Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor is a rare, benign neoplasm. It commonly affects the skull and jaw of infants.
Originating in the neural crest cells, this tumor is most prevalent within the first year of life. Characterized by its rapid growth and distinct pigmentation due to melanin production, melanotic neuroectodermal tumor poses diagnostic and treatment challenges. Despite its benign nature, it can behave aggressively and recur after removal.
Early detection and surgical excision are vital for a favorable outcome. The tumor’s uniqueness and the age of the affected population make research and case studies crucial for understanding its behavior and improving management strategies. Optimal care involves a multidisciplinary approach, integrating the expertise of pediatricians, oncologists, and surgeons. Parents should seek prompt medical attention for any unusual growths in their child’s facial region to ensure timely intervention.
Introduction To Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor
Imagine a rare puzzle that experts are eager to solve. That puzzle is Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor (MNT). It’s an unusual condition, not widely known. In this section, we dig deep into what MNT really is. We look into its history and how understanding has evolved over time.
Definition And Overview
Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor is a rare condition. It often occurs in infants within their first year. Despite being rare, knowing about MNT is crucial. This tumor primarily affects the jaw or the skull. But it can also appear in other body parts. MNT is both fascinating and complex. This tumor has cells that look like melanin-producing cells. Thus the name ‘melanotic’.
Historical Background Of Mnt
Tracing back to 1918 gives us the first glimpse of MNT. A scientist named Krompecher described it first. For years, scientists have studied MNT. They want to provide better care for those affected. This tumor’s origin remained a mystery for some time. But now, we associate it with the neuroectoderm. Hence, it has ‘neuroectodermal’ in its name. The history of MNT sheds light on the advances in medical science. It also shows our dedication to tackling rare conditions.

Credit: www.semanticscholar.org
Pathology Of Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor
The Pathology of Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor (MNT) reveals a rare entity. MNT most commonly affects infants within the first year of life. Understanding its pathology aids in prompt and accurate diagnosis, which is critical for effective treatment. This section explores the cellular and molecular characteristics, alongside the distinct histological features of MNT.
Cellular And Molecular Characteristics
Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor is complex at a cellular level. Its dual origins in both melanocytes and neural crest cells mark its unique profile. Here, we’ll delve into the key molecular hallmarks that characterize the tumor:
- High melanin content – a pigment common in skin and hair.
- Expression of neural markers like NSE (neuron-specific enolase).
- Gene alterations may be present, potentially influencing tumor behavior.
Histological Features
MNT’s diagnosis often depends on its unique histological presentation. The examination of tissue samples under a microscope provides valuable insights:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Small round cells | These are pigmented and resemble melanocytes. |
| Epithelioid cells | Larger, with clear cytoplasm, they form alveolar structures. |
| Connective tissue | Provides structure, separating cell clusters. |
The presence of melanin within tumor cells is a defining characteristic. Notable is the variable architecture throughout the tumor, ranging from trabecular to alveolar formations. Fibrous connective tissue separates these formations. This variety in microscopic appearance signifies the heterogeneity of MNT.
Epidemiology Of Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor
The melanotic neuroectodermal tumor is a rare condition. Experts study patterns to understand this disease better. They look at who gets it, where, and why. This info helps find risks and can lead to better care and prevention.
Incidence And Prevalence Rates
Doctors don’t see this tumor often. It occurs most in infants. Each year, only a few cases appear globally. Numbers show less than 1 in a million get this tumor. Data on how many have it at one time is not clear due to its rarity.
Hence, tracking this tumor is a challenge.
Demographic Variations And Risk Factors
Most cases happen in babies under one year old. There’s no clear gender preference it affects. This tumor has no known cause. But, it often appears in the jaw. Some think it could come from cell issues during the baby’s growth.
- Babies under one year old
- Equal in boys and girls
- Most common in the jaw area
Doctors continue to explore patterns in these patients. With more research, we can understand the risks and who it might affect more.
Clinical Manifestations
The Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumour is a rare condition. It often affects infants. Signs can vary. Knowing them helps early diagnosis. Here’s what to watch for.
