Canalicular adenoma is a benign salivary gland tumor predominantly affecting older adults. It typically occurs in the upper lips and minor salivary glands.
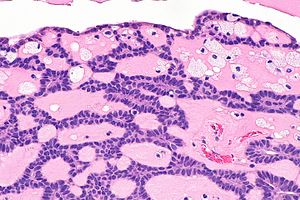
Canalicular adenoma presents as a slow-growing, painless mass that is firm and well-circumscribed. Representing less than 1% of salivary gland neoplasms, this lesion shows a slight female predilection and often surfaces in the seventh decade of life. The tumor is composed of columnar or cuboidal epithelial cells arranged in canaliculi or tubules, fostering its characteristic name.
Surgical excision is the standard treatment, with recurrence being rare post-removal. Though uncommon, awareness and accurate diagnosis are essential, particularly for dentists and oral surgeons, as the symptoms may mimic other conditions. Early detection and management ensure an excellent prognosis for affected individuals.

Credit: www.sciencedirect.com
Introduction To Canalicular Adenoma
The human body is a complex structure, teeming with different types of cells and tissues. Among these, sometimes, unusual growths can occur. These growths, though often benign, can impact our health. One such growth is canalicular adenoma, which notably arises in the salivary glands.
Definition And Overview Of Canalicular Adenoma
A canalicular adenoma is a rare type of benign tumor. It primarily affects the salivary glands, especially the upper lip and buccal mucosa. These tumors are slow-growing and usually non-cancerous. Patients might notice a small, painless lump in the affected area.
Historical Perspective And Discovery
The term canalicular adenoma was first introduced in medical literature many years after the study of salivary gland tumors began. Initial confusion categorized these growths with other salivary gland tumors. But with time and research, canalicular adenomas gained distinct recognition for their unique pathological features.
Epidemiology And Demographics
Despite their rarity, understanding who is more likely to develop a canalicular adenoma is essential. Data shows that these tumors are most common in older adults, with a slight predilection for women. They make up a small percentage of all salivary gland tumors, reinforcing their unusual nature.
| Age Group | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Adults (50+ years) | Most prevalent |
| Women | Slightly more common |
Clinical Presentation Of Canalicular Adenoma
Understanding the clinical presentation of Canalicular Adenoma is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. This benign tumor, often found in the salivary glands, has distinctive characteristics. Awareness of its clinical signs leads to prompt care, reducing potential complications.
Common Symptoms And Disease Onset
Canalicular Adenoma primarily affects older adults. It grows slowly, often without pain. Patients may notice:
- A small, firm lump in the mouth or face
- Sometimes, mild discomfort or interference with eating
Physical Examination Findings
On examination, dentists or doctors may find:
- A movable mass under the lining of the mouth
- Color of the mass matching the surrounding tissue
Typical Sites Of Presentation And Disease Progression
| Site of Presentation | Disease Progression |
|---|---|
| Upper lip and palate | Slow growth with low risk of malignancy |
| Minor salivary glands | Potential for cyst formation |
Diagnostic Evaluation
The journey to diagnose Canalicular Adenoma begins with understanding the condition’s unique characteristics. Proper diagnosis is pivotal, as early detection ensures optimal treatment outcomes. A methodical approach is essential to identify this benign salivary gland tumor accurately.
Imaging Techniques And Role In Diagnosis
Imaging plays a key role in the initial evaluation of salivary gland tumors.
- Ultrasound: Offers a quick glimpse of the mass, aiding in further diagnostic planning.
- CT Scan: Provides detailed images, crucial for surgical planning, if needed.
- MRI: Highlights soft tissue contrasts and boundaries of the tumor, guiding treatment decisions.
Histological Features And Biopsy
Biopsy is the definitive method to diagnose Canalicular Adenoma.
The tumor has a distinctive appearance under the microscope:
- Uniform columnar cells, typically arranged in a cord-like pattern
- Prominent basal cell layer with cells resembling those in the outer layer of the ducts
- Minimal mitotic activity, confirming its benign nature
Fine-needle aspiration or core-needle biopsy may be employed to gather tissue samples.
