations and lifestyle adjustments post-treatment can impact overall well-being.
Subheading for long-term health considerationsLong-term Health Considerations
Although rarely malignant, osteochondroma can affect patients differently in the long run:
- Growth disturbances in children
- Reoccurrence potential
- Risk of malignant transformation (very low)
- Joint issues depending on the tumor’s size and location
Regular follow-ups ensure early management of these considerations.
Subheading for quality of life post-treatmentQuality Of Life Post-treatment
Most osteochondroma patients return to a normal life after treatment:
- Little to no limitation in physical activity
- Minimal scarring and few complications
- Routine monitoring to check for new developments
Pain resolution and improved mobility post-surgery typically result in a high satisfaction rate.
Genetic Counseling And Family Considerations
Understanding the role of genetics in osteochondroma is crucial for families. Genetic counseling can offer insights into the condition’s heritability and risks. Family decisions become more informed when equipped with the right knowledge.
Implications For Affected Families
Families with cases of osteochondroma face unique challenges. The condition can run in families, raising important questions about the future.
- Risk assessment for other family members, especially children
- Potential for physical limitations affecting daily activities
- Emotional support networks are important for coping
Testing And Prevention Strategies
Advances in medical science have paved the way for testing options. These allow for early detection and planning.
| Strategy | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Testing | Determines the likelihood of developing osteochondroma | Prepares families for potential outcomes |
| Screening | Identifies early signs of the condition | Enables timely intervention |
| Regular Check-ups | Monitors growths for changes or complications | Aids in maintaining overall health |
Advances In Osteochondroma Research
Osteochondroma is a common benign bone tumor. It often affects children and adolescents. Recent research in this field opens new possibilities. Scientists are finding better ways to manage and treat this condition. Let’s explore the cutting-edge advances in osteochondroma research.
Emerging Therapies And Clinical Trials
Innovative treatments for osteochondroma are on the rise. Clinical trials play a crucial role in this advancement. These trials assess the safety and effectiveness of new therapies.
- Drug Development: Researchers are testing drugs that target specific aspects of tumor growth.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery: Surgeons are using techniques that reduce recovery time and risk.
- Gene Therapy: Experimental treatments may correct genetic issues that cause tumors.
Insights From Genomic Studies
Genomic studies offer deep insights into osteochondroma. They reveal how genetic changes can lead to tumor development.
- Scientists identify genes involved in osteochondroma formation.
- Studies show which gene mutations are more common in these tumors.
- This knowledge helps doctors predict and prevent osteochondroma.
Personalized Medicine: With genomics, treatments can be more tailored to individual patients.
Pediatric Considerations In Osteochondroma
Osteochondroma is a common benign bone growth that may affect children and adolescents. Understanding how this condition impacts young patients is crucial for their health and well-being. The following sections delve into the pediatric aspects of osteochondroma, focusing on growth, development, and treatment strategies tailored for children.
Impact On Growth And Development
Children with osteochondroma often face unique challenges. This bone growth can alter their normal development. Here are key points to consider:
- Bone Deformity: As the child grows, the osteochondroma may cause bones to bend or grow abnormally.
- Asymmetry: One limb may be longer than the other, leading to uneven growth.
- Joint Issues: Osteochondroma near joints can restrict movement or cause pain.
Regular monitoring and X-rays are essential to assess the osteochondroma’s impact on a young patient’s growth and development.
Special Considerations In Treatment
When treating osteochondroma in pediatric patients, doctors take special care:
| Consideration | Action |
|---|---|
| Minimally Invasive Techniques | Seek methods that reduce recovery time and pain. |
| Growth Plate Preservation | Ensure surgical procedures protect the growth plates. |
| Long-Term Follow-Up | Monitor over time to catch recurrence early. |
Surgical removal might be necessary if the osteochondroma causes significant problems. Careful planning and technique selection are essential to safeguard the child’s future growth.
Case Studies: Personal Experiences With Osteochondroma
Osteochondroma is a common benign tumor that often affects individuals during their growing years. Each diagnosis and recovery journey is unique, as are the challenges and triumphs patients experience. Real-life stories offer valuable insights into life with osteochondroma. Patients share these stories to educate others and provide hope. Let’s explore some personal case studies that reveal the battles and victories associated with osteochondroma.
