A cyst is a closed pocket of tissue that can contain fluid, air, or other substances. These non-cancerous growths can appear on any part of the body.
Cysts are common occurrences that the medical community understands well. They range in size and can develop due to infections, blockages of ducts, or around foreign bodies, like earrings. Some cysts form as part of a chronic condition, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or fibrocystic breast disease.
While most cysts are benign, their presence can sometimes signal an underlying issue and may require medical evaluation. Symptoms vary but can include swelling, pain, or discomfort in the affected area. Treatment options are diverse, from monitoring to surgical removal, depending on the cyst’s size, location, and potential impact on the individual’s health. Regular check-ups can help identify cysts early, ensuring better management and outcomes.
Understanding Cysts: A Comprehensive Overview
Our bodies are full of mysteries and surprises. One such curiosity is the formation of cysts. Often painless and harmless, these pockets of tissue can appear anywhere. Let’s dive into the intricate world of cysts and understand what they really are.
Defining Cysts: Types And Characteristics
Cysts come in many shapes and sizes. They’re fluid-filled sacs that can grow on organs, skin, or tissues. Each type has unique characteristics that doctors use to identify them. Below is a simplified layout of their diversity:
| Type | Location | Common Traits |
|---|---|---|
| Epidermoid | Skin surface | Slow-growing |
| Ovarian | Ovaries | May cause pain |
| Sebaceous | Skin glands | Blocked ducts |
The Biological Mechanisms Behind Cyst Formation
Ever wondered why cysts form? They’re usually your body’s response to a blockage. Cells that typically shed away start to multiply. This multiplication can create a sac. The sac fills with fluid or semi-solid material. Sometimes, infections or chronic conditions can prompt cyst growth as well. Identifying the cause is key for treatment.
The Prevalence And Epidemiology Of Cysts