Physical Signs And Symptoms
Physical indicators of this tumour are distinct. They appear early in a child’s life. Look for these signs:
- Rapidly growing mass in the facial region
- Blue or black pigmentation of the mass
- Displacement of teeth or delayed tooth eruption
- Swelling or asymmetry in the affected area
Symptoms may escalate. Feeding difficulties or signs of discomfort can emerge. Early medical advice is key.
Typical Presentation And Progression
Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumour usually presents within the first year of life. It’s often found in the jaw area. it Start small. Can grow quickly.
| Stage | Signs | Progression |
|---|---|---|
| Early | Small lump | May go unnoticed |
| Intermediate | Swelling, discoloration | Rapid growth, possible pain |
| Advanced | Large mass, teeth issues | Affects eating, needs intervention |
Understanding this progression aids in timely action. Regular check-ups spot changes early. This can affect treatment success.
Diagnostic Procedures
Understanding Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumour requires accurate diagnostic strategies. Detecting this rare condition involves a series of sophisticated tests. Health professionals use these tests to confirm the presence of the tumor and plan the best treatment.
Imaging Techniques
To visualize a Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumour, doctors start with imaging techniques. Images help to see the tumor’s size and location.
- X-rays: Offer a primary glimpse of bone involvement
- CT scans: Provide detailed images of the tumor and its impact on surrounding tissues
- MRI scans: Give the best resolution for soft tissue assessment
Biopsy And Histopathological Examination
To confirm a diagnosis, a biopsy is essential. A small tissue sample is taken from the tumor.
This sample undergoes histopathological examination. This test checks for cancer cells.
| Procedure | Objective | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Biopsy | Gather tissue sample | Sample analysis for cancer cells |
| Microscopic Exam | Examine cell types | Identify character of tumor |
| Immunohistochemistry | Detect protein markers | Confirm tumor type |
Pathologists study the cell types and protein markers to understand the tumor’s nature.
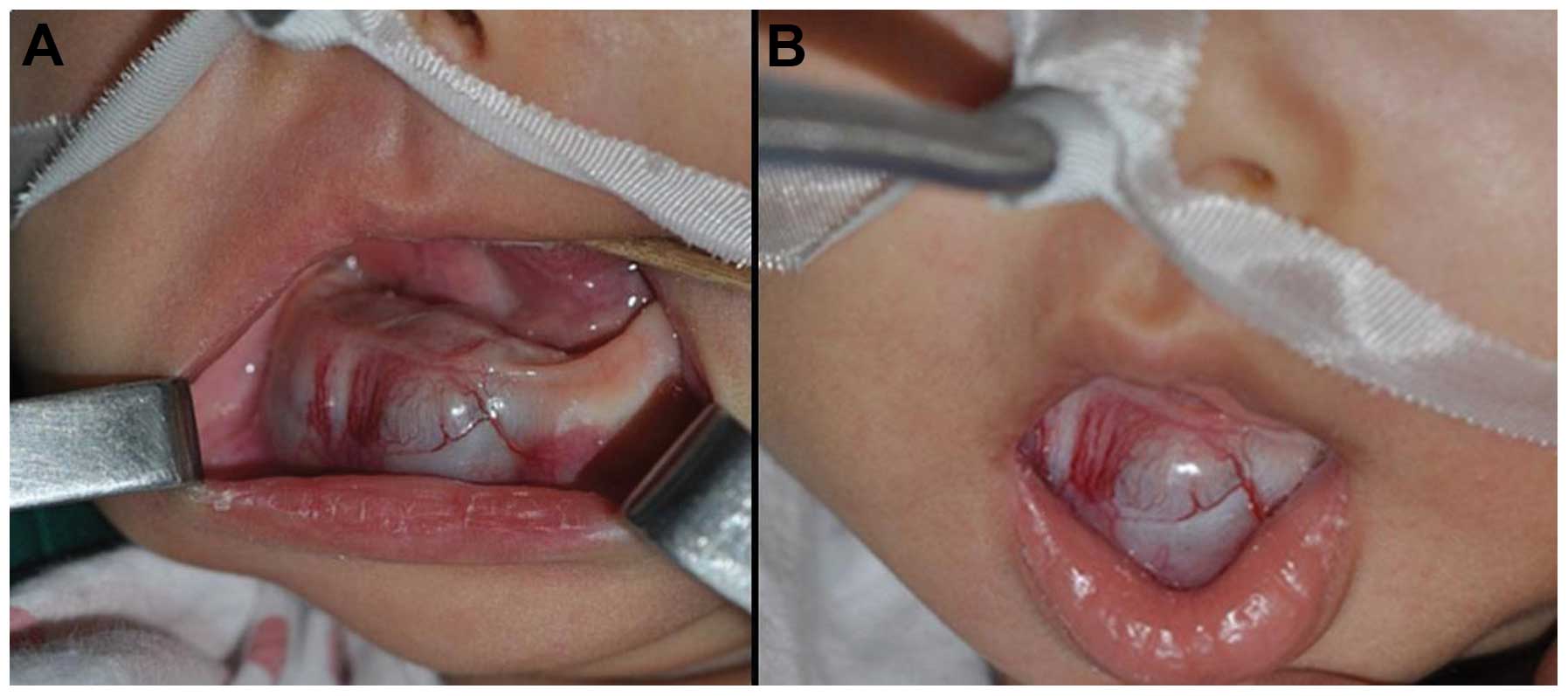
Credit: www.spandidos-publications.com
Genetic And Molecular Insights
Understanding a Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumour (MNT) takes us deep into our DNA. Genetic and molecular research shines light on this rare condition. Let’s dive into the chromosomal abnormalities and molecular pathogenesis that define MNT.
Chromosomal Abnormalities
DNA sequences can sometimes go awry. Such is the case with MNT. Chromosomal abnormalities play a crucial role. These are not your typical genetic changes.
Trisomy 11 is often tied to MNT. This means cells have three copies of chromosome 11, not two. Scientists also spot changes in other areas, like chromosome 1 and 19.
