Chondrosarcoma is a type of cancer that develops in cartilage cells. It’s typically found in the pelvis, legs, or arms.
Understanding Chondrosarcoma requires a look at its origin and impact. This rare cancer affects the tough, flexible tissue (cartilage) that cushions bones at their joints or which makes up other body parts like the nose and ears. Chondrosarcoma can occur anywhere in the body but is most commonly diagnosed in adults over the age of 40.
The disease progresses slowly and may not cause symptoms initially; thus, it’s often discovered in later stages. Treatment options vary depending on the cancer’s size, location, and growth rate, typically involving surgery and possibly radiation therapy or chemotherapy. Recognizing the signs and undergoing regular check-ups can help with early detection, which is pivotal for more effective treatment. Despite chondrosarcoma being relatively uncommon, awareness is crucial due to its aggressive nature.
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Understanding Chondrosarcoma
Chondrosarcoma is a type of cancer. It grows in cartilage cells. Cartilage is the tough, rubbery tissue in our bodies. It shapes and supports many areas. This cancer is rare and behaves differently than others. Some are slow to spread; others can be aggressive. Let’s dive deep to understand more about it.
Definition And Overview
Chondrosarcoma stands as a challenging bone cancer. It starts in cartilage cells. Cartilage is located at the end of bones and within joints. Unlike other bone cancers, it’s often resistant to chemotherapy and radiation. Surgery is the main treatment option for this stubborn cancer.
Epidemiology: Incidence And Prevalence
- Rarity: Chondrosarcoma is quite rare.
- Age group: It usually affects adults aged 50-70.
- Gender: Men are more likely than women to get it.
Pathophysiology: How Chondrosarcoma Develops
Cancer begins when cells change. Chondrosarcoma cells form in cartilage. They ignore signals to stop growing. These cells form a mass, or tumor, that can invade nearby tissues. If the cells spread to other body parts, it’s called metastasis. Early diagnosis can limit the spread.
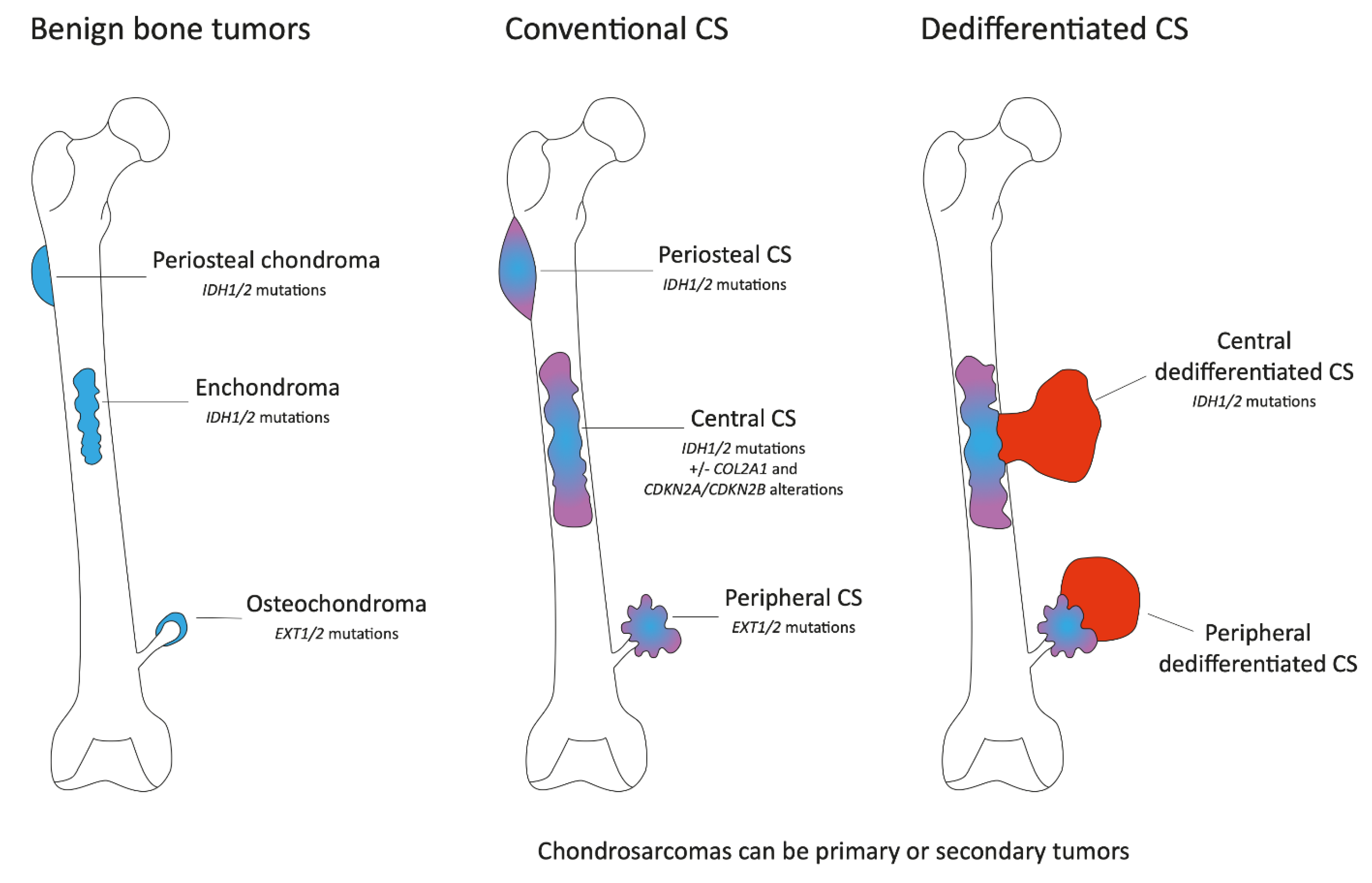