Cysts are common and can strike anyone, but some people may be more prone. Factors like age, gender, and genetic history play roles. Epidermoid cysts, for example, are seen more frequently in younger adults. Ovarian cysts primarily affect premenopausal women. Statistics show that most people will develop at least one cyst in their lifetime.
Credit: my.clevelandclinic.org
Classification Of Cysts: Identifying The Varieties
Understanding cysts begins with classification. Like a mysterious collection of sealed treasures, cysts come in various forms, each with unique characteristics and origins. Knowledge of these varieties aids in better diagnosis and treatment.
Functional Vs. Neoplastic Cysts
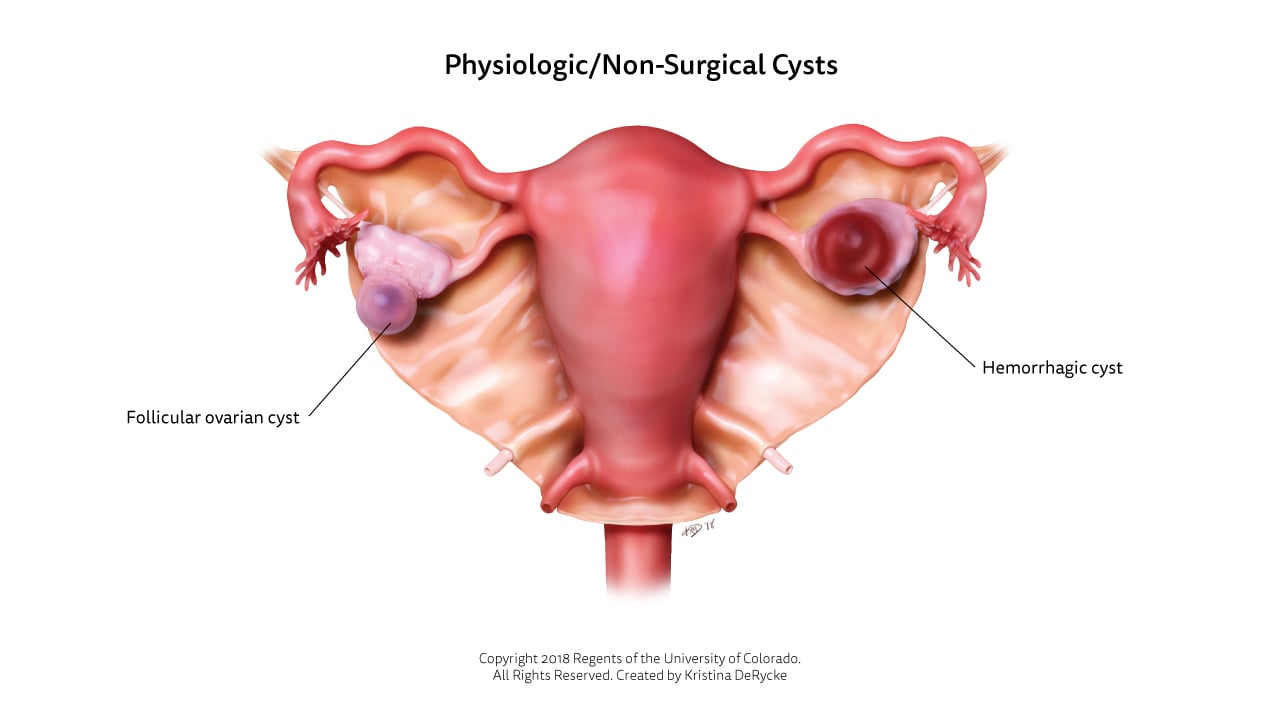
Functional cysts are part of your body’s natural cycle. Think of them as balloons that grow and shrink in harmony with your hormonal rhythm. Conversely, neoplastic cysts are the rebels, forming new growths that may require closer attention.
- Functional cysts usually resolve on their own.
- Neoplastic cysts may need surgical removal.
Location-based Categorization: Ovarian, Renal, And More
The location of a cyst tells its story. Ovarian cysts are like uninvited guests in the reproductive system, while renal cysts setup camp in your kidneys.
- Ovarian cysts relate to the female reproductive system.
- Renal cysts occur in the kidneys.
- Other locations include the liver, skin, and even the brain.
The Histological Perspective: Simple, Complex, And Dermoid Cysts
Under the microscope, cysts reveal their secrets. Simple cysts are plain with fluid, while complex cysts have solid components or irregular features. Dermoid cysts contain tissues like hair, skin, or teeth.
| Type | Main Feature | Common Site |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Cysts | Fluid-filled | Kidneys, liver |
| Complex Cysts | Solid components | Ovaries, breasts |
| Dermoid Cysts | Contains tissues | Ovaries, skin |
Signs And Symptoms: Recognizing Cystic Conditions
A cyst, a small pouch filled with fluid, can appear virtually anywhere in the body, often causing no troubles at all. But when they do make their presence known, it’s important to recognize the signs and symptoms. Identifying cystic conditions early can help manage and treat complications if they arise.
