Bruxism is a condition characterized by the involuntary grinding or clenching of teeth. It can occur during the day or night, often without the individual being aware.
Bruxism, commonly known as teeth grinding, can lead to various dental health issues, including jaw pain, worn tooth enamel, and increased tooth sensitivity. This condition affects people of all ages, and many might not even realize they have it until a dental professional identifies the telltale signs of wear on their teeth.
While the precise cause of bruxism is not always clear, stress and anxiety are frequently linked to this habit. Discovering effective management strategies is essential for preventing long-term dental complications. Regular dental checkups and being mindful of stress-related behaviors can help manage bruxism before it leads to more serious dental problems.
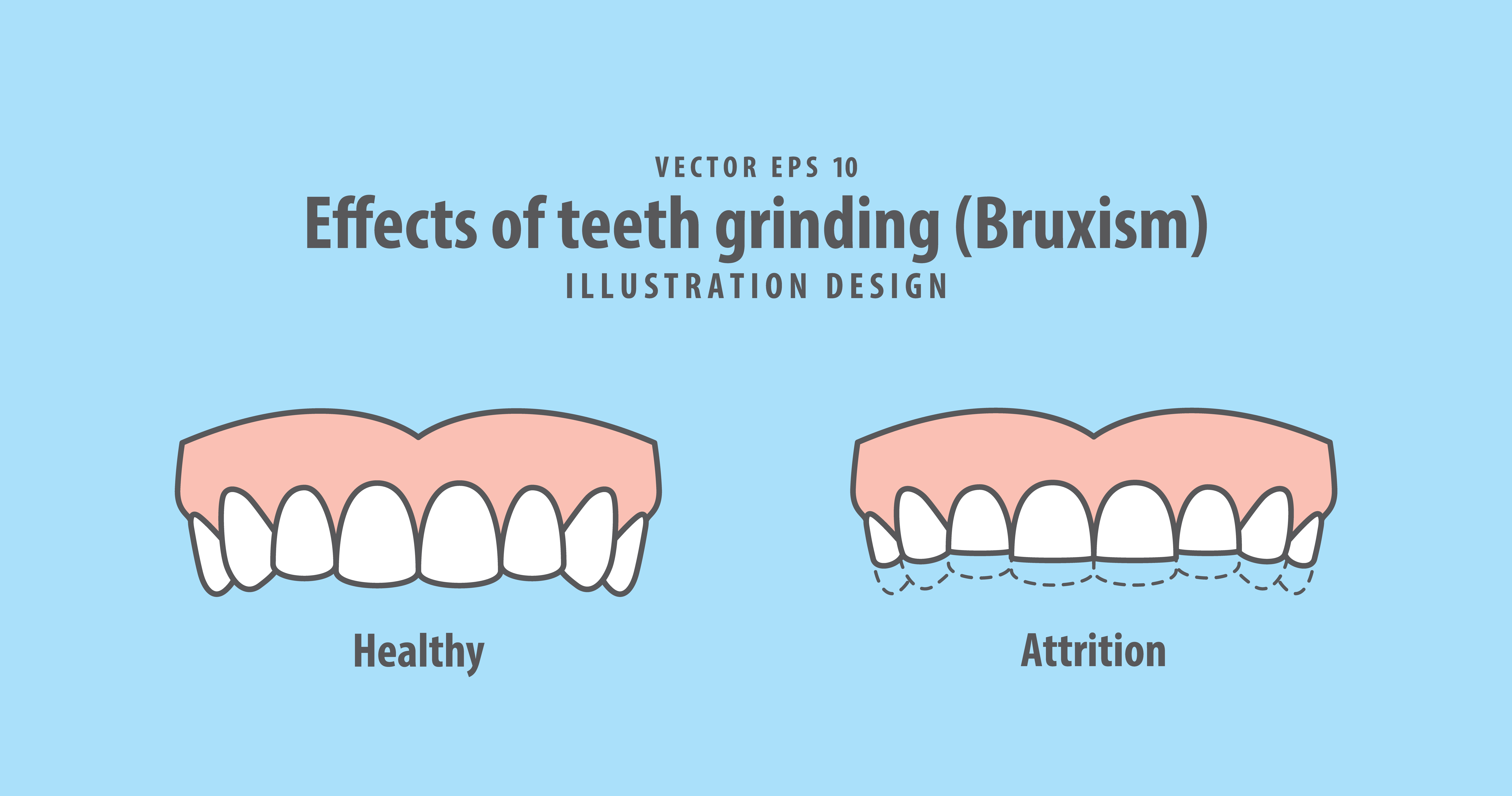
Credit: dentistrybeyondthetooth.com
Understanding Bruxism
Bruxism can sneak up on anyone, often without them even realizing it. Imagine teeth grinding and clenching hard enough to cause damage. That’s the hidden reality for many. This section dives deep into what bruxism is, who it affects, and how it intertwines with our dental anatomy.