Classifying Chondrosarcoma
Understanding Chondrosarcoma is like unraveling a complex puzzle. This rare type of cancer develops in the bone and cartilage. As with any puzzle, knowing how to categorize it is crucial. Classifying Chondrosarcoma helps doctors decide on the best treatment.
Primary Vs. Secondary Chondrosarcoma
Chondrosarcoma comes in two key forms, primary and secondary. Primary chondrosarcoma starts in healthy bone or cartilage. It is not caused by any other disease. Secondary chondrosarcoma develops from a pre-existing benign condition or tumor.
Grading System: From Low To High Grade
Doctors use a grading system for Chondrosarcoma. It looks at how cells appear under the microscope. There are three grades: low, intermediate, and high. Low-grade tumors grow slowly. High-grade ones are aggressive and spread faster.
Anatomical Locations And Common Types
Chondrosarcoma can grow in many body parts. Most often, it appears in the pelvis, hip, and shoulder. Different types include:
- Conventional Chondrosarcoma: This is the most common type and affects adults.
- Clear Cell Chondrosarcoma: Often found in the hip and thigh bones of young adults.
- Dedifferentiated Chondrosarcoma: A rare form that is highly aggressive.
- Myxoid Chondrosarcoma: Typically seen in the limbs and more common in men.
Causes And Risk Factors
Understanding what leads to chondrosarcoma can help in early detection and prevention. While the exact causes remain uncertain, research has identified key factors that increase risk.
Genetic Mutations And Hereditary Factors
Genetic factors play a crucial role in chondrosarcoma development. Certain genetic mutations can make people more prone to developing this bone cancer.
- Ollier disease and Maffucci syndrome are genetic disorders linked with higher risk.
- Inherited conditions may predispose individuals to chondrosarcoma.
Environmental And Lifestyle Influences
Lifestyle choices and environmental exposures also contribute as risk factors. However, such influences are less understood.
- Regular exposure to certain chemicals may increase risk.
- Some studies suggest that high doses of radiation might be linked to later chondrosarcoma development.
