Gum infection, or gingivitis, is often caused by poor dental hygiene which allows plaque to build up and harden. Early treatment typically includes professional cleaning and improved oral care practices.
Gum disease is a common condition that can lead to significant oral health issues if left untreated. The symptoms, ranging from mild redness and swelling to severe inflammation and tooth loss, are indicators that your gums require attention. A gum infection develops due to the accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria.
Regular brushing and flossing can remove plaque, but without proper oral hygiene, it turns into tartar, a harder substance that professional cleaning can tackle. Early intervention is key, as progressing to periodontitis can result in more invasive treatments and increased risk of health complications. Dental professionals usually perform thorough cleanings and might prescribe antibiotic treatments. Emphasis on daily dental care and routine check-ups cannot be overstated for preventing gum infections and maintaining overall oral health.
Understanding Gum Infections: An Overview
Understanding Gum Infections: An Overview begins with recognizing the significance of healthy gums. These soft tissues play a crucial role in oral health, but when infected, they can lead to discomfort and severe dental issues. This article delves into the anatomy, defines common infections, and explores their prevalence and impact.
The Anatomy Of Gums And Their Role In Oral Health
Also known as gingiva, gums are the protective pink tissues that surround your teeth and bone. They form a tight seal around your teeth to support the bones and provide a barrier against bacteria. Maintaining their health is vital, as they are not only the foundation for your teeth but also prevent disease-causing microorganisms from entering the body.
Defining Gum Infection: Gingivitis Vs. Periodontitis
Gum infections, often seen as swollen or bleeding gums, come in two main types: gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis is the early stage where gums become red and inflamed. It is often reversible with good oral hygiene. Periodontitis, however, is more severe. It occurs when untreated gingivitis spreads below the gum line, which can damage soft tissues and destroy the bone that supports your teeth.
The Prevalence And Impact Of Gum Diseases
- Gum diseases are extremely common and can affect anyone at any stage of life.
- They not only lead to tooth loss but are also linked to other health issues, such as heart disease and diabetes.
- The impact extends beyond oral health, affecting overall well-being and quality of life.
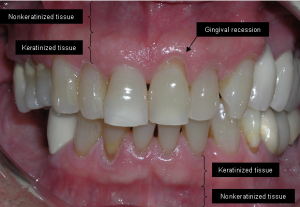
Credit: www.emergencydentistsusa.com
Identifying The Causes Of Gum Infection
Gum infection, also known as gingivitis, can lead to serious dental issues. Understanding the causes is the first step to prevention and treatment. Below we explore the key contributors to gum disease.
The Role Of Bacteria In Developing Gum Diseases
Bacteria in our mouths can form plaque, a sticky film on teeth. If not removed, plaque can cause infections harming gums and bones.
- Daily brushing removes plaque.
- Flossing cleans between the teeth.
- Regular dentist visits keep plaque in check.
Consequences Of Poor Oral Hygiene Practices
Neglecting oral hygiene can result in tartar build-up. Tartar is hardened plaque that only a professional cleaning can remove.
| Action | Effect on Gums |
|---|---|
| Sporadic brushing | Allows plaque development |
| Irregular flossing | Misses hidden plaque |
Lifestyle Factors That Increase Gum Infection Risk
Diet and habits play a part in oral health.
- Smoking impairs gum healing.
- Sugary foods feed harmful mouth bacteria.
- Stress weakens the immune system’s response.
Symptoms And Diagnosis Of Gum Infection
A gum infection, known as periodontal disease, can be silent, but there are key signs you should not ignore. Let’s explore the symptoms that signal a gum infection and understand how dental professionals diagnose this dental issue.
Recognizing The Signs Of Gum Infection
Gum infections come with noticeable symptoms. Be on the lookout for:
- Red, swollen gums: They might feel tender.
- Bleeding: Your gums may bleed during brushing or flossing.
- Bad breath: Persistent unpleasant breath or a bad taste in your mouth can be a clue.
- Receding gums: Gums pulling away from the teeth make your teeth look longer.
When To Seek Professional Diagnosis
Don’t wait to see your dentist if you notice symptoms. Early treatment can save your teeth and your smile. If bleeding, swelling, or pain in your gums persists, make an appointment with your dentist right away.