Differential Diagnoses And Exclusion Criteria
Several conditions can mimic Canalicular Adenoma. Accurate diagnosis requires excluding these possibilities.
| Condition | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Pleomorphic Adenoma | Presence of myxoid or chondroid stroma |
| Basal Cell Adenoma | Trabecular or solid growth pattern |
| Warthin’s Tumor | Oncocytic cells with lymphoid stroma |
| Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma | Perineural invasion and aggressive growth |
A combination of imaging studies, biopsy, and histological examination outlines a clear path to diagnosis.

Credit: en.wikipedia.org
Molecular And Genetic Aspects
Exploring the complex world of Cancericular Adenoma brings us face-to-face with its molecular and genetic intricacies. Uncover the scientific layers behind this rare glandular tumor to comprehend how it forms and progresses at a molecular level.
Genetic Mutations And Cellular Pathogenesis
Genetic mutations play a vital role in the abnormal growth of cells. In canalicular adenomas, specific genetic changes trigger uncontrolled cell division. Investigating these mutations helps us understand the onset of the tumor.
- Alterations in DNA replication
- Malfunctioning genes governing cell cycle
- Disruption in signaling pathways
Molecular Markers And Their Clinical Relevance
Molecular markers in Canalicular Adenoma offer clues about the tumor’s behavior. Identifying these markers aids in diagnosis and treatment planning. Clinicians rely on them to predict patient outcomes and tailor therapies accordingly.
| Marker | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|
| Marker A | Indicates aggressive growth |
| Marker B | Associated with better prognosis |
Hereditary Factors And Risk Assessment
Hereditary factors can increase the risk of developing Canalicular Adenoma. Understanding these elements is crucial for early detection and prevention strategies. Family history impacts risk assessment significantly.
- Evaluation of family health history
- Genetic counseling and testing
- Strategies for risk reduction
Treatment Modalities For Canalicular Adenoma
Canalicular adenoma targets salivary glands. It is often treated successfully. Understanding the options helps in making an informed choice.
Surgical Options And Techniques
Surgery is the mainstay for this adenoma. Various techniques ensure complete removal and minimize recurrence. Let’s explore:
- Excisional Biopsy – Complete tumor removal along with margin of healthy tissue.
- Superficial Parotidectomy – Involves removing part of the parotid gland when affected.
- Intraoral Approach – For tumors in the minor salivary glands, incisions are made inside the mouth.
Radiotherapy And Chemotherapy: Efficacy And Indications
These treatments are secondary options. They may be used when surgery isn’t possible. Here’s a quick overview:
| Therapy Type | Efficacy | Indications |
|---|---|---|
| Radiotherapy | Limited use due to good surgical outcomes | Adjunct to surgery or inoperable cases |
| Chemotherapy | Rarely used | Usually reserved for atypical presentations or metastasis |
Emerging Therapies And Clinical Trials
Research is ongoing in the field. New treatments are under evaluation. Participation in clinical trials is an option. Below are points of interest:
- Targeted therapy trials
- Gene therapy studies
- Immunotherapy investigations
Current trials aim to improve outcomes and reduce recurrence.
Consult with a specialist for the most current treatment options.
Prognosis And Outcomes
The future health of those with Canalicular Adenoma is a key focus. This benign tumor appears in the salivary glands, mostly in older adults. Treatment usually involves surgery with excellent outcomes. Understanding the survival rates, recurrence, and quality of life post-treatment helps patients and families know what to expect.
Survival Rates And Prognostic Factors
Canalicular Adenoma shows high survival rates. The nature of this tumor is non-cancerous. So, most patients recover well. The key factors for a good prognosis include:
- Early detection: Recognizing symptoms promptly can lead to better results.
- Complete removal: Ensuring the tumor is fully removed reduces the risk of return.
- Overall health: Patients in good health tend to have better outcomes.
Recurrence And Management Strategies
Though rare, Canalicular Adenoma can return. To manage this, doctors suggest:
- Regular follow-up visits: to catch and treat any return early.
- Effective surgical techniques: to reduce the likelihood of recurrence.
- Monitoring for symptoms: patients should report new symptoms right away.
Quality Of Life And Long-term Follow-up
After treatment, most lead a normal life. Follow-ups are crucial, even years later. These include:
- Imaging tests: These check for any change in the treated area.
- Physical exams: To assess overall health and detect irregularities.
- Patient support: Access to support groups can help address emotional concerns.
With these strategies, long-term health is often maintained, ensuring a good quality of life post-treatment.