Defining Bruxism And Its Types
Bruxism is when you grind, gnash, or clench your teeth. Most do it subconsciously, especially during sleep. This unwanted habit comes in two main types:
- Awake Bruxism: This occurs during the day. Stress often triggers it.
- Sleep Bruxism: This happens at night. It’s a sleep-related movement disorder.
Prevalence And Demographics
Bruxism doesn’t choose favourites. It affects both children and adults. Stats showcase:
| Age Group | Prevalence |
|---|---|
| Children | Up to 50% |
| Adults | 8-10% |
The Dental Anatomy And Bruxism
Your dental anatomy includes teeth, muscles, and bones. Bruxism can affect all parts of this system:
- Teeth can wear down, break, or become loose.
- It can strain your jaw muscles, leading to pain.
- Chronic grinding might hurt your jaw joint, the TMJ.
The Causes Of Bruxism
The Causes of Bruxism can be as complex as they are varied. Unraveling this mystery involves diving into psychological constructs, analyzing lifestyle choices, sifting through environmental triggers, and understanding one’s genetic blueprint. This section will explore each facet that might contribute to this involuntary grinding of teeth that affects many individuals during sleep or even waking hours.
Psychological Factors
Stress tops the list of psychological factors leading to bruxism. Anxiety, tension, and emotional stress can all trigger jaw clenching and teeth grinding. Mental health conditions, such as OCD and PTSD, might also play a role. Recognizing these triggers is paramount in managing the condition effectively.
Lifestyle And Environmental Triggers
Daily habits and surroundings greatly influence bruxism. Stimulants such as caffeine, found in coffee, tea, and certain soft drinks, encourage grinding. Similarly, smoking and alcohol consumption can exacerbate the propensity to clench or grind. A stressful environment, whether at home or work, also contributes to the issue.
Genetic Predisposition And Other Health Issues
Bruxism may run in families, indicating a genetic predisposition. Research suggests that specific genes might make individuals more susceptible. Other health concerns, such as sleep disorders, Parkinson’s disease, and hyperactivity disorders, are frequently associated with an increased risk of bruxism. Understanding these connections can help in developing tailored treatment protocols.
Symptoms And Diagnosis
Recognizing the signs and getting a proper diagnosis are the first steps to managing bruxism. Many people grind their teeth, especially during sleep without knowing. This guide will discuss how to identify and professionally diagnose bruxism.
Common Signs Of Bruxism
- Teeth grinding or clenching, often loud enough to wake a sleeping partner.
- Flattened, fractured, chipped, or loose teeth.
- Worn tooth enamel, exposing deep layers of the tooth.
- Increased tooth sensitivity.
- Jaw or face pain and soreness.
- Tired or tight jaw muscles after waking up.
- Headache originating at the temples.
- Indentations on your tongue.
Bruxism In Children Vs. Adults
Bruxism is not age-specific; it affects both children and adults. Children often outgrow bruxism.
| Children | Adults |
|---|---|
| Teeth grinding during deep sleep | Teeth grinding during any stage of sleep |
| Stress due to new environment or changes | Stress, anxiety, or lifestyle factors |
| Related to growth and development | May relate to dental misalignment |
Professional Diagnosis Of Bruxism
Diagnosis involves a combination of patient history and clinical examination. A dentist looks for signs of bruxism through:
- Dental examinations to check for
- Wear patterns on the teeth,
- Jaw tenderness,
- Damage to the inside of the cheeks.
- Medical history review which includes:
- Known cases of sleep disturbances,
- Stress levels,
- Lifestyle habits.
- Discussing sleep-related behaviors with a partner or family member.
The Impact Of Bruxism On Health
Bruxism, or teeth grinding, often occurs during sleep. It may seem harmless. Yet, it can lead to severe dental and health issues. Recognizing the impact of bruxism on health is vital. It can help prevent long-term problems.
Effects On Dental Health
Bruxism can take a heavy toll on teeth. It causes damage such as:
- Tooth wear: Grinding strips away tooth enamel.
- Fractures: Teeth may crack or break.
- Sensitivity: Worn enamel causes tooth pain.
Continuous grinding might lead to TMJ disorders. These disorders cause jaw pain and trouble chewing.
Consequences For Overall Health
Bruxism impacts more than just the mouth. It can cause:
- Headaches: Frequent teeth grinding can lead to tension headaches.
- Sleep disturbances: Bruxism can interrupt sleep patterns.
It can also contribute to earaches and facial pain. These repercussions highlight the need to address teeth grinding.
Psychosocial Implications
This condition can also affect social well-being. Signs include:
| Issue | Effect on Well-being |
|---|---|
| Stress | Bruxism can be a response to stress, creating a negative cycle. |
| Self-esteem | Dental damage may reduce confidence in one’s smile. |
Social interactions may suffer. Bruxism can also cause emotional distress.
