Basal cell carcinoma of the salivary gland is an extremely rare form of cancer. It originates from the basal cells in the salivary gland epithelium.
Basal cell carcinoma traditionally affects the skin, particularly areas exposed to the sun. Its occurrence in the salivary gland represents a unique and unusual presentation, attracting attention from medical professionals due to its rarity. Patients diagnosed with this type of carcinoma may experience symptoms like a painless mass or swelling in the mouth or face.
Early detection is crucial for effective treatment, which may involve surgery, radiation therapy, or a combination of both. Understanding this form of cancer is essential for those in the medical community and individuals at risk, with research ongoing to uncover more about its behavior and optimal management strategies. As awareness grows, so does the potential for improved patient outcomes and survival rates.

Credit: commons.wikimedia.org
Introduction To Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Salivary Gland
Welcome to a vital discussion on a rare but serious health condition: Basal Cell Carcinoma of Salivary Gland. Our goal is to shed light on what this disease is, how it impacts patients, and why understanding it is crucial.
Overview Of Salivary Gland Tumors
Salivary glands produce saliva, vital for digesting food. Tumors in these glands are uncommon and can be benign or malignant. Malignant tumors may spread and require immediate attention. Let’s explore their specifics:
- Salivary Gland Location: Major glands include the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands.
- Types of Tumors: Most tumors arise in the parotid gland, with varying degrees of aggression.
- Treatment Approaches: Options range from surgery to radiation, depending on the tumor’s nature.
Defining Basal Cell Carcinoma In Salivary Glands
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) in salivary glands is a rare form of cancer. It stems from basal cells in the gland’s epithelium. Unlike skin BCC, it manifests within the gland, leading to unique challenges:
- Identifying signs like a lump or pain.
- Undergoing thorough diagnosis through biopsies.
- Discussing treatment plans with oncologists.
Epidemiology And Significance Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
BCC of the salivary gland is rare and underrepresented in cancer research. It represents a small fraction of salivary gland malignancies. Awareness is critical:
| Age Group | Incidence |
|---|---|
| Adults | Primarily affects older adults |
| Kids | Extremely rare in children |
Due to its rarity, BCC of the salivary gland is not well-known, stressing the need for understanding its behavior and treatment.
Etiology And Risk Factors
Understanding Basal Cell Carcinoma of Salivary Gland’s origins and associated risks is crucial for early detection and prevention. This type of cancer remains rare but is no less serious, making knowledge of its causes and risk factors vital.
Genetic Predispositions And Mutations
In exploring the roots of Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Salivary Gland, genetic predispositions stand out. Certain genes can make individuals more susceptible to developing this illness.
- Mutations in PTCH1, a tumor suppressor gene, are often implicated.
- Gorlin syndrome or nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome, linked to genetic mutations, increases risk.
Environmental And Lifestyle Influences
Environmental factors also play a role in the emergence of Basal Cell Carcinoma within the salivary glands. Lifestyle choices can either contribute to or mitigate these risks.
- Excessive sun exposure can cause skin damage, influencing salivary gland health.
- Smoking has been shown to increase the risk of numerous cancers, including salivary gland tumors.
Understanding Risk Factors Specific To Salivary Glands
The salivary glands have unique aspects making them particularly susceptible to Basal Cell Carcinoma.
| Specific Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Previous Radiation Therapy | Past treatments involving radiation may elevate the risk of tumor development in salivary glands. |
| Industrial Workplace Exposure | Certain industrial chemicals have been linked to higher incidence of salivary gland neoplasms. |
Pathophysiology And Disease Progression
Understanding how Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) of the Salivary Gland develops is essential. The disease starts at the cellular level before it progresses. Let’s explore the pathophysiology and disease progression of BCC of the Salivary Gland.
Cells in the salivary gland can turn cancerous due to DNA damage. This damage may be from sunlight, radiation, or genetic factors. When damaged cells multiply without control, they form a tumor.
- Abnormal Cell Growth: Mutations in DNA cause cells to grow faster than normal.
- Basal Cells: These cells line the salivary gland ducts and can become malignant.
- Tumor Formation: As these abnormal cells cluster, they form a small bump or growth.
BCC typically grows slowly. It has different stages based on size, depth, and spread. Here are the usual stages:
- Stage 0: Cancer cells are only in the outer layer of the skin.
- Stage I: The tumor has grown but is still under 2 centimeters.
- Stage II: The tumor is larger than 2 centimeters.
- Advanced Stages: Cancer may have spread deeper into tissues or bones.
BCC rarely spreads to other parts of the body. However, if it does, it is more serious.
- Local Spread:
- Tumor may grow into nearby areas such as ear canal or facial nerves.
- Regional Spread:
- Cancer might move to nearby lymph nodes.
- Distant Spread:
- Though uncommon, BCC can spread to lungs or bones.