Common Physical Manifestations Of Cysts
Physical signs of a cyst can range from simple lumps to tender spots on the body. These characteristics are crucial in recognizing cystic conditions:
- Lumps or bumps beneath the skin
- Swelling or round shapes that are often visible
- Pain or discomfort when touched or pressed
- Redness or warmth around the affected area indicating inflammation
- Discharge of fluid or other material if a cyst ruptures
When To Seek Medical Attention: Warning Signs
Certain signs should prompt an immediate doctor’s visit. These warning signs include:
- Fast growth or sudden changes in size or shape
- Severe pain, which might indicate rupture or infection
- Complications such as fever, indicating potential infection
- Interference with daily activities or functions
- Appearance in sensitive areas, like the eye or genitals
The Asymptomatic Nature Of Some Cyst Types
Some cysts remain hidden, causing no symptoms. Regular check-ups are vital due to this asymptomatic nature:
| Cyst Type | Common Location | Often Diagnosed By |
|---|---|---|
| Ovarian Cysts | Ovaries | Ultrasound during pelvic exam |
| Renal Cysts | Kidneys | Imaging tests or CT scans |
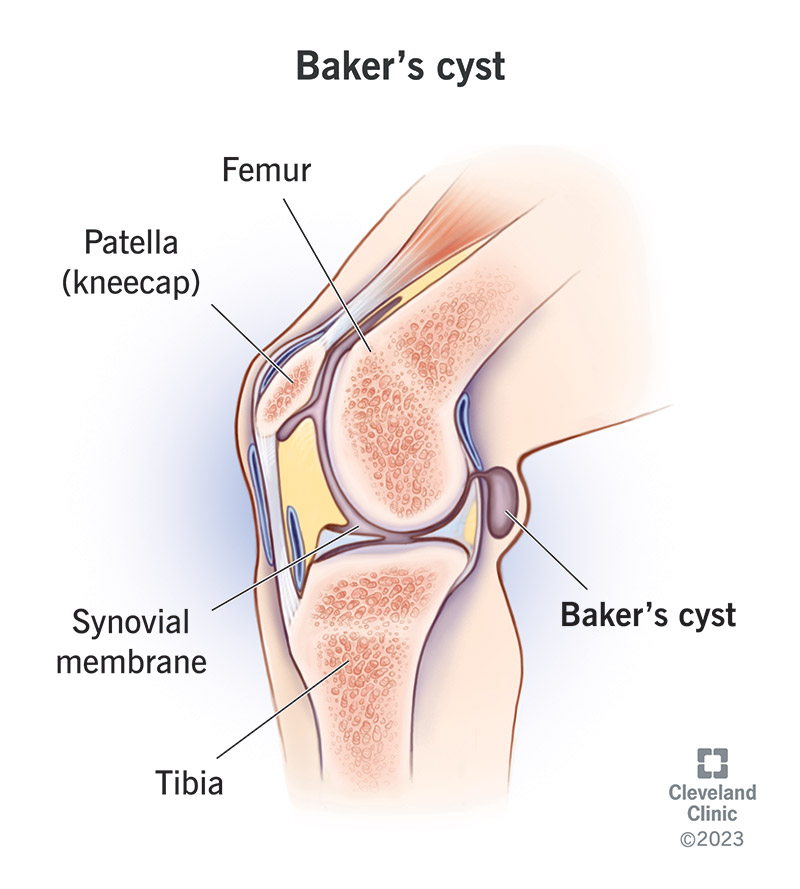
| Baker’s Cysts | Behind the knee | Physical examination or MRI |
Credit: www.childrenscolorado.org
Diagnostic Procedures: Detecting And Classifying Cysts
A cyst is a closed pocket of tissue that can occur almost anywhere in the body and may contain air, fluid, or semi-solid material. Discovering the nature and type of a cyst is crucial for effective treatment. Let’s explore the diagnostic tools and procedures doctors use to identify and classify these bodily anomalies.
Medical Imaging Techniques: Ultrasound, Mri, And Ct Scans
Ultrasound is often the first step in cyst detection. It uses sound waves to create images of soft tissues, making it great for examining cysts in organs like the liver or ovaries. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), with its detailed images, is especially useful for spotting cysts in the brain or spinal cord. Lastly, CT (Computed Tomography) Scans combine X-rays with computer technology to provide a comprehensive view that is particularly helpful for complex cases where cysts affect multiple body parts.
The Role Of Blood Tests In Cyst Detection
Blood tests can reveal markers that suggest the presence of a cyst. For instance, the CA 125 marker often elevates in women with ovarian cysts. While blood tests alone can’t confirm a cyst, they assist in forming a diagnosis when combined with imaging results.