- Extra chromosome 11: Leads to overactive cell growth.
- Loss of genetic material: Can happen on chromosomes 1 or 19.
- Diverse patterns: Each tumor can show different changes.
Molecular Pathogenesis
What makes these cells turn into a tumor? Molecular pathogenesis looks for clues in the cell machinery. Genes and proteins come under the microscope.
Oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes are key players. When they don’t work right, cells can grow out of control. CYT1 and TYR genes are in the spotlight.
| Gene/Protein | Role in MNT |
|---|---|
| Oncogenes | Speed up cell division. |
| Tumor Suppressors | Normally slow down cell growth. |
| CYT1 | May contribute to tumor formation. |
| TYR | Involved in pigment production. |
Mutations in these genes are like a green light for uncontrolled growth. The end result is a melanotic neuroectodermal tumor. Advanced research is ongoing to further understand this process.
Treatment Strategies For Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor
Parents and doctors often face a rare challenge with Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor. This rare condition impacts infants mostly. Knowing the right treatment makes all the difference. Here’s a guide on how to tackle it.
Surgical Approaches
Quick action often means surgery for removing the tumor. Doctors look at the tumor’s location and make a careful plan. The goal is to take out the tumor while keeping as much healthy tissue as possible.
- Remove the tumor: Doctors take out the whole growth.
- Save healthy tissue: Important to ruin as little as possible.
- Check nearby places: Make sure the tumor hasn’t spread.
Chemotherapy And Radiotherapy Options
Sometimes, surgery is not enough. This is where chemo and radio therapy come in. Doctors use these to kill any leftover tumor cells.
| Chemotherapy | Radiotherapy |
|---|---|
| Uses drugs to fight cancer. | Uses high-energy rays. |
| Targets the whole body. | Focuses on the tumor spot. |
Doctors pick the method based on the tumor’s type and spread. Kids may need both to beat the tumor.
Prognosis And Survival Rates
Understanding the prognosis and survival rates of Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumour is crucial for patients and their families. These metrics provide hope and help in making informed decisions about treatment. Let’s dive into the key factors that impact prognosis and what long-term outcomes may look like.
Factors Influencing Prognosis
Several factors play a role in the overall prognosis of a Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumour. Knowing these can guide expectations and treatment plans.
- Age at Diagnosis: younger patients often have better outcomes.
- Tumour Location: accessible tumors are easier to treat.
- Tumour Size: smaller tumors typically have better prognosis.
- Metastatic Spread: absence of spread indicates better survival.
- Treatment Response: positive response to treatment improves outlook.