Pre-existing Conditions And Bone Diseases
Individuals with underlying bone conditions may have an increased risk. This is particularly true for those with diseases that affect bone development or growth.
| Condition | Risk |
|---|---|
| Osteochondroma | Can evolve into chondrosarcoma |
| Paget’s disease of bone | Linked to secondary chondrosarcoma |
| Multiple hereditary exostoses | Potential for malignant transformation |
It’s important to note that having a risk factor does not mean certainty of developing chondrosarcoma. Similarly, without these risk factors, this cancer can still occur.

Credit: orthopedicreviews.openmedicalpublishing.org
Symptoms And Early Detection
Chondrosarcoma is a rare type of bone cancer that can be hard to spot early on. Understanding the symptoms and getting early detection are key to managing this condition. Here’s a look at the signs that may point to chondrosarcoma, as well as the ways doctors can detect it.
Common Signs And When To Seek Medical Attention
If you notice any unusual changes in your body, it’s important to pay attention. Chondrosarcoma often starts with pain in the affected bone. This pain might get worse at night or during activity. Here are some signs that you should take seriously:
- Consistent bone pain that doesn’t go away
- Swelling or a lump near a bone
- Difficulty moving if the tumor is near a joint
These symptoms can also be linked to less serious conditions, but don’t ignore them. If you have persistent pain or swelling, consult a doctor without delay.
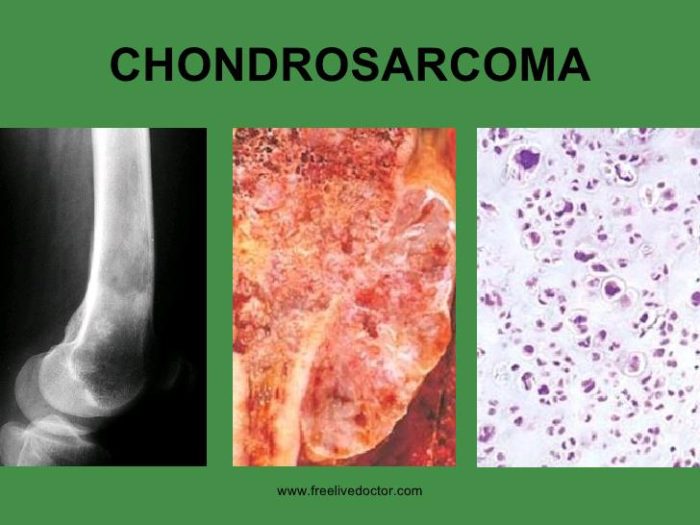
Diagnostic Procedures And Imaging Techniques
Doctors have several ways to look inside your body to check for chondrosarcoma. These include:
- Plain X-rays that show the structure of bones
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for detailed images
- Computerized tomography (CT) scans that combine X-rays from different angles
Biopsies are crucial too. A doctor takes a small sample of tissue to examine under a microscope. This helps confirm if the tumor is chondrosarcoma.
Emerging Biomarkers And Screening Methods
Science is always working to find better ways to detect cancers early. For chondrosarcoma, researchers are studying biomarkers, which are substances that can signal cancer in the body. New methods for screening might include blood tests or advanced genetic testing to identify these markers.
These advances aim to provide earlier and more accurate detection of chondrosarcoma.
Treatment Options For Chondrosarcoma
Dealing with Chondrosarcoma requires a detailed plan tailored to each patient. Different treatments can help take control of the cancer and improve life quality. Let’s explore the treatment options that medical teams often consider for battling Chondrosarcoma.
Surgical Interventions: Methods And Outcomes
Surgery stands as the primary treatment for Chondrosarcoma patients. It involves removing the tumor and some healthy tissue around it. This is to ensure no cancer cells remain.
Limb-sparing surgery is a common method, aiming to remove the cancer while keeping the limb functional. Amputation may be necessary if the tumor is too large or in a complex location.
- Wide Local Excision: Removes the tumor with a margin of healthy tissue.
- Curettage: Scrapes the tumor out of the bone, often with adjuvants like cryotherapy.
Outcomes depend on the tumor’s size, location, and grade. Early-stage tumors often have better outcomes when surgically removed.