Impact On Patient Life
Canalicular adenoma may not be a household name, but its effects can touch lives deeply. This benign salivary gland tumor, often occurring in the upper lip or buccal mucosa, may alter a patient’s lifestyle considerably. It’s essential to examine these changes to understand the journey of individuals coping with this condition.
Psychological Impact And Counseling
A diagnosis of canalicular adenoma can stir a range of emotions. Patients might grapple with fear, uncertainty, and anxiety. The visible nature of the tumor could also affect self-esteem and body image. Timely psychological support becomes crucial for maintaining mental well-being.
- Guidance from a counselor or psychologist can help manage emotions.
- Techniques like mindfulness and relaxation may reduce stress and anxiety.
- Engaging with peers who understand can provide a sense of community.
Challenges In Daily Living And Adaptation
The physical presence of a tumor can impede daily activities. Swelling or discomfort might make speaking or eating challenging. Adaptation strategies help patients regain control and continue with their daily tasks comfortably.
- Speech therapy to adjust communication techniques if speaking is affected.
- Special dietary adjustments to manage eating difficulties.
- Pain management regimes for relieving discomfort.
Patient Support Groups And Resources
Support systems play a vital role in the healing process. Patient groups create environments where experiences and tips can be shared, offering emotional relief and practical advice.
| Support Type | Resource | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Online Forums | Health Websites | Immediate access to shared wisdom and comfort |
| Local Meetings | Hospital Programs | Personal connection with individuals in similar situations |
| Informational Brochures | Clinic Handouts | Knowledge about the condition and its management |
Prevention And Screening
Understanding how to prevent and detect Canalicular Adenoma early is key. This condition involves benign tumors in the salivary glands. The right strategies reduce risks and foster early treatment. Below, learn about lifestyle choices and screening methods that can make a big difference.
Lifestyle And Environmental Risk Factors
While some factors are beyond control, others can be managed to decrease adenoma risks. Here’s what to consider:
- No use of tobacco products, which harm salivary glands.
- Moderate alcohol intake since excess can increase risk.
- A focus on good oral hygiene to prevent infections.
- Avoidance of excessive sun exposure to the face and neck.
Screening Strategies And Early Detection
Spotting signs of Canalicular Adenoma early gives the best chance for successful treatment. Pay attention to these points:
- Regular self-exams: Feel for unusual lumps around jaw and neck.
- Professional check-ups: Have glands assessed during dental visits.
Use technology to your advantage:
| Technology Type | How It Helps |
|---|---|
| Imaging Tests | Shows detailed gland structure. |
| Biopsies | Confirms nature of suspicious growths. |
Role Of Primary Care And Dentistry In Prevention
Doctors and dentists play a vital role in preventing Canalicular Adenoma. These health professionals should:
- Educate patients about risk factors and self-examination.
- Provide regular oral exams to spot early signs.
- Refer suspicious cases for specialist insight.
Together, we can work towards minimizing the impact of Canalicular Adenoma.
Current Research And Future Directions
The scientific community constantly explores new horizons in the study of Canalicular Adenoma, a benign salivary gland tumor. Significant strides in understanding and treating this condition offer hope for patients. In this section, discover the cutting-edge research fueling advancements and the potential that the future holds.
Advancements In Molecular Biology And Genetics
At the heart of modern medicine lies molecular biology and genetics. These fields are key to unveiling the intricacies of Canalicular Adenoma.
- Identifying genetic markers aids in early diagnosis.
- Exploring genetic mutations gives insight into the disease’s progression.
Innovations In Treatment Approaches
Revolutionary treatment methods raise the bar for patient care.
- Minimally invasive surgery presents fewer risks and quicker recovery times.
- Targeted therapy focuses on specific cellular processes for efficient treatment.
Future Research Areas And Potential Breakthroughs
Focused investigations aim to propel the field forward. Exciting potential breakthroughs loom on the horizon.
| Research Area | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Immunotherapy trials | Improved patient outcomes |
| Salivary gland regeneration | Enhanced recovery post-treatment |
Credit: librepathology.org
Conclusion
Understanding canalicular adenoma is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment. This rare benign tumor, primarily affecting older adults, can be managed effectively with early intervention. By staying informed about its symptoms and treatment options, patients can ensure better outcomes. Remember, regular dental check-ups play a key role in detection and health maintenance.