Exploratory Surgery And Biopsies: Confirming Diagnosis
If imaging and blood tests suggest a cyst but can’t confirm, doctors might suggest exploratory surgery. This allows direct viewing and occasionally removal of the cyst for analysis. A biopsy, taking a small sample of the cyst tissue, helps determine its nature, clearing the path for the right treatment plan.
Treatment Options For Cysts: Medical And Surgical Approaches
Understanding cysts and their treatment can provide relief to those affected. Medical professionals often consider factors such as cyst size, location, and symptoms before recommending treatment. This post explores the common ways to manage and treat cysts.
Not all cysts require immediate treatment. Some may resolve on their own over time. This approach, known as watchful waiting, is suitable for small, benign cysts. Regular monitoring by a doctor ensures they do not grow or cause complications.
Doctors may prescribe medication to treat certain types of cysts.
- Hormonal treatments may help to reduce ovarian cysts.
- Antibiotics work effectively for infected cysts.
Large or bothersome cysts might need surgery. The surgeon will choose a technique based on cyst characteristics.
- Laparoscopy: A minimally invasive procedure for small cysts.
- Laparotomy: Recommended for larger cysts.
Both methods aim to remove the cyst and ensure a smooth recovery.
Impact On Life Quality: Living With Cystic Conditions
Life with cystic conditions can challenge your well-being. Cysts are not always dangerous. But they can affect your daily life. They can cause pain and other issues depending on their size and location. It is vital to understand how they might impact your life quality.
Chronic Pain And Discomfort Associated With Cysts
Many people with cysts experience ongoing pain. This discomfort can limit daily activities. Simple tasks can become challenging. For example, ovarian cysts might cause sharp pain or cramps. Cysts in the kidneys can lead to back pain. Let’s look into the daily struggles patients might face:
- Persistent Aches: Depending on the cyst’s size and location
- Movement Limitations: Pain during walking or bending
- Interruptions in Sleep: Discomfort can prevent a good night’s sleep
Fertility Implications Of Ovarian Cysts
For women, ovarian cysts can be concerning. They can affect the reproductive system. Ovarian cysts can impact fertility. They may cause irregularities in menstrual cycles. They can sometimes lead to more serious conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). This is notable as it can influence a woman’s ability to conceive.
| Type of Cyst | Impact on Fertility |
|---|---|
| Functional Cysts | Often resolve without treatment |
| Endometrioma | Can affect egg quality |
| PCOS-related Cysts | May require medical intervention for conception |
Psychological Impacts: Anxiety, Stress, And Body Image Concerns
Living with cysts can be stressful and lead to anxiety. This is true especially when waiting for a diagnosis or treatment. Body image concerns can emerge if cysts are visible or cause bloating. This can affect self-esteem and social interactions. The psychological burden can include:
- Fear of Surgery: Worrying about potential medical procedures
- Social Withdrawal: Due to physical discomfort or appearance changes
- Mental Health Strains: Increased stress levels impacting overall health
Preventative Measures And Early Detection
Keeping cysts at bay starts with preventative measures and early detection. Small steps can lead to big changes in health. Let’s dive into the best practices for minimizing the risk of cysts and catching them early when they do arise.
Lifestyle Choices And Risk Reduction
Focusing on healthy living can steer you clear of risks. Sound choices can keep your body’s defenses up against cysts. Below, find tips for a cyst-resistant lifestyle:
- Eat balanced diets with lots of veggies and fruits.
- Stay hydrated to help your organs work well.
- Avoid tobacco and limit alcohol; these can up your risk.
- Regular exercise keeps your body strong and resilient.
- Maintain a healthy weight to ease body stress.
The Importance Of Regular Health Screenings
Getting checked often is key. It’s like the early bird catching the worm. Don’t wait for signs. Health screenings can spot cysts before troubles begin.
Doctor visits are your chance to flag worries or changes in your body. Your doc can use tests to peer inside and keep tabs on potential cyst growth.
Every year, a check-up is a smart move:- Women, discuss breast and ovarian screenings with your doc.