Radiation Therapy: Effectiveness And Limitations
Radiation therapy can be useful, particularly when surgery isn’t an option. It uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
Its effectiveness is limited, though. Chondrosarcoma cells are often resistant to radiation. Yet, it can help reduce symptoms or control tumor growth in some cases.
Proton beam therapy is a type of radiation that can be more precise, causing less damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
Chemotherapy And Targeted Treatments
Chondrosarcoma typically doesn’t respond well to chemotherapy. However, it’s still used sometimes, especially for certain types of chondrosarcoma or more advanced stages.
Targeted treatments focus on specific parts of cancer cells or their environment. These treatments can block the growth and spread of cancer cells while limiting damage to normal cells.
- Imatinib: Used for some types of tumors.
- Sirolimus: May be considered in certain advanced cases.
These therapies are part of ongoing research and may offer new hope for those with Chondrosarcoma.
Innovations In Chondrosarcoma Management
The treatment of chondrosarcoma has entered an exciting era. With research propelling forward, patients now have access to more precise and effective therapies. Specialists are using new methods to remove tumors and create medicines. These fresh approaches aim to improve survival rates and the quality of life for those battling chondrosarcoma.
Advances In Surgical Techniques
Surgical experts are adopting advanced techniques to remove chondrosarcoma. These methods help patients recover faster. They also make sure healthy tissue stays safe. Here’s how surgeons are changing the game:
- Minimally invasive surgery uses smaller cuts to reduce healing time.
- precise robotic systems aid surgeons in complex procedures.
- Advanced imaging guides precise tumor removal.
Breakthroughs In Chemotherapy And Drugs
New drugs are underway to fight chondrosarcoma more effectively. These drugs aim to target the cancer cells and spare the normal ones. Let’s investigate these groundbreaking developments:
| Drug Type | Function | Stage of Development |
|---|---|---|
| Targeted Therapies | Attack cancer cells specifically | Clinical trials |
| Immunotherapy | Boost the immune system to fight cancer | Research phase |
Impact Of Precision Medicine And Personalized Treatment
Precision medicine tailors treatment to each patient’s unique cancer. This approach makes sure the treatment is just right for every patient’s situation. Here are the ways precision medicine is changing the scene:
- Genetic testing helps find the specific traits of the tumor.
- Personalized plans are designed based on each patient’s genetic information.
- New technologies track the patient’s progress and adjust treatments as needed.
In summary, chondrosarcoma management is undergoing revolutionary changes that promise better patient outcomes. With surgical advances, innovative drugs, and tailored therapies, hope shines brighter for those facing this disease.
Prognosis And Quality Of Life
When someone receives a chondrosarcoma diagnosis, questions about the future arise. The outcome and life changes depend on many factors. These include tumor size, location, and stage. Let’s explore what patients might expect in terms of survival and day-to-day life.
Survival Rates And Patient Outcomes
Understanding survival rates helps set expectations after a chondrosarcoma diagnosis.
- Localized disease often leads to better outcomes.
- Early detection can improve survival chances.
- Five-year survival rates vary depending on the cancer stage.
For precise numbers, doctors use data from past cases to guide prognosis.
Dealing With Recurrence And Metastasis
Chondrosarcoma can sometimes come back or spread. Patients and doctors work closely to monitor signs of recurrence. Regular check-ups are crucial. If the cancer spreads, or metastasizes, treatment options evolve. This might include surgery, radiation, or new therapies.
Support Systems And Rehabilitation
A strong support network improves quality of life for patients. This network includes:
- Medical professionals familiar with the disease.
- Physical therapists who aid in recovery post-treatment.
- Counselors and support groups for emotional health.
Each person plays a role in helping patients cope and rehabilitate.
Credit: csfshayna.org
Conclusion
Understanding chondrosarcoma is key to battling this rare cancer. Early detection and treatment significantly improve outcomes. Patients should consult oncologists for personalized care plans. Knowledge empowers us to navigate chondrosarcoma’s complexities. Let’s keep seeking advancements in research for hope and healing.