Regular check-ups are vital for early detection and treatment of BCC.
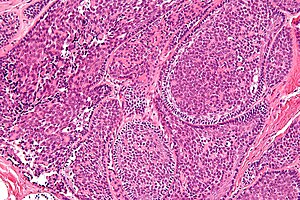
Credit: librepathology.org
Clinical Presentation And Diagnosis
Understanding Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) of the salivary gland begins with noting its clinical features. Recognizing symptoms and conducting accurate diagnostic tests is crucial. It leads to early intervention which can improve outcomes significantly.
Symptoms And Early Warning Signs
Familiarity with BCC signs helps in timely medical attention. Look for:
- Painless lump in mouth, face, or neck area
- Skin changes over the lump, like ulceration or color change
- Difficulty in swallowing or moving the jaw
- Numbness or weakness in the facial region
Diagnostic Methods: Imaging And Biopsy
Identifying BCC accurately involves two key steps:
- Imaging Tests: CT scans or MRIs visualize the lump.
- Biopsy: A small tissue sample confirms cancer.
Differential Diagnosis And Exclusion Of Other Conditions
Doctors rule out similar conditions to confirm BCC. This includes:
- Benign Salivary Gland Tumors: Non-cancerous growths.
- Other Skin Cancers: Such as squamous cell carcinoma.
- Non-Cancerous Skin Conditions: Cysts or skin tags.
Treatment Options
When faced with basal cell carcinoma (BCC) of the salivary gland, patients have several treatment avenues to consider. Careful planning can lead to effective management of the condition. Explore the latest surgical methods, the role of radiation and chemotherapy, and promising new therapies entering the medical field. A comprehensive approach can mean improved outcomes and better quality of life for those affected by BCC of the salivary gland.
Surgical Interventions And Approaches
- Wide local excision removes the tumor along with some healthy tissue.
- Parotidectomy targets tumors in the parotid salivary gland.
- Neck dissection may be necessary if cancer has spread.
- Reconstructive surgery helps restore appearance and function.
Each case of BCC requires a tailored surgical plan. The goal is to remove the cancer while sparing healthy tissue.
Role Of Radiation And Chemotherapy
- Radiation often follows surgery to kill remaining cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy is less common but used in advanced cases.
Post-operative radiation can prevent cancer recurrence. Chemotherapy may be used where cancer has metastasized.
Emerging Therapies And Clinical Trials
- Targeted therapy focuses on specific genetic markers of cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy enlists the body’s own immune system to fight cancer.
- Clinical trials offer access to groundbreaking new treatments.
Innovative treatments and trials continue to advance, offering hope for more effective management and potential cures for BCC of the salivary gland.
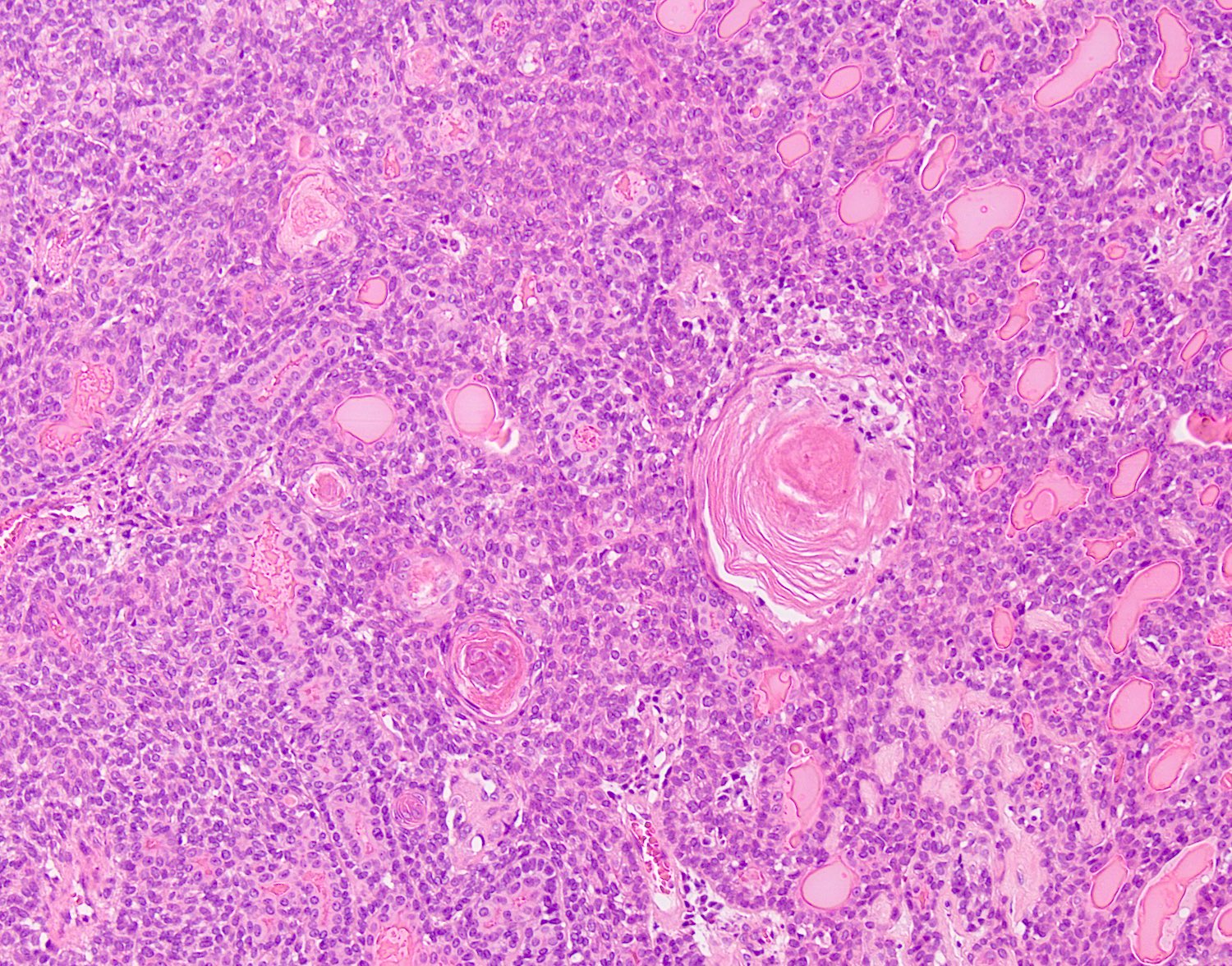
Credit: www.pathologyoutlines.com
Prognosis And Survival Rates
Understanding the prognosis and survival rates of Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) of the Salivary Gland helps patients and their families prepare for treatment outcomes. This section delves into the various factors affecting prognosis, statistical survival analyses post-treatment, and the impacts on long-term quality of life.