Long-term Outcomes
Long-term outcomes for Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumour patients can vary, but many live full lives post-treatment.
| Survival Rate | Time Frame |
|---|---|
| High | 1 Year |
| Varies | 5 Years |
| Depends on Factors | 10 Years |
Regular follow-ups are essential to monitor for recurrence. Education on symptoms of recurrence is vital for early detection.
Psychological Impact And Quality Of Life
The diagnosis and management of a Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumour can be a challenging journey. It’s not just the physical aspects that require attention. The emotional and psychological well-being of both the patient and their loved ones becomes a critical part of the treatment process. Understanding the psychological impact and how it affects the quality of life is essential for comprehensive care.
Impact On Patients And Families
The revelation of a Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumour diagnosis can trigger a storm of emotions. Patients and their families often face:
- Fear of the unknown and what lies ahead.
- Anxiety concerning the effectiveness of treatments.
- Stress from medical appointments and financial burdens.
This period requires a strong support system. Peer groups and counseling play a vital role. Patients tend to cope better when they feel supported and understood.
Quality Of Life Post-treatment
Surviving a Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumour is a milestone. Yet, the journey to normalcy continues. Post-treatment life can vary for each patient, but common experiences include:
| Aspect | Experience |
|---|---|
| Physical Health | Adjusting to changes in energy and ability |
| Emotional Well-being | Rebuilding confidence and healing emotionally |
| Social Life | Engaging with friends and returning to activities |
Follow-up care is important. Regular check-ups ensure the tumor has not returned. Patients are encouraged to embrace lifestyle changes. Healthy diets and exercise contribute to improved well-being.
Pediatric Considerations In Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor
Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor is a rare condition mostly found in children under one year. This tumor grows fast, but thankfully, it does not often spread to other places in the body. Treatment and care for kids with this tumor differ from adults because of their smaller size and ongoing development.
Special Concerns In Pediatric Populations
In young children, quick diagnosis and careful monitoring are crucial. Children’s bones and teeth are still forming, so tumors can lead to problems not seen in grown-ups. This condition can affect the child’s face structure and how their teeth come in. Doctors must think about how treatments will affect the child’s growth over time.
- Effects on tooth eruption and jaw development
- Psychological impact of facial tumors
- Long-term monitoring for tumor regrowth
Approach To Treatment In Children
Treating kids with this tumor is different because their bodies are still growing. The goal is to remove the tumor and make sure the child can grow up normally. Treatments can be surgery to take out the tumor or sometimes medicines. Each kid is different, so doctors work hard to find the best plan.
| Treatment Type | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Surgery | Low impact on growth, aiming for complete removal |
| Chemotherapy | Selected cases, considering the child’s health |
| Follow-up | Regular check-ups to spot any changes early |
Management Of Recurrence
Understanding how to manage the recurrence of Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumour is critical for the well-being of patients. Recurrences can occur, and being prepared with a solid action plan can ensure the best patient outcomes. The key elements for managing recurrence include careful monitoring and exploring the most effective treatment strategies.
Surveillance And Monitoring For Recurrence
Regular follow-ups are essential for detecting recurrences early. Patients should undergo routine medical imaging. This can include CT scans, MRIs, or X-rays, depending on the original tumor location.
- Follow-up schedules vary based on individual risk factors.
- Blood tests may also be appropriate to track tumor markers.
Dental check-ups are important too, especially if the tumor was in the jaw area. Watch for new symptoms and report them to your doctor immediately.
Treatment Options For Recurrent Tumors
Second surgery may be needed to remove the new growth. It’s often the first choice if the tumor returns.
| Treatment | Description | Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Chemotherapy | Drugs to kill cancer cells | Used when surgery isn’t possible |
| Radiation Therapy | High-energy rays to destroy cells | Less common, might follow surgery |
Each case requires a customized approach. Factors like tumor size, location, and patient health matter. Newer therapies, like targeted therapy, are evolving and could be options.
Differential Diagnosis
The process of identifying Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor (MNT) can be challenging. Doctors must differentiate MNT from other health conditions. This is called ‘Differential Diagnosis’. It ensures patients receive the right treatment.