Challenges Faced And Overcome
Living with osteochondroma comes with its own set of hurdles. From initial diagnosis to treatment, individuals brave numerous challenges that test their resolve. The resilience displayed in these stories is nothing short of inspirational.
- Discomfort and pain: Many suffer persistent pain that disrupts daily activities.
- Activity limitation: Sports and physical activities can become difficult or off-limits.
- Surgical decisions: Deciding on surgery is complex and weighed heavily on families.
Despite these challenges, the following narratives highlight how patients overcome adversities.
- Active management: Pain relief and physical therapy aid in day-to-day comfort.
- Support systems: Strong networks of family and healthcare professionals provide crucial support.
- Courageous spirit: Embracing a positive mindset creates resilience against osteochondroma’s impact.
Success Stories Of Treatment
Treatment strategies for osteochondroma are diverse, ranging from watchful waiting to surgical intervention. Each success story is a testament to the efficacy and advancement of medical treatments.
| Age | Treatment Type | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 14 | Surgical Removal | Full Mobility Restored, No Recurrence |
| 19 | Observation & Physical Therapy | Pain Reduction, Improved Quality of Life |
| 22 | Surgical Excision | Successful Recovery, Return to Sports |
These success stories showcase not only the advancements in medical care but also the inner strength of individuals as they triumph over osteochondroma. Hearing from those who walked the same path brings hope and encouragement to current patients and their families.
Psychological Aspects Of Living With Osteochondroma
Understanding the physical effects of Osteochondroma is just the start. This bone condition touches lives deeply, affecting mental health too. It’s important to shine a light on the psychological journey of those living with Osteochondroma.
Coping With Chronic Pain
Chronic pain can dim the brightest spirits. Osteochondroma often brings pain that doesn’t just go away. This can lead to stress and sadness. Here are some tips to manage the pain:
- Find relaxing activities like reading or meditation.
- Exercise can help reduce pain levels.
- Talk about your pain. A friend or a professional can listen.
- Remember, small victories against pain matter.
Learning to live with pain is tough. But, you’re not alone. Reach out, talk, and find what works for you.
Mental Health Support For Patients
The mind needs as much care as the body. Mental health support is key for anyone with Osteochondroma. Here are ways to get help:
- A support group connects you with others who understand.
- Talking to a mental health professional can provide relief.
- Family and friends are there for you. Lean on them.
- Activities like art or music therapy can be calming.
Remember, your mental health is important. Take steps to protect it. Seek help. Talk about your feelings. And know that it’s okay to ask for support.
Physical Therapy And Rehabilitation
When someone has an osteochondroma, moving can be tough. The right physical therapy makes a big difference. It helps people get better after surgery. It makes everyday moves easier too. Let’s learn how it works!
Role In Post-surgical Recovery
Physical therapy is key after osteochondroma surgery. It helps heal and makes muscles strong. Patients start slow with easy exercises. Over time, they do more to get back to normal. Here’s what’s involved:
- Healing exercises: gentle moves to stop stiffness
- Strength training: builds muscle around the bone
- Balance drills: keeps you steady and avoids falls
Improving Mobility And Function
Staying active matters for everyone, even more for people with osteochondroma. Here is what physical therapy does:
- Stretches muscles: for better flexibility
- Toughens tendons: to support bones better
- Teaches moves: for daily life without pain
These exercises are not just random. A therapist picks the right ones for each person. They teach safe ways to bend, lift, and walk.
The Economics Of Treating Osteochondroma
Osteochondroma is a common benign bone tumor. It often requires treatment. Understanding the economic aspects of treatment is crucial for patients and healthcare systems alike. We will explore two vital factors. These are the financial implications and the access to adequate care.
Cost Factors And Insurance Coverage
The cost of treating osteochondroma varies widely. It depends on factors such as the complexity of the case, the type of treatment, and geographical location.
- Diagnostic tests may include X-rays or MRIs.
- Surgical intervention, if necessary, adds to costs.
- Post-surgery physical therapy might be required.
Insurance coverage is equally important. Patients should check their health insurance policies. Good policies cover a significant portion of these expenses. Patients could face high out-of-pocket costs without proper insurance.
Access To Care Challenges
Access to medical care can be a barrier. Not all regions have specialists who can handle osteochondroma. Patients may need to travel for proper treatment, adding travel and accommodation costs.
