Trismus, commonly known as “lockjaw,” is a condition characterized by the inability to fully open the mouth. It can result from various medical and dental issues.
Experiencing restricted jaw movement can be concerning and uncomfortable. Trismus may arise due to complications from dental procedures, trauma, infections, or associated with conditions like tetanus or TMJ disorders. Nevertheless, pinpointing the exact cause is crucial for effective treatment. Early recognition and management of trismus help in preventing further complications and facilitating a smoother recovery process.
It’s essential for individuals to seek prompt medical advice upon noticing limitations in jaw mobility to address the underlying issue. Accurate diagnosis often involves a combination of physical examinations and imaging studies, guiding appropriate therapeutic interventions.

Credit: together.stjude.org
Understanding Trismus
Imagine not being able to open your mouth wide enough to eat your favorite sandwich. This is what trismus, often known as “lockjaw”, feels like. It affects many people and stops them from doing simple things like talking, eating, and sometimes breathing. Let’s explore what trismus is all about.
Defining Trismus: Origins And Symptoms
Trismus is a medical condition. It limits how far you can open your mouth. The main cause is often muscle spasms. Other times, it comes from an infection, surgery, or radiation therapy. Look below to see the common signs of trismus:
- Jaw pain when opening or closing your mouth.
- Difficulty with eating or speaking.
- A feeling of stiffness in the jaw muscles.
- Limited movement of the mouth.
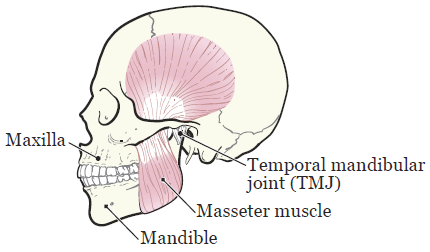
Anatomical Overview: The Mechanics Of Jaw Movement
The jaw moves smoothly thanks to several parts working together. Muscles, bones, and joints all play a part. Here’s a simple breakdown:
| Part | Role in Jaw Movement |
|---|---|
| Temporalis and Masseter Muscles | Help in closing the jaw. |
| Pterygoid Muscles | Aid in opening and moving the jaw side-to-side. |
| Mandible (Lower Jaw) | The bone that moves to open and close the mouth. |
| Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) | Acts like a hinge and a sliding track. |
Trismus involves these parts not working right. Sometimes the muscles are too tight, or the joint is not moving smoothly. This can cause sharp pain and make it hard to chew or talk.
Causes Of Trismus
Understanding the various causes of Trismus is crucial for both prevention and treatment. Also known as “lockjaw,” Trismus refers to the difficulty or inability to open the mouth widely. This condition affects a person’s ability to eat, speak, and maintain oral hygiene. Different triggers can lead to the development of Trismus. Let’s explore them in detail.
Oral Health And Trismus: The Role Of Dental Issues
Good oral health is key to avoiding Trismus. Poor dental hygiene, impacted wisdom teeth, and severe tooth decay can lead to infections. These infections may stiffen the jaw muscles. Dental procedures, like tooth extractions, can also contribute to the condition. It is essential to follow dentist guidelines closely to prevent complications.
Impact Of Trauma And Surgery On Jaw Mobility
Physical injuries to the face or jaw can result in Trismus. Such traumas might cause inflammation, muscle damage, or disruption of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). Jaw surgeries, especially corrective ones, often lead to temporary Trismus. Exercises and rehabilitation are necessary for restoring jaw movement after these events.
Infections Leading To Trismus: From Local To Systemic
- Tetanus: A bacterial infection causing severe muscle spasms.
- Peritonsillar abscess: Pus-filled swelling near the tonsils.
- Odontogenic infections: Originating from the teeth or its surrounding tissues.
- Systemic infections: Such as mumps, that can affect the jaw muscles
Infections can lock the jaw by inflaming the muscles or the TMJ. Treating the underlying infection is often the first step to relieve Trismus.
Trismus In Oncology: Effects Of Radiation And Chemotherapy
Cancer treatments impact the body in numerous ways. Both radiation and chemotherapy can cause scarring and inflammation of the jaw muscles and tissues. This complication can severely restrict jaw mobility. Patients undergoing head and neck cancer treatments are at a higher risk of developing Trismus. Coordinated care between oncologists and physical therapists can help manage symptoms.
Diagnosis Of Trismus
Facing the challenge of a stiff jaw? Known as Trismus, this condition often points towards an underlying dental or medical issue. Symptoms include restricted jaw movement and difficulty with everyday activities like talking or eating. To pinpoint the cause and tailor the most effective treatment, a thorough diagnosis is crucial. Medical experts employ several methods to diagnose Trismus accurately.