Management And Treatment Options
Management and Treatment Options for bruxism are vital to prevent long-term damage to the teeth and reduce the discomfort caused by this condition. A range of effective strategies is available, from dental interventions to behavioral therapies and even pharmacological treatments. Tailoring the approach to the individual is key to mitigating the symptoms and reducing the impact of bruxism on daily life.
Dental Interventions
Dentists can offer several solutions to shield teeth from the effects of grinding:
- Mouthguards or Splints: Custom-fitted devices worn at night to protect teeth.
- Dental Correction: Reshaping teeth surfaces if bruxism has caused uneven wear.
- Orthodontics: Addressing misaligned teeth which may contribute to bruxism.
Behavioral And Cognitive Therapies
Strategies that focus on behavior modification and stress management include:
- Stress Reduction: Techniques such as meditation or yoga help ease the tension.
- Behavioral Changes: Training to alter jaw positioning and avoid teeth grinding.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This therapy changes patterns that trigger bruxism.
Pharmacological Treatments
In some cases, medication can also play a role in managing bruxism:
| Medication Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Muscle Relaxants | Temporarily ease muscle tension at night. |
| Anti-Anxiety Drugs | Reduce stress that may lead to teeth grinding. |
| Botulinum Toxin | Help relax jaw muscles when other treatments fail. |
All these treatments aim to reduce discomfort, protect teeth, and address the underlying causes of bruxism. Consulting with healthcare professionals determines the best course of action.

Credit: avantdental.com.au
Prevention And Lifestyle Modifications
Bruxism can lead to painful jaws, headaches, and damage to your teeth. Preventing bruxism with lifestyle changes can save you from discomfort. Here’s how:
Stress Reduction Techniques
- Deep breathing to calm your mind
- Yoga to relax your body
- Guided meditation to ease tension
- Regular sleep for a healthier routine
Diet And Exercise
- Calcium-rich foods strengthen teeth
- Magnesium to help relax jaw muscles
- Water intake to stay hydrated
- Exercise to release endorphins
Avoidance Of Aggravating Factors
Some habits make bruxism worse. Avoid these:
| Aggravating Factor | What to Do |
|---|---|
| Chewing gum | Chew less often |
| Alcohol | Drink less |
| Caffeine | Limit intake |
| Teeth grinding | Conscious effort to relax jaw |
Technological And Innovative Therapies
Bruxism, or teeth grinding, wears down your smile. But fear not! The latest tech helps us fight back. Bite into the future with these new therapies:
Biofeedback And Wearable Devices
Break the habit with smart gadgets. These tools track grinding and teach control.
- Wearable sensors sit in your mouth – they alert when you grind.
- Headband devices measure muscle activity – they signal to relax.
Advances In Dental Appliances
Dentists have new tools to shield your teeth. Forget old, clunky guards. These new protectors are tailor-made and comfy.
| New Guards | Features |
|---|---|
| 3D Printed | Perfect fit for you |
| Smart Guards | Track your grind, send data |
New Research And Alternative Approaches
Scientists keep digging and discovering. They find fresh ways to ease bruxism.
- Studies show Botox can ease muscle tension.
- New herbs relax nerves and help stop grinding.
- Stress management apps target bruxism’s root cause.
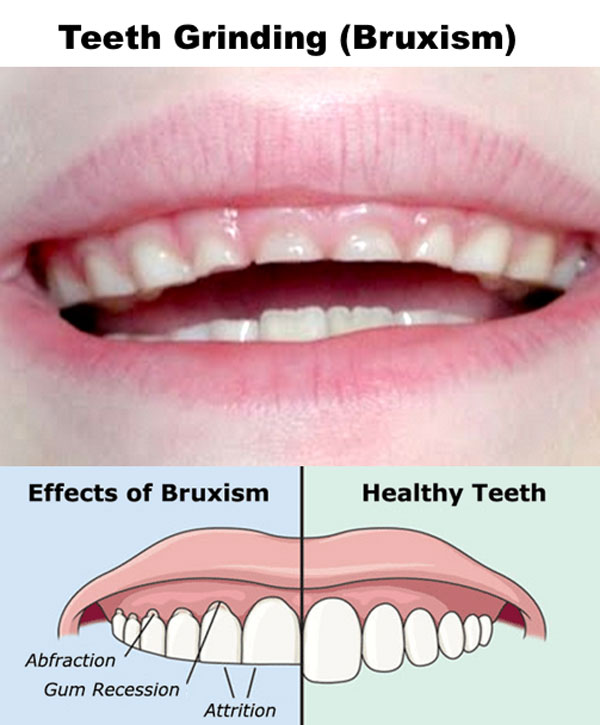
Credit: www.midlandparkfamilydentistry.com
Case Studies And Real-life Stories
Exploring the personal battles with Bruxism shines a light on the human side of this condition. Through case studies and real-life stories, we can understand the struggles and successes of those affected. These narratives offer invaluable insights into effective strategies and the importance of a strong support network.