- Guys, testicular exams should be on your radar.
- General health panels look at your whole wellness picture.
Advances In Predictive Genetics And Personalized Medicine
Science is a game-changer for health. Your genes hold secrets to your body’s cyst fight. Predictive genetics and personalized medicine take your unique self into account.
| Advancement | How It Helps |
|---|---|
| Genetic testing | Reveals your risk levels before cysts show up. |
| Personalized plans | Crafts a health blueprint that’s all about you. |
| Targeted therapies | Treats not just any cyst, but your cyst. |
Embrace these scientific strides. They can be your suit of armor against cysts.
Pediatric Considerations: Cysts In Children And Adolescents
Children and adolescents may encounter cysts just like adults. Understanding the types of cysts that are common in younger populations is vital. It is equally important to consider treatment options and their potential impact on growth and development. In this section, we delve into the specifics of cysts within this age group.
Common Cyst Types In Younger Populations
Various cysts may appear in children and teens. Below is a list of some common types:
- Epidermoid Cysts: Small lumps beneath the skin, often found on the face, neck, and trunk.
- Ovarian Cysts: Seen in teen girls; these are fluid-filled sacs on the ovaries.
- Pilonidal Cysts: Occur near the tailbone, more common in teens and young adults.
- Dermoid Cysts: Growths that may contain hair, skin, or teeth; typically present from birth.
Treatment And Management For Pediatric Patients
Approaches to treatment vary based on the cyst type and symptoms present. Some common management strategies include:
- Monitoring: Observation over time for changes or complications.
- Medication: Anti-inflammatory drugs or hormone treatments for specific cysts.
- Surgery: Necessary if the cyst is large, painful, or impacts a child’s activities.
Parents should work closely with a healthcare provider to decide the best treatment.
Long-term Monitoring And Impact On Growth
Growth and development can be affected by cysts if they interfere with normal tissue function. Long-term monitoring ensures:
| Monitoring Aspect | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Size and Symptoms | To check for potential complications or need for intervention. |