Clinical Examination: Assessing Jaw Motion
During a physical assessment, the focus is on measuring the range of jaw movement. Health professionals look for signs of discomfort or pain during jaw motion. Evaluating these dynamics is key for a Trismus diagnosis. Specialists may utilize tools like a gnathometer to quantify jaw opening.
| Jaw Motion | Normal Range | Trismus Range |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Opening | > 35mm | <= 35mm |
| Lateral Movement | > 7mm | Reduced |
Imaging Techniques: X-rays And Mris In Identifying Trismus
Imaging plays a pivotal role in revealing the bones and soft tissues contributing to Trismus. X-rays provide a picture of the jaw’s skeletal structure highlighting abnormalities. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) goes deeper, offering details on soft tissues like muscles and ligaments.
- X-rays: Uncover bone damage, joint dislocation, or tumors.
- MRI: Detect inflammation, tissue scarring or entrapment.
Role Of Patient History In Diagnosing Jaw Disorders
Understanding a patient’s medical past is critical for identifying Trismus causes. Clinicians enquire about prior surgeries, infections, jaw trauma, or radiation treatment. Equally important is the patient’s oral health history, such as past tooth extractions or oral surgeries. Patient accounts concerning the onset and duration of symptoms contribute vital clues.
- Timeframe of symptoms
- Prior health incidents
- Previous dental procedures
Credit: www.mskcc.org
Treatment Strategies For Trismus
Trismus, commonly known as “lockjaw”, restricts jaw movement. Effective treatment strategies often combine various methods tailored to individual needs. Below, explore proven treatments helping patients regain jaw mobility and enhance quality of life.
Physical Therapy: Exercises And Devices
Physical therapy plays a central role in trismus treatment. Regular jaw exercises increase flexibility and strength. Therapists may recommend:
- Stretching exercises to improve jaw opening.
- Strengthening exercises to enhance muscle function.
- Mobility exercises to maintain joint motion.
Using therapeutic devices can also aid treatment. These might include:
- Dynamic bite splints for guided movement.
- Jaw motion rehabilitation systems for structured exercise.
- Therapeutic putty for resistance training.
Pharmacological Approaches: Medications And Pain Relief
Pharmacological treatments address pain and inflammation. Commonly prescribed medications include:
| Medication Type | Usage |
|---|---|
| Anti-inflammatories | Reduce swelling and pain. |
| Muscle relaxants | Ease muscle tightness. |
| Analgesics | Provide pain relief. |
For severe pain, stronger medications such as opioids may be considered with caution due to potential dependency risks.
Surgical Interventions: When Non-invasive Treatments Fail
Surgery is a last resort when other treatments don’t suffice. Surgical options include:
- Arthroscopy to remove scar tissue.
- Joint replacement for damaged jaw joints.
- Myotomy to cut affected muscles.
Patient-specific factors determine the need for surgery. Surgery aims for long-term jaw function restoration.
Complications And Management Of Chronic Trismus
Chronic trismus, often known as lockjaw, creates more than just discomfort. The inability to open the mouth widely affects eating, speaking, and daily activities. Proper management is key to mitigating its complications which range from nutritional deficits to social distress.
Nutritional Challenges And Diet Modification
Eating with chronic trismus proves challenging. The restricted mouth opening limits food intake, potentially leading to nutritional deficiencies. A key strategy involves diet modification. Here’s how:
- Opt for soft or liquid foods that require minimal chewing.
- Use nutrient-dense supplements to maintain a balanced diet.
- Seek help from a nutritionist for personalized meal planning.
Psychosocial Impacts: Dealing With Communication And Aesthetics
The psychological effects of chronic trismus are significant. Communication barriers can lead to social isolation. Here are ways to mitigate these impacts:
- Utilize alternative communication methods like writing or speech apps.
- Participate in therapy for emotional support and coping strategies.
- Engage in facial exercises to improve muscle function and aesthetics.
Long-term Treatment Plans For Persistent Cases
Persistent trismus often requires a long-term treatment strategy. This includes a mix of therapies and interventions:
| Therapy | Objective |
|---|---|
| Physical Therapy | Improve jaw mobility |
| Medications | Manage pain and inflammation |
| Surgery | Correct structural abnormalities |
Consistency in these treatments is crucial for enhancing mouth mobility and quality of life.
Preventing Trismus
Preventing Trismus involves understanding and addressing potential risk factors.
Early detection and preventive strategies play key roles in avoiding this painful condition.
Preventive Measures In Dental And Surgical Procedures
Dental and surgical interventions can sometimes lead to Trismus. Practitioners take special care during these procedures to prevent it.