Factors Influencing Prognosis
Several factors determine the prognosis for patients with Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Salivary Gland:
- Stage of Cancer: Early detection often leads to better outcomes.
- Tumor Size: Smaller tumors generally have a higher success rate for treatment.
- Location: Tumors in accessible areas are easier to treat effectively.
- Metastasis: Cancer that has spread poses more challenges for positive prognosis.
- Overall Health: Good health contributes to a patient’s recovery abilities.
- Treatment Response: How well the cancer responds to therapy affects survival.
Statistical Analysis Of Survival Following Treatment
Survival rates post-treatment provide a quantitative measure of treatment success:
| Treatment Success | 5-Year Survival Rate |
|---|---|
| Complete Removal | 90-100% |
| Partial Removal | 70-85% |
| Recurrent Cases | 50-60% |
Note that individual circumstances can significantly affect these numbers.
Long-term Outcomes And Quality Of Life
Surviving cancer is one phase of a journey.
Long-term quality of life depends on:
- Effectiveness of initial treatment.
- Management of potential recurrences.
- Addressing any treatment-related side effects.
- Regular check-ups for vigilance.
Patient support systems and rehabilitation play crucial roles in enhancing life post-treatment.
Prevention And Early Detection
Prevention and Early Detection play a pivotal role in managing Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) of the Salivary Gland. This rare form of cancer requires awareness and proactive steps. Understanding and implementing precautionary measures significantly reduce risks. Early identification of symptoms promotes better outcomes. Let’s delve into how regular screenings, lifestyle changes, and modern detection methods can make a difference.
Importance Of Regular Screening
Screening plays a crucial role in detecting BCC at its onset. Regular checks allow health professionals to spot abnormalities early. Early intervention often leads to more effective treatment. Experts suggest annual screenings for individuals with risk factors.
Lifestyle Modifications And Preventive Measures
Adopting healthy habits lowers the chances of developing BCC. Key lifestyle changes include:
- Avoiding excessive sun exposure.
- Using sunscreen with high SPF.
- Wearing protective clothing outdoors.
- Maintaining a nutrient-rich diet.
- Avoiding tobacco and reducing alcohol consumption.
These practices form a robust defense against BCC development.
Advancements In Early Detection Techniques
Medical advancements enhance BCC detection. Cutting-edge techniques include:
- High-resolution ultrasound.
- Digital imaging and biopsy.
- Molecular testing for genetic indicators.
New technologies allow for precise and non-invasive detection methods. They significantly boost early diagnosis rates.
Conclusion
Understanding basal cell carcinoma of the salivary gland is vital to early detection and treatment. This rare condition demands prompt medical attention. By recognizing symptoms and seeking professional advice, one can significantly reduce potential health complications. Stay informed, be vigilant about changes in your health, and always consult with your healthcare provider for the best outcomes.