| Growth Patterns | To ensure the cyst isn’t inhibiting natural growth and development. |
Regular check-ups aid in detecting any issues early, thus protecting a child’s health.
Emerging Research And Innovative Therapies For Cyst Treatment
Emerging Research and Innovative Therapies for Cyst Treatment
Cysts, the benign sacs filled with fluid, can occur in different parts of the body and cause discomfort. Traditional treatment often includes medication or invasive surgery. Now, research lights a path to less invasive, more effective remedies. This article shines a spotlight on novel strategies for tackling cysts.
Clinical Trials And New Pharmaceutical Agents
Scientists are constantly testing new medications in clinical trials. These trials are the backbone of medical advancements. The objective is to create drugs that target cysts with precision, improving outcomes for patients. Today’s clinical trials focus on pharmaceutical agents that could:
- Reduce the size of cysts
- Prevent cyst formation
- Minimize recurrence after removal
Advances In Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
The shift towards minimally invasive procedures has been groundbreaking. Surgeons use tiny cuts and state-of-the-art equipment. This approach results in:
- Shorter- hospital stays
- Less post-operative pain
- Faster recovery times
The Future Of Regenerative Medicine And Cyst Disorders
Regenerative medicine holds promise for cyst treatment. This field uses the body’s own cells to repair and replace damaged tissues. Innovations in this area offer hope for patients with recurrent or persistent cysts. Key areas of focus include:
| Regenerative Approach | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Stem cell therapy | Promotes healing and prevents regrowth |
| Tissue engineering | Builds cyst-resistant tissue |
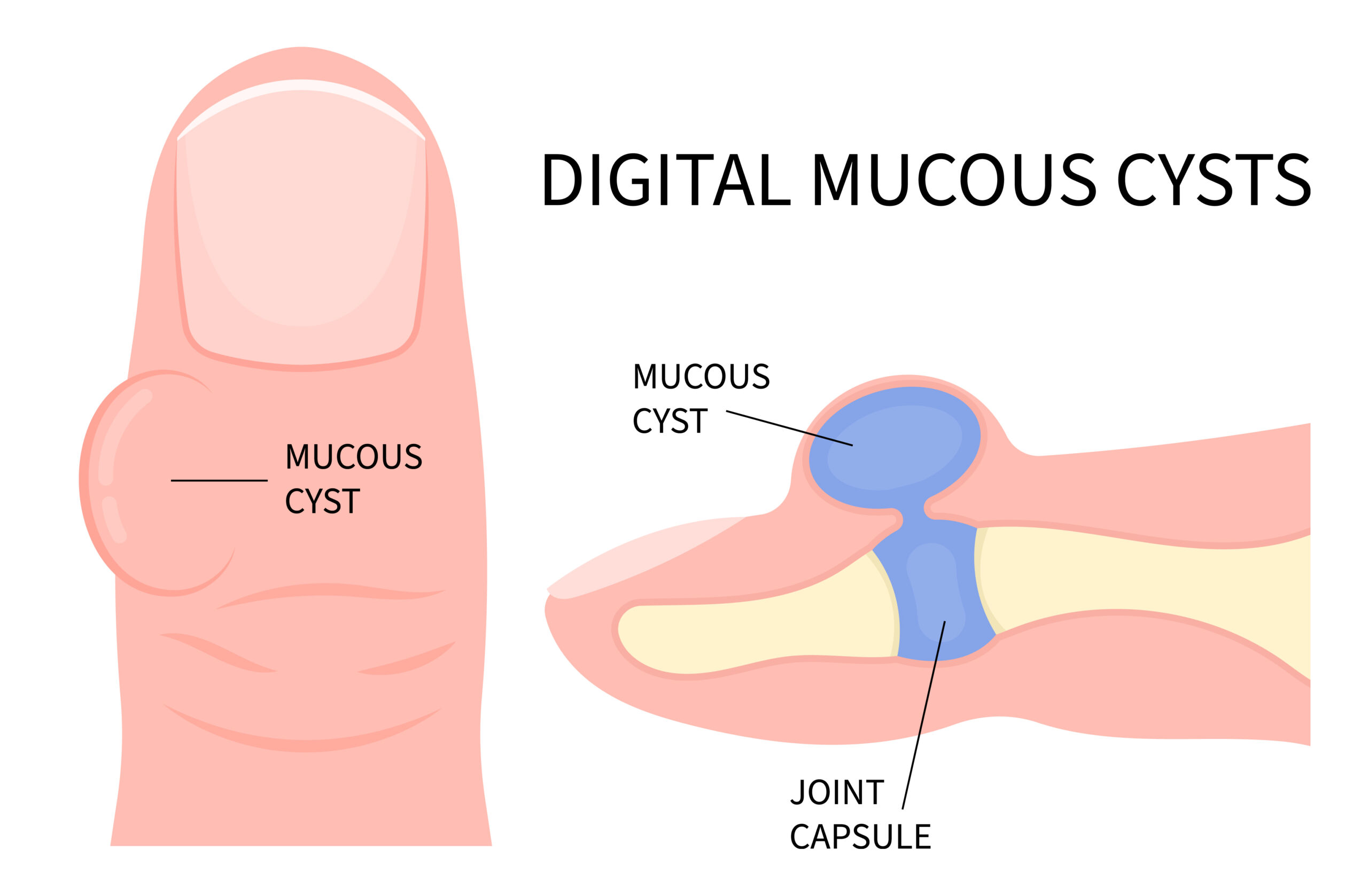
Credit: www.goldenstateortho.com
Conclusion
Understanding cysts is crucial for managing your health. Various types often call for different treatments. Consult a doctor if you have any concerns. Early detection can make a significant difference. Share this knowledge; it could be a game-changer for someone’s wellbeing.