Recovery Journeys
Every individual’s fight against Bruxism is unique. We’ve collected inspiring stories revealing how different treatments and lifestyle changes have facilitated recovery. These tales often start with the discovery of teeth grinding during sleep or the onset of jaw discomfort.
- Emma’s Story: Diagnosis after increased morning headaches.
- Jason’s Path: Noticed improvement with a custom mouthguard.
- Luke’s Triumph: Managed stress and reduced Bruxism episodes.
The Role Of Support Systems
A robust support system is paramount for enduring the journey of managing Bruxism. Stories reveal how family, friends, and dental professionals play a critical role in navigating this condition.
| Support System | Impact on Recovery |
|---|---|
| Family Encouragement | Provides motivation and emotional support. |
| Dentist’s Advice | Offers professional guidance and treatment plans. |
| Peer Support Groups | Shares experiences and coping strategies. |
Long-term Management Successes And Challenges
Ongoing management is key to limiting the effects of Bruxism. Successes celebrate the milestones achieved, while challenges remind us of the continuous nature of the condition.
- Use of Night Guards: Significant success in preventing tooth wear.
- Behavioral Therapy: Useful in reducing stress-related grinding.
- Dietary Adjustments: Lessened jaw strain from softer foods.
Challenges often involve adapting to stress management techniques or the discomfort of wearing oral devices. Yet, with persistence, many find a balance that works, which includes regular dental check-ups and self-care routines.
Navigating The Emotional Terrain Of Bruxism
Navigating the Emotional Terrain of Bruxism can often be as challenging as dealing with its physical aspects. Bruxism, the medical term for teeth grinding and jaw clenching, is not just a physical ailment. It intertwines with our mental and emotional well-being. Recognizing this connection is vital. Individuals need strategies to manage the stress and anxiety that frequently accompany bruxism.
Mental Health Considerations
Bruxism may occur due to psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, or depression. Acknowledging these mental health considerations is crucial. Notably, bruxism can also impact one’s mental well-being. Signs may include mood changes, sleep disturbances, or heightened anxiety. A proactive approach involves consulting healthcare professionals who specialize in dental and mental health.
Support Groups And Counseling
- Engaging with support groups offers a sense of community. Peers share experiences and practical tips.
- Counseling provides professional guidance. Therapists can teach effective stress management techniques.
- Online platforms and local meetups act as accessible resources for support and advice.
Building Resilience And Coping Strategies
Developing resilience and coping strategies enhances one’s ability to mitigate stress. Techniques such as mindfulness, relaxation exercises, and regular physical activity prove beneficial. Consistent practice leads to improved stress response and symptom relief for bruxism sufferers.
Let’s break down some effective strategies:
| Strategy | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Mindfulness | Focus on the present moment | Reduces anxiety |
| Yoga | Combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation | Alleviates stress |
| Exercise | Regular physical activity | Enhances overall well-being |
Remember, overcoming bruxism involves a holistic approach. This integrates the physical, emotional, and mental facets of health for optimal well-being. By acknowledging the emotional struggles and employing effective coping mechanisms, individuals can better manage bruxism and lead more comfortable, fulfilling lives.
Further Research And Future Directions
Our understanding of bruxism continues to evolve. Yet, the quest for deeper insights remains. To improve treatments and outcomes, researchers must address existing gaps, leverage digital innovations, and promote cross-disciplinary collaborations.
Gaps In Current Bruxism Research
Despite progress, unanswered questions linger in bruxism studies. Key areas include:
- Bruxism triggers and modifiers: What factors increase grinding?
- Long-term effects: How does bruxism impact overall health over time?
- Personalized treatments: What works best for each person?
Potential For Digital Health Innovations
Digital tools present opportunities for breakthroughs in bruxism management. Potential advancements encompass:
- Monitoring apps: Track bruxism patterns on smartphones.
- Wearable technology: Devices that detect and notify about grinding episodes.
- Data analysis: Big data could unveil trends and effective treatments.
Collaborations For Holistic Care Approaches
Multidisciplinary teams can transform bruxism care. A holistic approach might integrate:
- Dental experts: Leading the way in dental-specific bruxism research.
- Physicians: Addressing associated medical conditions.
- Mental health professionals: Exploring psychological aspects.
Conclusion
Untreated bruxism can lead to long-term dental issues. Remember, recognizing the signs early fosters prompt action and effective management. Regular dental check-ups and stress-relief strategies are your best defense. Embrace a bruxism-free lifestyle for a brighter, healthier smile. Seek professional advice and conquer the grind.