The Process Of Diagnosing Gum Disease By Dental Professionals
Dentists have a specific process to diagnose gum disease, which includes:
- Reviewing medical history to identify conditions or factors that may contribute to symptoms.
- Examining your gums for signs of inflammation.
- Measuring the depth of the grooves between your gums and teeth.
- Taking dental X-rays to check for bone loss in areas where your dentist observes deeper pocket depths.
Remember, successful treatment starts with an accurate diagnosis, so it’s crucial to follow these steps with a dental professional.

Credit: auroradentalgroup.com
Preventive Measures Against Gum Infection
Gum infection, also known as periodontal disease, can lead to serious dental issues. But, it is preventable. Understanding and adopting proper measures can keep gums healthy. Let’s explore how to stop gum disease before it starts.
Effective Oral Hygiene Practices To Prevent Gum Disease
Brushing teeth twice a day is crucial for removing plaque. Use a fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled brush. Reach all areas, especially the gum line.
Flossing daily helps get rid of hidden food particles and plaque between teeth.
- Use about 18 inches of floss.
- Wrap most around your middle fingers.
- Hold tight and glide gently up and down between teeth.
Don’t forget to replace your toothbrush every three to four months, or sooner if bristles are frayed.
Consider an antiseptic mouthwash to help kill bacteria and clean hard-to-brush areas.
The Role Of Diet And Nutrition In Gum Health
The right nutrients keep gums fit. Calcium and vitamin C are gum superstars. Stick to a balanced diet filled with fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
Avoid sugary snacks and drinks, as they increase the risk of plaque and bacteria.
Stay hydrated. Drinking water helps wash away food particles and keeps your mouth moist.
Regular Dental Check-ups And Cleanings
Schedule visits to the dentist every six months. Professionals can spot early signs of gum disease.
During check-ups, dentists remove tartar—the hardened plaque that brushing and flossing can’t clear.
They also give personalized tips to improve your oral hygiene routine.
Professional Treatment Options For Gum Infection
When your gums ache or bleed, you could be facing a gum infection. This can be scary. But fear not! Doctors have many ways to make your gums healthy again. Let’s talk about how experts can fix your gum woes.
Non-surgical Treatments For Early Stage Gum Disease
Caught early, gum disease is easier to treat. No need for surgery. Cleanings and special treatments can do the job.
- Scaling: A deep clean under the gums to remove bad stuff.
- Root Planing: Smoothing out the teeth roots to help gums stick to teeth.
- Antimicrobial Agents: Special medicines put below the gums to kill germs. Comes as gels, fibers, or strips.
Surgical Interventions For Advanced Periodontitis
When gum disease is big, you might need surgery. Don’t worry. This helps stop damage and saves teeth.
- Flap Surgery: They lift the gums up, get rid of tartar, then put gums back so they’re tight around the teeth.
- Grafts: If gums or bone are gone, they can add new material to fix it.
- Guided Tissue Regeneration: This helps your own body make new bone and tissue where it’s needed.
Emerging Technologies And Treatments In Periodontics
New tech makes treating gum disease exciting. These options are getting more popular and can really help. Check them out:
| Technology/Treatment | Benefits |
| Laser Therapy | Less pain, faster healing. |
| Local Antimicrobial Therapy | Targets germs right at the sick spot. |
| Host Modulation | Helps your body fight the infection better. |
Home Remedies And Natural Treatments For Gum Infections
Gum infections can cause discomfort and lead to serious dental issues if left untreated. However, alongside professional dental care, certain home remedies can aid in alleviating symptoms and promote gum health. This section explores natural remedies supported by evidence, ensuring the safety and effectiveness of these treatments, and how they can complement professional dental care.
Evidence-based Natural Remedies For Gum Health
Gum health is vital for overall wellness. Here are some natural remedies supported by scientific research:
- Saltwater Rinse: Reduces inflammation and kills bacteria.
- Tea Tree Oil: Natural antiseptic that fights bacterial growth.
- Aloe Vera: Soothes gum inflammation and accelerates healing.
- Coconut Oil Pulling: May reduce plaque and gingivitis risk.