Distinguishing Mnt From Other Neoplasms
MNT is rare. It needs clear separation from other tumors. This is vital for treatment plans. Doctors look at tumor location and patient age. They also study the tumor’s look and behavior. MNTs are typically in the jaw of infants. But, they can be in other places, too. Knowing these details helps doctors.
- Age matters: MNT mostly shows up in babies.
- Location is key: MNT often happens in the jawbone.
- Appearance: MNT usually has distinct cells and pigment.
Clinical And Diagnostic Challenges
Diagnosing MNT can be tricky. Imaging like X-rays and CT scans help. Blood tests look for specific markers. But the best way is a biopsy, where doctors test the tumor cells. With this, they can say for sure if it is MNT.
- Imaging scans: Show the tumor’s size and place.
- Blood tests: These can find tumor markers.
- Biopsy: The most reliable way to diagnose MNT.
Recognizing MNT early is important. It can grow fast and needs quick treatment. Wrong diagnosis can lead to wrong treatment. This is why getting it right is so important.
Case Studies And Clinical Reports
Case Studies and Clinical Reports offer invaluable insights into the uncommon and often perplexing condition known as Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor. Such reports are essential to understanding how this rare tumor behaves. They provide crucial information for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning. Examining individual cases in detail highlights patterns, outcomes, and potential clinical approaches that are beneficial for medical professionals worldwide.
Notable Case Studies
A number of case studies have shed light on this rare tumor. Distinct characteristics are often revealed through detailed examination. Many case studies detail instances where tumors presented in infants and young children, thereby assisting in constructing a demographic profile for the condition. Let’s explore a few significant reports that have contributed greatly to the medical community’s knowledge base.
- An infant presented with a rapidly enlarging facial mass, diagnosed as a melanotic neuroectodermal tumor.
- A toddler had a tumor in the skull, leading to a discussion on surgical approaches and reconstruction techniques.
- A rare case where the tumor occurred in an adult, providing insights into adult onset and progression.
Lessons Learned From Clinical Experience
Each clinical report not only documents the tumor’s behavior but also emphasizes the lessons learned. Understanding treatment responses and long-term outcomes help refine patient care strategies.
| Treatment Type | Outcomes | Follow-Up Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Surgery | High success in early-stage tumors | Minimum 1 year |
| Chemotherapy | Mixed results depending on tumor location | Varies by case |
| Radiation Therapy | Considered for recurrent cases | Long-term monitoring required |
Key aspects like early detection and the multidisciplinary approach to treatment have been underscored as best practices. Regular follow-ups are deemed essential to monitor for potential recurrence—an insight that can only be gained through exhaustive clinical scrutiny.
Advances In Research
The quest to unravel the mysteries of Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor (MNT) is on the rise. In recent years, remarkable strides in research have provided new hope for patients and medical experts. This post delves into the latest scientific advancements and explores how current studies are shaping our understanding of MNT.
Recent Scientific Discoveries
- Genetic Mapping: Scientists have identified crucial genes that may influence MNT development.
- Cellular Behaviors: Studies show unique behaviors in MNT cells that could lead to targeted treatments.
- Diagnostic Techniques: Advanced imaging has improved the accuracy of MNT diagnoses.
These breakthroughs not only enhance our grasp of MNT but also pave the way for novel treatments. They reflect untiring efforts of researchers worldwide.
Ongoing Clinical Trials
Comprehensive clinical trials are currently underway, aiming to test new therapies for MNT patients.
| Trial Name | Primary Goal | Status |
|---|---|---|
| MNT-Targeted Therapy Trial | Evaluating drug efficacy | Active, not recruiting |
| MNT Radiation Study | Assessing radiation treatments | Recruiting |
These clinical trials are instrumental in the fight against MNT. They offer insights into potential new treatments, improve patient outcomes, and contribute to the scientific community’s understanding of this rare tumor.
Multidisciplinary Approach To Care
Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor is a rare condition. Special attention is vital. A team of experts is often needed. They work together. This way, patients get the best care. This is known as a multidisciplinary approach to care.
Role Of Different Medical Specialties
A variety of medical professionals are key in treatment. Let’s look at who they are:
- Pediatric Oncologists – They treat cancer in kids.
- Surgeons – They remove tumors carefully.
- Pathologists – They study the tumor under a microscope.