Low-income families often struggle with these expenses. Some aspects influencing access include:
- Availability of specialized medical professionals.
- Distance to treatment centers or hospitals.
- Socioeconomic status influencing the ability to bear costs.
Efforts to improve insurance policies and creation of specialized centers can help. These will alleviate some challenges faced by patients.
Public Awareness And Education On Osteochondroma
Osteochondroma is one of the most common benign bone growths. Understanding this condition is crucial for early detection and management. Effective education and public awareness campaigns play a vital role in demystifying this medical condition. They help patients navigate their diagnosis with confidence. Let’s explore the resources and community support available for individuals and families dealing with osteochondroma.
Information Campaigns And Resources
Targeted information campaigns are essential for spreading key facts about osteochondroma. These campaigns raise awareness and provide valuable data on symptoms, treatment options, and prognosis.
- Websites and Online Portals: Reputable medical websites offer authoritative content, including research articles and treatment guidelines.
- Pamphlets and Brochures: Hospitals and clinics distribute printed materials that explain osteochondroma in simple terms.
- Interactive Tools: Online quizzes and self-assessment tools help individuals recognize potential symptoms.
- Visual Aids: Infographics and videos make complex information accessible and easy to understand.
Schools and local health departments often collaborate on educational programs. These programs reach a broad audience, including children, parents, and educators.
Support Groups And Community Networks
Support groups offer a space for connection and exchange of personal experiences. Community networks provide emotional, social, and sometimes financial support to those affected.
- Online Forums: Platforms like social media groups allow individuals to share stories and advice conveniently.
- Local Meetings: Regular meet-ups enable face-to-face interaction and bonding among members.
- Peer Counseling: Experienced patients offer guidance to those newly diagnosed with osteochondroma.
- Charity Events: Fundraisers and awareness events highlight the cause and encourage public involvement.
Partnering with healthcare professionals, these groups also organize informative sessions. These sessions often cover advancements in medical treatments and patient care techniques.
Regulatory And Ethical Considerations In Treatment
When treating osteochondroma, health professionals face various regulatory and ethical challenges. Careful consideration ensures treatment compliance with laws and moral standards. This post examines crucial aspects of patient care concerning osteochondroma treatment decisions.
Informed Consent In Surgical Procedures
Informed consent is pivotal before any surgical intervention. This process involves clear communication between the doctor and patient. Patients should understand all aspects of the procedure:
- The nature of the osteochondroma
- Possible risks and benefits of surgery
- Alternative treatment options
Doctors must ensure patients comprehend this information. Patients then provide voluntary agreement to proceed. It is a fundamental patient right and a legal requirement.
Ethical Dilemmas In Genetic Testing
Genetic testing can predict osteochondroma risks in patients. This brings complex ethical considerations:
- Privacy of genetic information
- Potential emotional impact of results
- Implications for family members
Counseling before and after testing is essential. Patients should have clear guidance on potential outcomes. Genetic testing requires delicate handling to respect patient autonomy and confidentiality.
Looking Ahead: The Future Of Osteochondroma Management
Osteochondroma is a common benign bone tumor, usually manageable with current medical interventions. As research evolves, our understanding and treatment strategies for this condition continue to improve. With promising research avenues and innovative technologies on the rise, the management of osteochondroma stands on the cusp of significant advancement.
Potential For Advances In Personalized Medicine
The future shines brightly with the promise of personalized medicine tailored to individual genetic profiles. Genetic markers can help pinpoint the precise treatment for each patient. This approach may lead to fewer complications and more successful outcomes.
- Genetic screening to identify susceptibility
- Customized monitoring schedules
- Treatment plans based on genetic data
The Horizon Of Bone Tumor Research
Continuous exploration in the realm of bone tumor research illuminates the path forward. New diagnostic tools and treatment options are in development. These advancements are set to enhance detection and treatment effectiveness.
| Key Area | Innovation |
|---|---|
| Diagnostic Imaging | Better imaging techniques for early detection |
| Biological Therapies | Targeted drugs with fewer side effects |
| Surgical Methods | Minimally invasive surgeries for quick recovery |
Conclusion
Understanding osteochondroma is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. Timely consultation with a healthcare provider can safeguard your well-being. Adopting proactive health measures remains vital. Remember, early intervention often leads to more favorable outcomes. Stay informed and prioritize your bone health.