- Gentle techniques reduce tissue trauma.
- Minimizing tissue inflammation helps maintain jaw mobility.
- Using post-procedure exercises aids in preserving jaw function.
Lifestyle Adaptations To Minimize Risks
Making simple changes in daily habits can shield you from Trismus.
| Lifestyle Aspect | Adaptations |
|---|---|
| Chewing Habits | Opt for soft foods; chew slowly. |
| Hydration | Drink plenty of water. |
| Stress Management | Practice relaxation techniques. |
Early Intervention And The Importance Of Regular Check-ups
- Recognize symptoms early.
- Seek prompt medical attention.
- Regular dental visits can spot issues early on.
Regular screenings by a professional help prevent complications.
Patient Education And Support
Understanding Trismus, or lockjaw, is crucial for those affected. Strong patient education and support can ease the journey. Reliable resources guide through treatment while support groups foster community strength. Together, these pave the way to better management and quality of life.
Guiding Patients: Resources And Information Dissemination
Educational materials are key in helping patients grasp Trismus. Clinics offer pamphlets outlining symptoms, causes, and treatments. Online platforms provide up-to-date research and practical advice.
- Websites: Authoritative health sites share comprehensive details.
- Videos: Visual aids demonstrate exercises that can help.
- Apps: Track progress and set reminders for medication and exercises.
| Resource Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Pamphlets | Easy to understand; Accessible anytime |
| Online Articles | Comprehensive; Constantly updated |
| Interactive Tools | Personalized; Engaging |
Support Groups: Sharing Experiences And Strategies
Support groups unite patients. They exchange strategies to cope with Trismus. This interaction is a safe space to share feelings and breakthroughs. Emotional support complements medical treatment and propels healing. Both online forums and local meet-ups serve this purpose.
- Online communities: Connect with others from home.
- Regular meetings: Face-to-face interaction and empathy.
- Wellness workshops: Experts teach and discuss coping mechanisms.
Patient experiences provide real-life context to Trismus. These stories inspire and guide new patients on their path to recovery. They encourage continued education and engagement with available resources.
Research And Future Directions In Trismus Treatment
Trismus, often known as “lockjaw,” causes significant discomfort and difficulty in jaw movement. Patients and clinicians alike search for better solutions. Ongoing research introduces exciting possibilities and aims to enhance treatment efficacy.
Advancements In Medical Technology And Treatment Modalities
Recent years have witnessed groundbreaking advancements:
- Personalized physical therapy programs now adapt to individual needs.
- Robot-assisted interventions promise precision and consistency in rehabilitation.
- Novel drug therapies focus on muscle relaxation and pain reduction.
Enhanced imaging techniques, such as MRI and ultrasound, facilitate accurate diagnosis and therapy planning.
Exploring New Horizons: The Potential Of Stem Cell Therapy And Regenerative Medicine
The field of regenerative medicine offers hope:
- Stem cell therapy could regenerate damaged tissues in the jaw.
- Research focuses on restoring muscle function and alleviating pain.
- Clinical trials are crucial in determining the safety and efficacy of these treatments.
Advancements in this area may soon lead to breakthroughs that transform trismus treatment.
Conclusion: Living With Trismus
Many people face the challenge of living with Trismus. This condition can affect daily life. But with the right approach, it can be managed. Let’s explore how to cope and what to expect in the future.
Summary Of Trismus Management
Effective management is key for anyone with Trismus. The goal is to improve mouth opening. Here’s a quick look at essential management steps:
- Exercises: Mouth-opening exercises help stretch muscles.
- Tools: Devices like ‘jaw stretchers’ or ‘stacked tongue depressors’ assist in increasing jaw mobility.
- Medication: Pain killers and muscle relaxants might be used to reduce discomfort.
- Therapy: Physical therapy can strengthen and relax jaw muscles.
- Regular check-ups: These ensure progress is tracked.
The Journey Ahead: Prognosis And Health Outcomes For Trismus Patients
The outlook for Trismus patients often varies. Some key points include:
| Factors | Impact |
|---|---|
| Early diagnosis | Better outcomes |
| Consistent management | Improved jaw function |
| Professional guidance | Custom care plan |
| Emotional support | Reduced stress and better coping |
Remember, staying positive is crucial. Stay engaged with your support system and health care team. They will help you through this journey.

Credit: www.emdocs.net
Conclusion
Wrapping up our discussion on trismus, remember it’s treatable. Early diagnosis and consistent therapy are key. For ongoing support, consult healthcare professionals, and don’t neglect prescribed exercises. Managing trismus effectively can restore comfort and quality of life. Stay proactive and informed on your journey to recovery.