- Radiologists – They take detailed pictures of the tumor.
- Nurses – They care for the child’s daily needs.
Integrated Patient Care
Integrated care brings everyone together. Teams meet and talk about the patient. They decide on the best treatment. This helps the child in many ways.
- Teams share ideas and knowledge.
- The patient receives coordinated treatment.
- Each team member knows the patient’s progress.
Parents and caregivers are part of this team too. They help at home. Their input is very important. They tell the team how the child is doing.
Patient Advocacy And Support
Dealing with a diagnosis of Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor (MNT) can often be overwhelming. Patient advocacy and support are vital during this time. They provide a guiding hand through the medical maze and a shoulder to lean on.
Resources And Support Groups
Finding reliable resources and support groups is crucial for patients and their families. These resources offer comfort, education, and a community who understand this rare journey.
- Online Forums – Join conversations and connect with others affected by MNT.
- Charities – These often have helplines and provide financial or counseling services.
- Local Support Groups – Face-to-face meetings help share experiences and advice.
- Professional Associations – They provide latest research and treatment options.
Navigating Healthcare With Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor
Accessing the right care quickly and seamlessly is critical. Below are steps to help navigate the healthcare system:
- Understand Your Health Insurance – Know what is covered and the process for claims.
- Ask for a Patient Advocate – They can help with medical jargon and decision-making.
- Prepare for Appointments – Bring a list of questions and a friend or family member.
- Maintain Records – Keep a file of all healthcare documents and notes from appointments.
Controversies And Debates In Management
Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor can spark intense dialogue among medical professionals. Its rarity and complex nature lead to disagreements on the best way to manage it. Understanding these debates is crucial for making informed decisions. Identifying the best course of action remains a challenge due to varying approaches and outcomes. In this article, we dive into the core of these discussions.
Ethical Considerations In Treatment
Doctors face ethical dilemmas while treating this tumor. The tumor often affects infants, raising concerns about consent and post-treatment quality of life. Long-term impacts are uncertain, making decisions tougher. It’s vital to balance aggressive treatment with the potential for adverse effects. The medical community strives to find common ground on these ethical issues.
- Consent – Who makes the call?
- Risks vs. Benefits – Is the treatment worth it?
- Quality of Life – What will the child’s future look like?
Debates Over Standard Of Care
The standard of care for this tumor sparks much debate. Options range from surgery to chemotherapy, but consensus is lacking. Doctors must weigh the risks and effectiveness of each treatment. This debate continues as research evolves and new treatments emerge.
Key points of debate include:- Surgery – Is it always the first step?
- Chemotherapy – When should it be introduced?
- Follow-up – What’s the best approach to monitor progress?
| Treatment Type | Risks | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Surgery | Potential complications | Often effective |
| Chemotherapy | Side effects | Varies by case |
| Monitoring | Non-invasive | Essential for early detection |

Credit: www.sciencedirect.com
Future Perspectives
Future Perspectives: As we look ahead, the frontier of melanotic neuroectodermal tumor (MNET) is shifting. Innovative treatments and technologies are on the horizon. These changes promise better outcomes for patients.
Potential Advances In Treatment
The battle against MNET is evolving with new treatment strategies. Researchers are harnessing the power of genetics and immunotherapy to fight tumors.
- Gene therapy: Tailored treatments can shut down tumor genes.
- Immunotherapy: Boosting the immune system targets cancer cells.
- Targeted drugs: These drugs attack specific parts of tumor cells.
Impact Of Emerging Technologies On Diagnosis And Management
Emerging tech tools are turning the tide for MNET diagnosis and management.
A.I. and Machine Learning: Smart algorithms can spot tumors earlier.
Radiomics: This tech reads complex imaging data, revealing tumor secrets.
| Technology | Benefits |
|---|---|
| A.I. Diagnostics | Fast, accurate tumor identification |
| 3D Imaging | Detailed views of tumor growth |
| Genomic Sequencing | Insight into individual tumor behavior |
Conclusion
Understanding melanotic neuroectodermal tumors is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. With advancements in medical research, prognosis for patients can be optimistic. Remember, recognizing symptoms and seeking prompt care can lead to effective management. Embrace awareness and consult health professionals for any concerns.
Your health journey matters.