The Efficacy And Safety Of Home Remedies
Understanding the safety and effectiveness of home remedies is crucial. Use them wisely:
| Remedy | Efficacy | Safety |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Pulling | Good for reducing plaque | Safe if not swallowed |
| Tea Tree Oil | Antibacterial properties | Dilute before use |
| Honey | May aid in healing wounds | Do not apply if allergic |
Integrating Natural Treatments With Professional Care
For optimal results, combine home remedies with dentist recommendations:
- Consult a dentist before starting any home treatment.
- Use natural remedies as complementary therapies.
- Schedule regular dental check-ups.
Long-term Management And Recovery From Gum Infection
The journey to recovery after battling a gum infection is crucial. Proper long-term management ensures not only the restoration of oral health but also the prevention of future complications. Knowing the recovery process, maintaining oral health, and preventing potential complications are keys to successful long-term outcomes.
Recovery Process And Timeframe Post Treatment
Healing times can vary based on the severity of the infection and the treatment received. Here’s a general overview:
- 1-2 weeks: Gums heal from non-surgical treatments.
- 1 month: Reevaluation of gum health post-surgery.
- 3-6 months: Gums fully heal; continued care needed.
Follow-up visits are important for monitoring recovery and ensuring the treatment’s success.
Maintaining Oral Health After Gum Disease Treatment
Post-treatment oral hygiene is critical. Stick to these steps to keep gums healthy:
| Daily Habits | Professional Care |
|---|---|
|
|
Potential Complications And Recurrence Prevention
Be vigilant to avoid complications or a return of infection:
- Attend all scheduled follow-ups.
- Quit smoking, as it hinders recovery.
- Control diabetes; it affects gum health.
- Report any signs of infection immediately.
Educate yourself about signs of gum disease, and take action early to prevent recurrence.
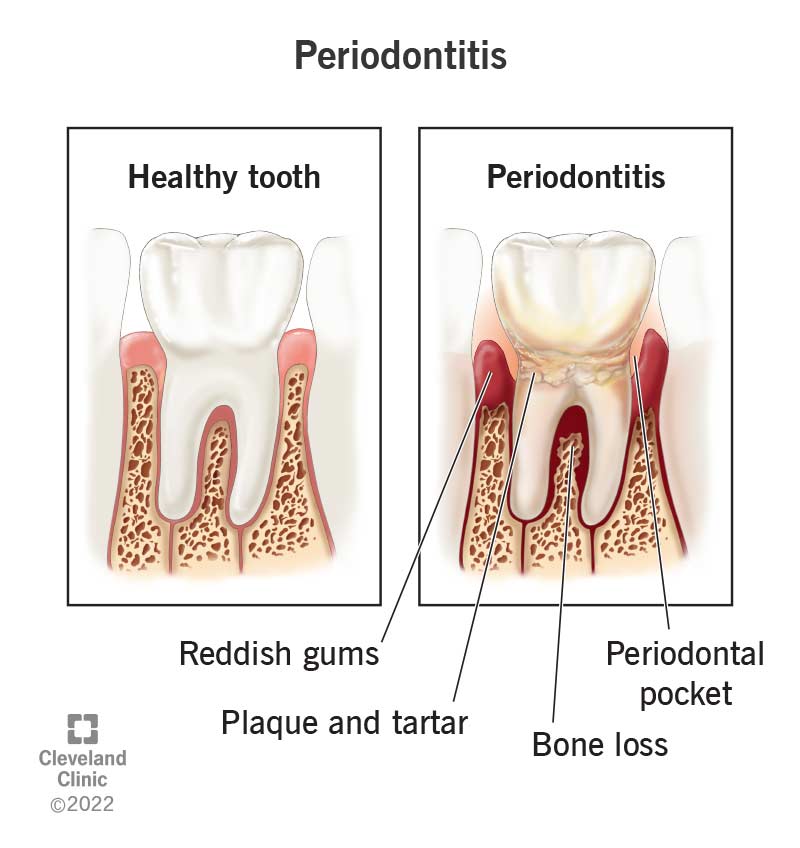
Credit: my.clevelandclinic.org
Conclusion
Understanding gum infection causes and treatments is essential for maintaining oral health. Prompt intervention can prevent progression and safeguard your smile. Embrace daily hygiene and regular dental check-ups. Should symptoms arise, seek professional care immediately. Protect your gums to ensure lasting dental wellness.

